Uncategorized
Resources
Style
Planning
View All
By: Josie Mangano
Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
It’s commonplace for women to are trying to conceive to track their menstrual phases. However,
did you know that whether or not you’re trying to conceive, tracking the phases of your
menstrual cycle can be a valuable tool for assessing overall health and wellbeing? If you have
PCOS or are experiencing symptoms related to hormone imbalance, fertility awareness may
help you understand the cues your body is giving you in order to address the root causes.
Irregular menstrual cycles are linked to nutritional deficiencies, energy deficits, hormonal acne,
and even loss of bone density in the long-term. Put simply, your hormone health is important
even before you are trying to conceive.
What is Fertility Awareness?
Fertility awareness — is a set of practices that are used to determine the fertile and infertile
phases of your menstrual cycle.
The techniques used to track menstruation and ovulation are known as Fertility Awareness
Methods (FAMs). But first, let’s review what you should know about the menstrual cycle, the
fertile window, and what the patterns of a normal cycle look like.
What You Need to Know About the Menstrual Cycle
A normal menstrual cycle lasts anywhere between 24-35 days. The first day of your period
(when flow begins) is always considered day 1 of your cycle. Normal menstruation lasts
between 3-7 days.
In the days following menstruation, your ovaries release an egg into the fallopian tubes — this
process is called ovulation. This egg stays in your fallopian tubes and, if not fertilized by a
sperm, will dissolve after 12-24 hours. Contrary to the myth that ovulation occurs 14 days after
your period starts, ovulation typically happens between days 10-23, depending on the length of
your cycle. It is essential to note that sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to
5 days. Therefore, your fertile window is classified as the 5 days before ovulation, the day of
ovulation, and the following day (7 days total).
During the fertile window, the sperm present in the female reproductive tract may fertilize an egg
and implant itself in the uterine lining, thus marking the beginning of pregnancy. If the egg is not
fertilized and the egg is reabsorbed, hormones drop, and menstruation occurs, marking the
beginning of a new cycle. After the fertile window passes, pregnancy is not possible because
the egg is no longer present for fertilization. The days after ovulation and before menstruation
are referred to as the post-ovulatory phase.
With that covered, we can dive into the science-backed tools we use for fertility awareness cycle
tracking.

The 3 main fertile signs to pay attention to are:
1. Cervical mucus
2. Basal body temperature (BBT)
3. Cervical position
Let’s review each of these signs more closely and learn how they may be related to underlying
causes such as hormone imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, and/or underlying health conditions.
Cervical Mucus
The presence of cervical mucus (CM) is indicative of your fertile window. CM plays an essential
role in natural conception by matching the pH of sperm, creating the perfect environment for it to
stay alive for up to 5 days in the otherwise hostile female reproductive tract.
There are two kinds of cervical mucus that are often referred to when it comes to reproductive
health. The first is “peak mucus” which is an optimal environment for sperm and is also an
indicator of a healthy cycle when present in the fertile window. Peak mucus is clear, stretchy,
and is comparable to egg whites. There is also “non-peak mucus” which is cloudy, white, and similar to creamy hand lotion. Non-peak mucus is not as optimal because it is hostile to sperm.
It is usually present shortly after menstruation and later in the menstrual cycle (luteal phase).
However, it is important to note that all mucus is fertile in the pre-ovulatory phase! Pregnancy
can occur in the presence of either kinds of CM in the fertile window

If your experience with CM differs, there are some red flags we can look for to assess
underlying hormonal imbalances and/or health conditions.
Cervical Mucus Red Flags
Limited or no mucus — can indicate an issue with hormone production, the cervix, or other
related issues including HPV, cervical dysplasia, or use of medications like hormonal birth
control, fertility drugs, or antihistamines. Can indicate inadequate nutrient intake of cholesterol
(to support estrogen and progesterone production), vitamin A, and B vitamins (folate). Can
indicate endocrine issues such as thyroid disorder, HPA axis dysregulation, hypothalamic
amenorrhea, etc.
Continuous mucus — can indicate an issue in the cervix, or presence of infection,
inflammation, or hormone imbalance.
Continuous creamy/lotiony (non-peak) mucus — may indicate an overgrowth of
yeast/bacteria. During the luteal phase, low progesterone production may contribute to
continuous non-peak mucus.
Continuous clear/stretchy (peak) mucus — seen in women with PCOS and/or women
experiencing food sensitivities, IBS, and other gut-related issues in the pre-ovulatory phase.
Yellow-tinged mucus – can be indicative of infection.
Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
Basal Body Temperature can be measured by taking your temperature first thing in the morning,
before getting. It is important that you do this immediately after waking up for an accurate
reading, before eating or drinking.
Tracking these temperatures provides us with the information we need to confirm when
ovulation occurs, but keep in mind that there is no way to predict when ovulation will occur due
to extraneous factors like travel and stress which may delay ovulation. You can keep track of
your BBTs by either logging them manually on a BBT chart or by using a fertility tracking app.
Normal pre-ovulatory temperatures should consistently be above 97.5° F ranging up to about
98.2 °F. Normal post-ovulatory temperatures should be higher than the pre-ovulatory range with
at least one temperature higher than 98.6 °F. Temperatures that fall consistently lower than this
range indicate potential health issues and nutrient deficiencies.

What are Some Possible Causes of Low Basal Body Temperatures?
Possible causes of low BBT include nutrient deficiencies of nutrients involved in thyroid function
such as zinc, iron, selenium, and iodine. Iron deficiency may also contribute to low BBTs since
iron is highly involved in body temperature regulation. Zinc and iron supplementation have
independently been shown to improve thyroid hormone levels and thus increase BBTs in
deficient women.
Low BBTs may also result from inadequate calorie consumption from skipping meals or failing
to consume enough calories to offset exercise levels. Poor sleep may also contribute to low
BBTs by offsetting natural circadian rhythms. Finally, thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism
and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis play a role in lowering BBTs.
Cervical Position
The final indicator of fertility is cervical position, which changes throughout the menstrual cycle.
By regularly checking cervical position we can better understand our bodies through common
patterns that we notice throughout our cycles.
But what is the cervix and how can we use it to track our cycles?
The cervix is the small, muscular organ that connects the vagina to the uterus. It’s a round,
prominent structure with a hole in the middle that’s roughly an inch in diameter. It produces
cervical mucus, expels menstrual flow, allows sperm to pass through during ovulation, and acts
as a barrier against infections.
During ovulation, high estrogen levels cause the cervix to rise closer to the top of the vagina.
The cervix often feels softer during the fertile window. As mentioned previously, the cervix is
responsible for producing peak CM during this time.
After ovulation (luteal phase), the position of the cervix lowers to prepare for menstruation. This
cervix tends to lower or “drop” on average a week to 10 days before menstruation begins.
During menstruation, the cervix remains low and opens slightly to release the menstrual blood
flow. The cervix feels firm to the touch during this time and will continue to feel this way until
after your period ends.
In early pregnancy, the position of this cervix is high in the vagina, similar to its position during
ovulation. The cervix is known to feel soft during this time, however it is important to use a
pregnancy test to confirm pregnancy as cervical position is not a guarantee in confirming early
pregnancy.
For more information on how to check your cervical position, click here.
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork of cycle tracking, let’s discuss some specific nutrients and
how they uniquely benefit cervical health!
Key Nutrients to Support Cervical Health
1. Folate — has been shown to reverse abnormal (precancerous) cervical cells and reverse
cervical dysplasia. Folate plays a key role in supporting healthy cell division, most notably
during early pregnancy in the formation of the spinal cord.
2. Vitamin A (retinol) — has been shown to reverse abnormal cervical cells when applied
topically to the cervix. Vitamin A is critical for fertility and plays a role in preparing the uterine
lining for implantation. Pregnant women should avoid all forms of vitamin A supplementation.
Dark leafy greens, red/orange vegetables, beef, eggs, and dairy products are rich in vitamin A.
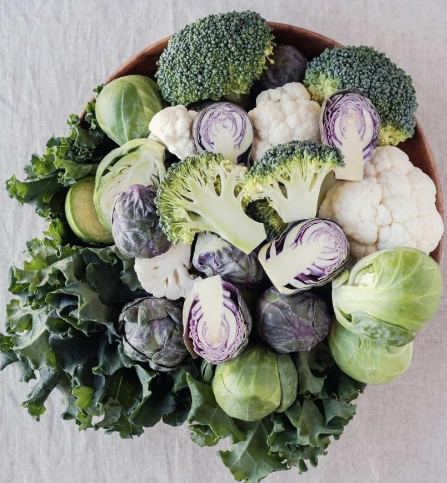
3. Indole-3-Carbinol – has been shown to reverse abnormal cervical cells in clinical trials.
I3C plays a role in modulating estrogen metabolism and is a compound found in cruciferous
vegetables like broccoli, brussels sprouts, kale, and cauliflower

There you have it — the 3 main fertile signs to pay attention to and related cues that can give us
powerful insights into our hormonal and reproductive health. If you feel passionate about using
fertility awareness as a guide to managing hormonal imbalances, managing PCOS, or preparing
your body for the healthiest pregnancy possible, consider reaching out to our team at Wellspring
Nutrition for 1:1 functional nutrition counseling and a personalized plan to achieve your unique
health goals.
References
Hendrickson-Jack L. Women’s Health Nutrition Academy (WHNA). “Unlocking the Secrets of the
Menstrual Cycle: How Fertility Awareness Cycle Tracking Can Help Your Nutrition Practice”.
Sumner C. Cervix positions: What they mean & how to check them. Natural Cycles. Published
June 28, 2022. https://www.naturalcycles.com/cyclematters/cervix-positions-explained

What’s Blocking Your Fertility? Root Cause Quiz Development
Growing my nutrition practice taught me that most women struggling with fertility don’t just need another meal plan or supplement. They need help uncovering the underlying issues that are making conception so difficult. Clients often come to me feeling exhausted, bloated, anxious, or inflamed, yet they can’t connect the dots between these symptoms and their reproductive health. When I discovered Interact, a quiz‑building platform, I realized that an interactive diagnostic quiz could meet people right where they are—online—and guide them toward identifying possible root causes of their fertility challenges.

Interactive quizzes aren’t just fun; they’re powerful marketing tools. The Blogsmith notes that on average a quiz is shared 1,600 times, and in January 2015 nine out of ten of the most‑shared Facebook posts were quizzestheblogsmith.com. 70 % of marketers say interactive content is effective at converting visitors, and 88 % say it differentiates their brandtheblogsmith.com. The average lead‑capture rate for quizzes is 31.6 %, far above the 1–5 % typical for email opt‑instheblogsmith.com. Leveraging these statistics, I set out to build a quiz that wasn’t just entertaining—it needed to deliver meaningful, actionable information while capturing leads for my practice.
The Idea: A Diagnostic Quiz for Fertility Root Causes
My program, The Root Cause Fertility Method, focuses on helping women improve fertility through a holistic lens. Many clients experience sugar cravings, energy crashes, bloating, headaches, acne, insomnia, or chronic stress, yet don’t realize these are often connected to hormonal imbalances, digestive dysfunction, or nutrient deficiencies. I wanted a simple tool to help women start connecting these symptoms to possible underlying causes before they even book a consultation.
Choosing a point‑based system
To do this, I created a 25‑question quiz called “What’s Blocking Your Fertility?” Each question offers two answers—a symptom is either “yes” or “no.” Here’s a sample:
| Symptom category | Sample question | Answer A (points) | Answer B (points) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood‑sugar/insulin | Do you experience intense sugar or carb cravings, especially in the afternoon? | “Yep! Feel this all the time” (1 point) | “No, not really” (0 points) |
| Digestion/gut health | Do you often feel bloated even when eating healthy foods? | “Yes, I’m constantly unbuttoning my pants” (1 point) | “No, I rarely feel bloated” (0 points) |
| Inflammation/autoimmunity | Do you feel stiff or achy in the morning? | “Yes, I feel like I’m twenty years older” (1 point) | “No, I’m a spring chicken” (0 points) |
| Nutrient deficiencies | Do you notice brittle nails or hair thinning? | “Yes, I’m constantly finding hair everywhere” (1 point) | “No, my hair and nails are healthy” (0 points) |
| Adrenal/stress | Do you feel wired but tired at night? | “Yes, I’m tired all day and scrolling at night” (1 point) | “No, I have a solid bedtime routine” (0 points) |
Each “yes” answer in a category adds one point to that root‑cause bucket. At the end of the quiz, the category with the highest score indicates the user’s most likely area of imbalance—blood sugar/insulin, digestion/gut health, inflammation/autoimmunity, nutrient deficiencies, or adrenal/stress dysfunction. Every result page offers targeted suggestions (for example, balancing blood sugar with protein and fiber at meals, supporting digestion with probiotics and mindful eating, addressing inflammation through anti‑inflammatory foods, or prioritizing sleep and stress management). This point‑based design makes the quiz feel personalized and diagnostic without overstepping into medical diagnosis.
Building the quiz with Interact
Why Interact?
After researching quiz platforms, I chose Interact because the software is intuitive and flexible. The Blogsmith review highlights that Interact’s user interface is “ridiculously easy to use and navigate,” with a clean design that makes quiz creation straightforward. It allows you to add your branding basics, customize a quiz cover, create result pages, and then jump back and forth between sections as you refine questions (theblogsmith.com). I knew I wanted to design a quiz that looked polished and aligned with my brand, but I also needed the flexibility to adjust questions and scoring logic on the fly.

Customizing my quiz
- Branding and cover – I started by uploading my logo and choosing colors consistent with the Wellspring Nutrition brand. Interact prompts you to set up your quiz cover first, which ensures a cohesive look.
- Result pages – Before drafting questions, I defined five result types corresponding to the root‑cause categories above. Interact lets you add as many result pages as you need and edit them at any time. Each result page includes an explanation of the likely imbalance and a call to action directing readers to schedule a consultation or download a free fertility guide.
- Question & answer creation – Interact allows text‑based or image‑based questions, so I selected images of happy families and healthy food to make the quiz visually appealing. Adding questions is simple: you type your question, write the answer options, and use the points feature to assign values. The platform makes it easy to edit correlations so that one answer can map to multiple results.
- Scoring logic – I enabled the “scored quiz” option. For each answer, I assigned points to the appropriate categories. Interact automatically tallies points as users progress and displays the result page with the highest score when they finish. The platform supports multiple quiz types—including personality, knowledge tests and scored quizzes—so you can choose what fits your goals.
- Lead‑capture form and segmentation – Interact’s integrations with email service providers allow you to add an opt‑in form before revealing results. I connected the quiz to my email service and mapped each result to a segmented list. For example, someone with high blood‑sugar points receives a follow‑up email with tips for balancing insulin and information about my blood‑sugar reset program. Personalized segmentation like this automates nurture sequences without manual tagging.
- Embedding the quiz – Once the quiz was finalized, Interact generated an embed code that I inserted into a dedicated landing page on my website. It also offers a WordPress plugin, but I opted for the code to ensure full control over the page design. I added share buttons because social media is crucial for quiz success.
Following best practices
Interact’s internal data from over 40 k quizzes and 5 million leads has shaped a list of best practices, which was so helpful when creating the quiz. Here are some guidelines I followed:
- Keep it short: Aim for about 2 minutes or 7 questions to maintain engagement. My quiz has 25 questions but each is a quick yes/no, so completion time averages under three minutes.
- Use 3–6 answer options: I limited each question to two choices to reduce decision fatigue
- Offer an opt‑out: I allow users to skip the opt‑in if they just want to see their results, which avoids capturing unqualified leads.
- Call to action: Each result page directs users to book a free discovery call or download my fertility checklist.
Insights from quiz data
In its first month, the quiz attracted seven participants with an 87 % completion rate on early questions. Interestingly, the highest “yes” rates corresponded to symptoms of poor blood‑sugar control: sugar cravings, energy crashes after eating, and waking up between 2–4 a.m. Many respondents also reported digestive issues like bloating and irregular bowel movements, suggesting that gut health is a significant blocker for fertility in my audience. This data is incredibly valuable; it confirms patterns I see in one‑on‑one consultations and helps me tailor my content and offers to address the most common root causes.
The quiz also acts as a conversation starter. Women who score high in the adrenal/stress category often share stories about feeling overwhelmed and emotionally exhausted, and we talk about creating sustainable self‑care routines. Those who score high for nutrient deficiencies are often surprised when we connect brittle nails and hair loss to minerals like iron and magnesium. I always remind users that this quiz is a starting point, not a medical diagnosis. Nevertheless, it invites them into a coaching relationship where we can run functional lab tests and design personalized protocols.
Why interactive quizzes matter
Interactive quizzes drive engagement and segmentation more effectively than static content. Statistics show they convert visitors into leads at a higher rate than traditional email sign‑ups and are widely shared across social platforms. They also help automate personalization; Interact’s integrations let you segment users based on their answers and trigger tailored follow‑up sequences. For practitioners like me, quizzes are not just marketing tools; they’re educational resources that empower people to take the next step on their health journey.
Final thoughts
Creating my root‑cause fertility quiz with Interact was both fun and strategic. The platform’s intuitive interface, customizable design and flexible scoring system allowed me to build a diagnostic‑style quiz that engages visitors and delivers personalized results. The data I’ve collected so far confirms that blood sugar and gut health are the most common blockers for fertility in my audience, which helps me refine my services and content. For example, in my Root Cause Fertility Method program we include a continuous glucose monitor AND the GIMAP stool test because we know that blood sugar and gut health are the top two root causes our audience is working on.
If you’re a health professional or coach looking to generate leads while genuinely serving your audience, I highly recommend experimenting with interactive quizzes. They can be designed for personality‑based insights, knowledge tests, or scored diagnostics, and you’ll gain invaluable insights along the way. To see how my quiz works and discover what could be blocking your fertility, head over to my website and take the quiz yourself! And let me know what you think! 🙂

Written by: Lauren Chamberlain
Edited and Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
Dealing with endometriosis is already a challenge—pain, fatigue, and the frustratingly long journey to diagnosis. But for many, one of the hardest realities to face is how this condition might impact fertility. Whether you’re actively trying to conceive or simply thinking about the future, it’s natural to wonder: Will I be able to get pregnant? Will it take longer? Am I at risk for complications?
Let’s break it down—why does endometriosis make conception more difficult? And what can be done to improve fertility outcomes?
Fertility and Endometriosis: The Numbers
Studies suggest that up to 50% of people with endometriosis may experience fertility challenges, and about half of those diagnosed with infertility have underlying endometriosis. However, a diagnosis doesn’t mean pregnancy is impossible! It may take longer, require medical support, or necessitate lifestyle adjustments—but many people with endometriosis go on to conceive and carry healthy pregnancies.
Now that we’ve covered the statistics, let’s explore why endometriosis affects fertility in the first place.
Understanding the Connection: Why Endometriosis Affects Fertility
Endometriosis is a complex condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, leading to inflammation, scarring, and hormonal imbalances. These factors can contribute to fertility struggles in multiple ways:
1. Chronic Inflammation and Hormonal Imbalances
Endometriosis is associated with chronic inflammation, which plays a key role in fertility challenges. The condition causes an increase in inflammatory cytokines—proteins that regulate immune responses. These cytokines can interfere with ovulation, fertilization, and implantation by creating a hostile uterine environment. Chronic inflammation may also impair the function of the corpus luteum, the structure responsible for producing progesterone after ovulation. Since progesterone is critical for preparing the uterine lining for implantation, low levels may result in implantation failure or early miscarriage.
Additionally, endometriosis is often linked to estrogen dominance. Excess estrogen can thicken the endometrial lining abnormally, disrupt the menstrual cycle, and contribute to a suboptimal hormonal balance for conception.
2. Reduced Egg Quality and Oxidative Stress
Endometriosis has been linked to oxidative stress, a condition where an excess of reactive oxygen species (ROS) damages cellular structures, including eggs. This oxidative damage can lead to:
- DNA fragmentation in eggs, reducing their ability to be fertilized.
- Lower embryo quality, decreasing the likelihood of successful implantation.
- Higher rates of aneuploidy (chromosomal abnormalities), which can lead to failed pregnancies or birth defects.
Research suggests that targeted nutritional strategies, such as increasing antioxidant intake (e.g., vitamin C, vitamin E, and CoQ10), can help mitigate oxidative stress and improve egg quality.
3. Decreased Ovarian Reserve and Endometriomas
Many individuals with endometriosis develop ovarian cysts known as endometriomas. These cysts, filled with old blood, can impact ovarian function in several ways:
- Damage to ovarian tissue: As endometriomas grow, they can infiltrate and compromise healthy ovarian tissue, reducing the number of viable eggs.
- Lower response to fertility treatments: Studies indicate that individuals with endometriomas often have a lower ovarian response to stimulation during assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like in vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Surgical risks: While surgical removal of endometriomas may relieve symptoms, it can also reduce ovarian reserve if healthy ovarian tissue is inadvertently removed during the procedure. Those considering surgery should discuss fertility preservation strategies, such as egg freezing, beforehand.
4. Blocked Fallopian Tubes and Pelvic Adhesions
Endometriosis can cause adhesions—bands of fibrous scar tissue that develop between organs. These adhesions may:
- Block or distort the fallopian tubes, preventing eggs from traveling to meet sperm.
- Interfere with ovulation, making it more difficult for the ovaries to release eggs effectively.
- Cause fluid buildup in the fallopian tubes (hydrosalpinx), which can create an inhospitable environment for embryos and decrease implantation success.
For those with significant tubal damage, natural conception may be challenging, and assisted reproductive technologies like IVF may be necessary.
5. Implantation Challenges and Uterine Dysfunction
Successful pregnancy depends on a fertilized egg implanting into a healthy uterine lining. Endometriosis can interfere with this process due to:
- Abnormal endometrial receptivity: The endometrium (uterine lining) may not develop properly due to chronic inflammation, hormonal imbalances, or scarring.
- Increased uterine contractility: The uterus may contract excessively, making it harder for an embryo to implant and remain stable.
- Altered immune response: Inflammatory and immune factors in the uterine environment may mistakenly attack the embryo, leading to implantation failure or early miscarriage.
Pregnancy with Endometriosis: Risks & Considerations
While many individuals with endometriosis achieve healthy pregnancies, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and considerations:
1. Increased Risk of Obstetrical Complications
Studies have identified a higher incidence of certain complications in pregnant individuals with endometriosis:
- Preterm Birth: There is an elevated risk of delivering before 37 weeks of gestation.
- Placenta Previa: The placenta may implant low in the uterus, covering the cervix, which can lead to bleeding and necessitate a cesarean section.
- Hypertensive Disorders: Conditions like preeclampsia, characterized by high blood pressure and potential damage to other organ systems, are more common.
- Gestational Diabetes: An increased likelihood of developing diabetes during pregnancy has been observed.
- Cesarean Delivery: The necessity for cesarean sections is higher among those with endometriosis.
These findings underscore the importance of vigilant prenatal care for individuals with endometriosis to monitor and manage potential complications effectively.
2. Impact of Surgical Treatment on Pregnancy Outcomes
Surgical interventions for endometriosis, such as laparoscopic excision, aim to alleviate symptoms and improve fertility. However, the effects of surgery on pregnancy outcomes are complex:
- Adhesion Formation: Post-surgical adhesions can lead to chronic pelvic pain and may impact fertility.
- Ovarian Reserve: Surgical removal of endometriomas (ovarian cysts associated with endometriosis) can reduce ovarian reserve, potentially affecting fertility.
Therefore, surgical decisions should be individualized, weighing the benefits against potential risks, and discussed thoroughly with a healthcare provider.
3. Importance of Preconception Counseling
Given the potential challenges associated with endometriosis and pregnancy, preconception counseling is highly recommended. This process involves:
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Assessing the extent of endometriosis and its impact on reproductive organs.
- Fertility Assessment: Evaluating ovarian reserve and tubal patency to determine the best conception strategies.
- Risk Discussion: Understanding the potential obstetrical risks and planning appropriate monitoring and interventions.
Engaging in preconception counseling allows for informed decision-making and the development of a tailored care plan to optimize pregnancy outcomes.
4. Nutritional and Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting specific dietary and lifestyle changes can positively influence fertility and pregnancy outcomes in individuals with endometriosis:
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Consuming foods rich in antioxidants can reduce oxidative stress and improve egg quality.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in moderate exercise can enhance overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Stress Management: Incorporating stress-reduction techniques like yoga or meditation may improve hormonal balance.
Implementing these modifications can support reproductive health and may increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy.
5. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
For those experiencing difficulty conceiving naturally, ART options such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be considered. While endometriosis can impact the success rates of ART, individualized treatment protocols and close monitoring can enhance outcomes. Consulting with a fertility specialist can provide personalized guidance on the most appropriate interventions.
Ultimately, while endometriosis can pose challenges to conception and pregnancy, understanding the potential risks and proactively managing them with a healthcare team can lead to successful outcomes.
What Can You Do?
If you have endometriosis and are concerned about your fertility, there are steps you can take to optimize your chances of conception:
- Adopt an anti-inflammatory diet: Eat foods rich in antioxidants, such as leafy greens, berries, turmeric, and omega-3 fatty acids, to combat oxidative stress and support egg quality.
- Consider medical treatment: Hormonal therapies like GnRH agonists, birth control pills, or progestin therapy may help manage symptoms and improve fertility outcomes.
- Support gut health: A balanced gut microbiome helps regulate inflammation. Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut, or consider a high-quality probiotic supplement.
- Optimize lifestyle factors: Engage in regular, low-impact exercise like yoga or walking to reduce inflammation and support reproductive health. Prioritize stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, and ensure you’re getting enough quality sleep.
- Work with a fertility specialist: A reproductive endocrinologist or fertility dietitian can assess your specific needs and create a personalized plan, whether you’re trying to conceive naturally or exploring medical interventions.
- Discuss fertility preservation: If you’re not trying to conceive yet but may want to in the future, options like egg freezing can help safeguard your reproductive potential.
Final Thoughts
Endometriosis may make conception more challenging, but it doesn’t mean it’s out of reach. Every fertility journey is different, and while endometriosis can present obstacles, there are many ways to take control of your reproductive health. Whether through lifestyle changes, medical treatments, or working with a specialist, you have options. If you’re struggling, reach out to a healthcare provider to explore the best path for you. Knowledge is power, and by understanding the impact of this condition, you can approach your fertility journey with confidence and clarity.

Sources
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9983692
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8224039
https://www.rbmojournal.com/article/S1472-6483(13)00007-2/fulltext
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8065992
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7226034
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9528818
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10058497/#sec5-life-13-00654
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10820275

For individuals and couples struggling to conceive, the road to parenthood can be filled with emotional and physical challenges. One lesser known yet significant factor in infertility is progesterone deficiency, a hormonal imbalance that plays a crucial role in the reproductive process. Understanding this condition and addressing it can make a profound difference in achieving conception and maintaining a healthy pregnancy.
What is Progesterone and Why Is It Important?
Progesterone is a steroid hormone primarily produced by the ovaries after ovulation, during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
It is essential for:
- Preparing the Uterine Lining: Progesterone thickens the endometrium, creating an optimal environment for a fertilized egg to implant.
- Maintaining Pregnancy: Once implantation occurs, progesterone supports the early stages of pregnancy by preventing the uterine lining from shedding.
- Regulating Menstrual Cycles: It balances estrogen levels, ensuring a regular and healthy cycle.
- Supporting Embryonic Development: Adequate progesterone levels contribute to the development of the placenta and the overall health of the embryo.
- Brain Health: Progesterone acts as a neurosteroid, promoting brain health, reducing anxiety, and supporting restful sleep. Progesterone’s calming effects can help mitigate stress and its negative impact on reproductive hormones.
Causes of Progesterone Deficiency

Progesterone deficiency, also known as luteal phase defect (LPD), can result from several underlying conditions or lifestyle factors, including:
- Ovulatory Disorders: Irregular or absent ovulation leads to inadequate progesterone production.
- Chronic Stress: Elevated cortisol levels can suppress progesterone synthesis. Chronic stress diverts resources from progesterone production to cortisol creation, exacerbating hormonal imbalances.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can disrupt progesterone production.
- Thyroid Dysfunction: Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can interfere with progesterone levels.
- Hypothalamic Amenorrhea: A condition often caused by excessive exercise, low body weight, or chronic stress. It disrupts the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis, preventing ovulation and leading to low progesterone levels.
- Insulin Resistance: High insulin levels can alter ovarian function, reducing progesterone production and contributing to irregular cycles.
- Brain Injury: Trauma or injuries affecting the brain can disrupt the signaling between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovaries, leading to hormonal imbalances and inadequate progesterone production.
- High Prolactin Levels: Elevated prolactin, often due to pituitary gland issues or breastfeeding, can suppress ovulation and reduce progesterone output.
- Hormonal Birth Control: Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives can suppress natural ovulation and progesterone production, sometimes leading to imbalances even after discontinuation.
- Steroid or Opioid Medications: Chronic use of these medications can interfere with the HPO axis and suppress ovarian function, impacting progesterone levels.
- Age: Natural declines in progesterone occur as women approach menopause, but they can also affect younger individuals.
- Poor Nutrition: A lack of key nutrients, such as vitamin B6, magnesium, and zinc, may impair hormone production.
Symptoms of Progesterone Deficiency
Recognizing the symptoms of progesterone deficiency is essential for early intervention. Progesterone plays a key role in regulating several aspects of health, particularly related to the menstrual cycle, mood, and cognitive function. When progesterone levels are insufficient, a wide array of symptoms may manifest, signaling the need for further evaluation.
Common Signs and Symptoms Include:
- Shortened Menstrual Cycles or Spotting Between Periods:
Progesterone plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy menstrual cycle. A deficiency can lead to shorter cycles, often less than 21 days, or cause spotting or bleeding between periods. This happens because insufficient progesterone may prevent the endometrial lining from fully developing, resulting in early shedding. - Difficulty Conceiving or Recurrent Miscarriages:
Progesterone is crucial for preparing the uterus for implantation and sustaining pregnancy. A deficiency can impair implantation, increase the risk of miscarriage, or lead to early pregnancy loss, particularly in the first trimester. Couples who have difficulty conceiving or who experience multiple miscarriages may find progesterone testing and support beneficial in addressing this issue. - Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) Symptoms, Such as Mood Swings and Irritability:
Low progesterone can disrupt the delicate balance between estrogen and progesterone during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, exacerbating PMS symptoms. Common mood-related symptoms include increased irritability, mood swings, anxiety, and emotional sensitivity. These hormonal fluctuations can also make it harder to manage stress or negative emotions during the premenstrual phase. - Breast Tenderness or Swelling:
Progesterone affects the mammary glands and contributes to breast tissue changes throughout the menstrual cycle. A deficiency can lead to discomfort, tenderness, or swelling of the breasts, especially in the days leading up to menstruation. - Fatigue and Low Energy Levels:
Progesterone is involved in regulating energy metabolism and promoting restorative sleep. Low levels can lead to chronic fatigue, feelings of sluggishness, or low energy levels. This can impact daily activities and create challenges in maintaining productivity and an active lifestyle. - Insomnia or Disrupted Sleep:
Progesterone has a calming effect on the nervous system, and low levels can interfere with sleep quality. Individuals with progesterone deficiency may struggle with insomnia or experience broken sleep, often waking up in the middle of the night. The disruption of sleep patterns can exacerbate other symptoms, such as fatigue and irritability. - Anxiety or Depression:
Progesterone has neuroprotective properties that support brain health and mood regulation. A deficiency may contribute to heightened feelings of anxiety, depression, or general emotional instability. Progesterone’s calming influence is essential for regulating the body’s stress response, and without it, individuals may feel more vulnerable to stressors. - Brain Fog and Difficulty Concentrating: Since progesterone plays a role in cognitive function, low levels can lead to brain fog, memory lapses, and difficulty concentrating. This is particularly noticeable during the luteal phase when progesterone naturally rises and falls. Women may find it harder to focus or process information, leading to decreased productivity and mental fatigue.

Additional Symptoms of Progesterone Deficiency May Include:
- Hot Flashes or Night Sweats:
Though more commonly associated with menopause, hot flashes and night sweats can also occur in individuals with low progesterone levels. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and disrupt daily routines or sleep. - Changes in Libido:
Progesterone contributes to a balanced hormonal environment, which includes regulating sexual desire. A deficiency may lead to a decreased libido or difficulty achieving sexual satisfaction. - Dry Skin or Hair Loss:
Low progesterone can disrupt the balance of other hormones, like estrogen, that support healthy skin and hair. As a result, individuals may experience dry or thinning skin, hair loss, or brittle nails. - Headaches or Migraines:
Progesterone deficiency can contribute to hormonal headaches or migraines, especially in the days leading up to menstruation. These headaches may be triggered or worsened by fluctuating hormone levels. - Digestive Issues:
Some individuals with progesterone deficiency may experience gastrointestinal symptoms like bloating, constipation, or changes in appetite. This is often linked to hormonal fluctuations that affect digestion and gut health.
Why Early Intervention Matters
Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking treatment is crucial to prevent long-term hormonal imbalances that can affect fertility and overall well-being. If multiple symptoms are present, especially if they interfere with daily life or reproductive health, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and to explore potential treatments.
How Progesterone Deficiency Impacts Fertility
A deficiency in progesterone can significantly affect fertility in the following ways:
- Implantation Failure: Without adequate progesterone, the uterine lining cannot sustain an implanted embryo.
- Early Pregnancy Loss: Low progesterone levels increase the risk of miscarriage, particularly in the first trimester.
- Irregular Ovulation: Insufficient progesterone disrupts the hormonal feedback loop necessary for regular ovulation.
- Impaired Stress Resilience: Low progesterone can amplify the body’s stress response, further hindering reproduction.
Diagnosing Progesterone Deficiency
Diagnosing progesterone deficiency requires a multifaceted approach:
- Symptom Assessment: A detailed medical history and symptom evaluation provide initial clues.
- Blood Tests: Measuring serum progesterone levels during the luteal phase can confirm deficiency.
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Charting: Tracking BBT helps identify ovulation and luteal phase length.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Evaluates ovulation and the thickness of the uterine lining.
Treatment Options for Progesterone Deficiency
The good news is that progesterone deficiency is often treatable. Here are some commonly recommended approaches:
Treating PCOS, thyroid disorders, or other contributing factors is critical for restoring hormonal balance.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Stress Management: Incorporate yoga, meditation, or other relaxation techniques to lower cortisol levels. Managing stress is a cornerstone of restoring hormonal balance.
Nutrition: Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, including leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins. Consuming foods that support progesterone production, such as vitamin B6-rich bananas and magnesium-rich spinach, is crucial.
Exercise: Moderate physical activity can improve hormonal balance without overtaxing the body.
Nutritional Supplements:
Vitamin B6: Supports progesterone production and helps regulate hormonal balance.
Magnesium: Aids in reducing stress and supporting endocrine health.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Promotes overall reproductive health.
Chasteberry (Vitex): An herbal remedy that can stimulate progesterone production by improving luteal phase function.
Hormonal Therapies:
Progesterone Supplements: Available as oral capsules, vaginal suppositories, or injections.
Clomiphene Citrate: Stimulates ovulation in cases of anovulatory cycles.
HCG Injections: Triggers ovulation and supports the corpus luteum.
Addressing Underlying Conditions:
Consider Acupuncture and Traditional Medicine
Acupuncture, a cornerstone of traditional Chinese medicine, has shown promise in improving reproductive health. By stimulating specific points in the body, acupuncture can enhance blood flow to the ovaries and uterus, regulate the menstrual cycle, and promote the release of hormones like progesterone. Consult a licensed acupuncturist with experience in fertility support for the best results.
Address Environmental Factors

Environmental toxins, known as endocrine disruptors, can interfere with hormone production. These chemicals, often found in plastics, cosmetics, and household products, mimic or block hormones, contributing to imbalances.
- Reduce Plastic Use: Opt for glass or stainless steel containers instead of plastic for food storage.
- Choose Clean Beauty Products: Look for skincare and makeup brands free from parabens, phthalates, and other hormone-disrupting chemicals.
- Filter Your Water: Install a water filtration system to reduce exposure to contaminants like pesticides or heavy metals that can interfere with reproductive health.
Build a Strong Support System
Hormonal imbalances, including progesterone deficiency, can feel isolating. Surrounding yourself with a support network can alleviate stress and provide encouragement. This might include:
- Joining fertility support groups to share experiences and gain emotional support.
- Seeking guidance from a holistic health practitioner, such as a naturopath, who specializes in hormone balance.
- Leaning on family and friends for reassurance and positivity throughout the journey.
When to Seek Help
If you suspect progesterone deficiency or have been trying to conceive without success for over a year (or six months if over 35), it’s time to seek professional guidance. Recurrent miscarriages or irregular menstrual cycles are also red flags that warrant medical evaluation.
Empowering Yourself Through Education and Advocacy
Understanding the impact of progesterone deficiency empowers individuals to advocate for their reproductive health. By recognizing symptoms, seeking appropriate medical care, and adopting a proactive approach to wellness, overcoming this hidden barrier to conception is possible.
Final Thoughts
Progesterone deficiency, though often overlooked, can profoundly impact fertility and overall well-being. With the right interventions and support, many individuals can overcome this challenge and achieve their dream of starting a family. Whether through lifestyle changes, nutritional support, or medical treatments, addressing progesterone deficiency is a key step toward reproductive success.
For anyone navigating infertility, remember you are not alone, and solutions exist. With persistence, knowledge, and the right healthcare team, the journey to conception becomes a shared effort with a hopeful destination.
Sources
https://drbrighten.com/boost-low-progesterone
https://drbrighten.com/hormones-affect-brain-health
https://integrative-medicine.ca/progesterone-in-functional-medicine/ https://whnacademy.com/courses/dutch/

Understanding PCOS and Fertility Challenges
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition that affects a woman’s hormone levels, leading to a myriad of health issues including infertility. Women with PCOS produce higher-than-normal amounts of male hormones, which can cause skipped menstrual periods and make it harder to get pregnant.
One of the main challenges of PCOS is insulin resistance. Many women with PCOS have difficulty using insulin effectively, which increases their risk of Type 2 diabetes. Elevated insulin levels can also increase androgen production, exacerbating symptoms like irregular periods and ovulatory dysfunction.
Further complicating the picture, recent research has highlighted the role of gastrointestinal flora in PCOS. Alterations in gut bacteria may lead to chronic inflammation and malabsorption, further impacting metabolic and reproductive health. This chronic inflammation is believed to underpin both insulin resistance and ovarian dysfunction, clearly illustrating the complexity of PCOS.
Infertility in women with PCOS is often due to anovulation, where the ovaries do not release an egg during a menstrual cycle. This can be deeply frustrating for those trying to conceive. However, the pathway to managing these fertility challenges lies in a holistic approach involving lifestyle changes, medications, and crucially, the right supplements.
The Role of Supplements in Boosting PCOS Fertility
When grappling with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), understanding how supplements can support your fertility journey can make a significant difference. Supplements often serve as the necessary booster shot, nurturing your body’s complex systems to better handle the challenges of PCOS. So, which supplements should you consider?
Firstly, let’s explore the importance of Inositol, an essential component for managing PCOS symptoms and enhancing fertility. Inositol, particularly in the forms of myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol, has garnered attention for its benefits like reducing blood triglyceride levels, improving insulin function, and even promoting ovulation. Combining inositol with folic acid might offer even greater advantages, including a reduced risk of gestational diabetes and preterm birth.
Another standout is Vitamin D. This ‘sunshine vitamin’ not only supports bone health but also plays a crucial role in maintaining regular menstrual cycles and promoting healthy ovulation. Studies indicate that women with PCOS often have lower levels of Vitamin D, so supplementing can bridge this gap, helping to regulate your cycle and improve your fertility prospects.
Omega-3 fatty acids deserve a special mention too. These healthy fats are pivotal in reducing the inflammation often associated with PCOS. Additionally, Omega-3s have been shown to balance hormones, thereby improving the chances of ovulation and subsequently increasing fertility. Sources of Omega-3s include fish oil supplements, flaxseeds, and chia seeds.
Lastly, consider adding antioxidants like Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and Vitamin E to your regimen. These supplements combat oxidative stress, a factor that can negatively impact ovarian health. By incorporating antioxidants, you create a healthier environment for your eggs, enhancing their quality and your overall reproductive health.
Top Vitamins for Enhancing Fertility in Women with PCOS
When it comes to boosting fertility, certain vitamins can make a significant difference, especially for women dealing with PCOS. Each vitamin plays a unique role in supporting reproductive health and managing symptoms associated with PCOS.
Vitamin B9 (Folate): Folate, commonly known as vitamin B9, is crucial for anyone trying to conceive. Not only does it help prevent neural tube defects in developing fetuses, but folate also plays a vital role in DNA synthesis and repair, which is essential for healthy egg development. Women with PCOS who take folate supplements may experience improved ovulation and a reduced risk of gestational complications.
Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 works in tandem with folate to ensure proper cellular function and fertility. This vitamin is particularly important for maintaining healthy red blood cells and nerve function. A B12 deficiency can lead to increased levels of homocysteine, a substance that, in high levels, can impair fertility. Supplementing with B12 can help manage homocysteine levels and, consequently, support a more favorable environment for conception.
Vitamin E: Known for its antioxidant properties, vitamin E is pivotal in protecting reproductive cells from oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can damage eggs and sperm, reducing the chances of successful fertilization. By including vitamin E in your supplement regimen, you may enhance the quality of your eggs, thus improving your fertility prospects.
Vitamin C: Another powerful antioxidant, vitamin C, plays a significant role in hormone regulation and immune function. For women with PCOS, vitamin C can help boost progesterone levels and enhance overall hormonal balance. This is crucial for regular menstrual cycles and optimal fertility. Additionally, vitamin C is vital for the formation of the endometrial lining, where a fertilized egg implants and grows.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Including omega-3 fatty acids in your diet can work wonders for your fertility health. Rich in anti-inflammatory properties, these fatty acids are essential for maintaining hormonal balance and improving insulin sensitivity — a common issue in women with PCOS. Omega-3 supplements can also help reduce the occurrence of ovarian cysts and improve blood flow to the reproductive organs.
Integrating these vitamins into your daily routine can provide a substantial boost to your fertility, serving as a supportive foundation as you navigate the complexities of PCOS. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplementation regimen to ensure it’s tailored to your specific needs.
The Power of Inositol: A PCOS Fertility Game-Changer
Inositol, a type of sugar related to the B-vitamin family, has shown immense potential in the management of PCOS-related fertility challenges. Often categorized into myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol, these naturally occurring compounds play a significant role in the regulation of insulin and hormone levels.
Numerous studies highlight inositol’s efficacy. For instance, myo-inositol has been found to improve insulin sensitivity, a critical factor because insulin resistance is a common issue among women with PCOS. By enhancing insulin function, myo-inositol helps lower insulin levels, which in turn can reduce androgen levels – often responsible for symptoms like irregular periods and ovarian cysts.
Notably, inositol doesn’t just stop at regulating insulin. It also significantly improves ovulation rates and menstrual regularity. This is crucial for women trying to conceive, as regular ovulation increases the likelihood of successful fertilization. Combining myo-inositol with D-chiro-inositol has been particularly effective, with research suggesting this duo can restore ovary function and bring metabolic balance.
For those concerned about safety, inositol is generally well-tolerated. Current research supports its use as both an effective and safe treatment option for PCOS. The combination of myo-inositol and folic acid is particularly noteworthy, offering benefits like reduced blood triglyceride levels and improved blood pressure, alongside its fertility-boosting capabilities.
Whether you’re hoping to manage PCOS symptoms better or actively trying to conceive, inositol offers a promising, natural pathway to improved reproductive health. Always consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it’s suitable for your specific scenario.
The Benefits of Vitamin D for PCOS and Fertility
Vitamin D, often dubbed the “sunshine vitamin,” plays a pivotal role in various bodily functions, including hormone regulation and reproductive health. For women grappling with PCOS, adequate levels of Vitamin D can offer significant benefits.
Additionally, Vitamin D plays a critical role in reducing inflammation, which is often a concern in PCOS. This reduction in inflammation can help manage symptoms and improve your reproductive health. Elevated inflammatory markers are common in women with PCOS and addressing these can boost your chances of conception.
Not to mention, Vitamin D is also essential for maintaining bone health, which can sometimes be compromised in women with hormonal imbalances. Ensuring adequate levels of this vitamin can be a simple yet effective way to support your fertility journey.
In conclusion, while the benefits of Vitamin D for overall health are numerous, its specific role in enhancing insulin sensitivity and promoting a regular menstrual cycle makes it a powerful supplement in the battle against PCOS-related fertility challenges.
How Omega-3 Fatty Acids Can Improve PCOS Symptoms
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that your body can’t produce on its own, often found in foods like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. These fats play a key role in managing PCOS symptoms and improving overall fertility.
Reduces Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a common issue for individuals with PCOS. Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce this inflammation, which in turn may alleviate some symptoms of PCOS.
Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Women with PCOS often struggle with insulin resistance, and Omega-3 fatty acids can enhance insulin sensitivity. This helps in managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risks associated with insulin resistance, such as Type 2 diabetes.
Balances Hormones: The hormone-balancing effect of Omega-3s can be particularly beneficial. These fatty acids can reduce levels of androgens (male hormones) which are often elevated in women with PCOS, leading to symptoms like acne, hair loss, and hirsutism (excess body hair).
Supports Heart Health: Heart disease risk is higher in women with PCOS due to factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity. Omega-3 fatty acids help lower blood pressure, reduce triglycerides, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
To reap these benefits, you might consider taking Omega-3 supplements such as fish oil. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement to ensure it’s appropriate for you.
NAC: N-Acetyl Cysteine NAC, a potent antioxidant, has shown promise for improving insulin sensitivity, a major concern for women with PCOS. By helping to regulate blood sugar levels, NAC can potentially enhance overall fertility. It also plays a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress, which can be a contributing factor to infertility in PCOS patients.
Furthermore, research suggests that NAC may assist with ovulation. One study found that women with PCOS who took NAC experienced a higher rate of ovulation compared to those who didn’t. This can be particularly beneficial for those trying to conceive, as regular ovulation is key to increasing the chances of pregnancy.
In addition to its fertility benefits, NAC can also support liver health, which is often compromised in individuals with PCOS due to increased fat storage and inflammation. By boosting glutathione production, an essential antioxidant for detoxifying the liver, NAC helps in maintaining overall liver function.
Overall, incorporating NAC into your supplement regimen could be a valuable step towards enhancing fertility and managing PCOS symptoms. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement to ensure it aligns with your individual health needs.
Herbal Supplements: Natural Remedies for PCOS Fertility
Herbal supplements have long been used as natural remedies for various ailments, and PCOS fertility is no exception. Many women with PCOS turn to herbal solutions not only for their potential efficacy but also because they often come with fewer side effects than pharmaceutical options.
Vitex (Chaste Tree Berry)
Vitex agnus-castus, commonly known as chaste tree berry, is one of the most popular herbal supplements for women with PCOS. It helps balance hormone levels by regulating the pituitary gland, which controls the production of several key hormones. Studies suggest that Vitex can increase progesterone levels and potentially improve menstrual regularity and ovulation.
Maca Root
Maca root is another well-known herb used for balancing hormones and enhancing fertility. Native to Peru, this adaptogenic herb may help regulate hormone imbalances, support adrenal function, and improve overall energy levels. Women with PCOS often report reduced symptoms and improved menstrual cycle regularity after consistent use of maca root.
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is not just a flavorful spice; it can also be beneficial for women with PCOS. Research indicates that cinnamon may help improve insulin sensitivity, which is often compromised in women with PCOS. Improved insulin sensitivity can lead to better regulation of hormones and, consequently, enhanced fertility.
Spearmint Tea
Spearmint tea is another natural remedy that has shown promise in addressing PCOS symptoms. Drinking spearmint tea regularly can help lower testosterone levels, which can reduce unwanted hair growth and improve the menstrual cycle. Sipping on this refreshing tea may provide comfort while contributing to hormonal balance.
Tribulus Terrestris
Tribulus terrestris is an herb often used in traditional medicine to improve fertility and sexual health. Some studies suggest that Tribulus can help stimulate ovulation and normalize menstrual cycles, making it a useful herbal supplement for women with PCOS.
When considering herbal supplements, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure they’re appropriate for your specific situation. While herbs can offer a gentle and natural approach to managing PCOS symptoms and improving fertility, they can interact with other medications and should be used with caution.
Consulting Your Healthcare Provider Before Starting Supplements
Before you introduce any supplement into your routine, it’s crucial to have a conversation with your healthcare provider. This is particularly important for women with PCOS, as individual health profiles and specific needs vary widely. By consulting with a healthcare professional, you can tailor your supplement regimen to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Discussing any new supplement, like inositol, with your doctor will help determine the appropriate dosage and form that’s best for you. Inositol supplements, for instance, are generally well-tolerated but varying dosages can influence their effectiveness and potential side effects. Your healthcare provider can guide you on the right path, taking into account your medical history and existing treatments.
Moreover, it’s essential to consider safety, especially if you are pregnant, planning to conceive, or breastfeeding. While some supplements can offer numerous health benefits, more research is needed to confirm their safety in these specific conditions. Consulting your doctor ensures that you are making informed choices that support your reproductive health goals without compromising your well-being.
In sum, while supplements can be a valuable addition to managing PCOS and enhancing fertility, professional guidance is key. This step not only optimizes your health journey but also provides peace of mind, knowing that your approach is both safe and personalized.
Key Takeaways:
To boost fertility in women with PCOS, certain supplements can make a significant difference. Inositol, particularly, stands out as a game-changer, potentially improving ovarian function and boosting fertility. Similarly, Vitamin D plays a crucial role in regulating menstrual cycles and improving insulin resistance, both vital for managing PCOS symptoms.
Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to reducing inflammation and regulating hormone levels, further enhancing fertility prospects. Herbal supplements like Vitex, Maca Root, Cinnamon, Spearmint Tea, and Tribulus Terrestris offer natural solutions to balance hormones and support reproductive health.
Remember, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen. This ensures the chosen supplements align with your unique health needs and treatment plans.
In summary, while supplements can provide significant benefits, they should be a part of a comprehensive approach that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and medical guidance. Always prioritize safety and informed choices in your fertility journey.

Oatmeal contains high levels of minerals, such as magnesium and zinc, in addition to fiber and B vitamins. This makes it a great food option if you are struggling with PCOS. Oatmeal can be your quick fiber-rich breakfast, an afternoon snack or eaten really anytime of day! The ingredients are minimal, and you probably have them in your pantry already. It’s a win-win.
Which type of oats is best for PCOS?
The less processed it is the better! Instant oatmeal is the most processed form of oats. Then it’s old fashioned oats and lastly steel cut oats. Steel cut oats have a sharper texture than old fashioned oats that some people don’t enjoy. If it’s your preference, old fashioned oats would still be a healthy choice!

Which breakfast is best for PCOS?
The best breakfast for PCOS is well balanced with lean protein, healthy fats, and whole grains/complex carbohydrates. As a bonus you could even add in some veggies, like if you were having a smoothie or eggs.
Examples of lean protein choices for breakfast include:
- Eggs
- Nut butter (peanut, almond, etc.)
- Nuts and seeds (chia seed, ground flaxseed, etc.)
- Greek yogurt
- Leftover fish or chicken — Hey, who says breakfast has to be “breakfast food”? 😉
- Tofu
- Some plant-based milks with protein like Ripple
Healthy fats such as polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats are also important in helping us to feel full. These fats give us energy to start the day off right! We can get these healthy fats from foods such as salmon, sardines, avocado, nuts (walnuts, pistachios) and seeds (for example chia and ground flaxseeds).
And last but not least, don’t forget the healthy carbs! Most women with PCOS think they have to avoid carbs and this is simply not true. Fruit, whole grains/complex carbohydrates are considered healthy carbs.
Best fruit choices for PCOS:
- Whole, fresh fruit – all kinds!
- Frozen fruit
- Most of the time frozen fruit does not have added sugar. So there is nothing wrong with eating frozen fruit.
- Dried fruit without added sugars
- Double check the nutrition facts label and try to avoid dried fruit with sugar.
- If it does have sugar remember this quick tip: Keep total added sugars under 25 grams per day for women.
Examples of whole grains/complex carbs for breakfast include:
- Whole grain bread or English muffin
- Oatmeal
- High fiber, low sugar cereal
- Low sugar granola
- Plantains/potatoes
Best Oat Recipes For PCOS

Chocolate Peanut Butter Cup Oatmeal:
1/4 cup rolled oats
1/2 cup unsweetened nut milk
1 tbsp all-natural peanut butter
1 serving chocolate protein powder
2 tsp ground flax seeds
1 tsp chia seeds
sea salt to garnish
Instructions:
Mix oats, flax seeds, chia seeds and nut milk in a bowl.
Microwave for 1-2 minutes
Stir in peanut butter and protein powder.
Top with a sprinkle of sea salt.
Looking for more Support?
Be sure to check out our Free Live Masterclass all about the top 3 ways to naturally enhance your fertility (perfect for those struggling with PCOS and hormone imbalances!)

The Preconception Playbook
This free playbook provides specific actionable tips to get started on your fertility journey, as well as what to avoid while you're trying to conceive.
Get the free playbook