Resources
Style
Planning
View All
THE blog
Many women with PCOS struggle to find an effective treatment plan due to its complex nature. However, recent research has begun to shine a light on the crucial role the gut microbiome plays in managing this condition. Your gut does more than just digest food; it influences hormone regulation, inflammation, and even your overall metabolic health.
This article dives into how optimizing your gut health can significantly impact PCOS management. From understanding the gut-hormone link to practical dietary changes you can make, you’ll gain valuable insights to improve your wellbeing.
Understanding PCOS: A Brief Overview
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects a significant portion of women around the world, with implications that go beyond just the reproductive system. At its core, PCOS is a hormonal disorder known for causing irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries. But, it doesn’t stop there. This complex condition often brings a host of other challenges, including insulin resistance, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular issues.
The exact cause of PCOS remains a subject of ongoing research, but genetics and lifestyle factors both appear to play substantial roles. Women with PCOS frequently exhibit elevated insulin levels, which can exacerbate symptoms and contribute to the imbalance of sex hormones. What’s more, the syndrome can profoundly impact mental health, leading to conditions like anxiety and depression.
With no known cure, managing PCOS involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, and medical treatments tailored to alleviate specific symptoms. Because PCOS affects different women in different ways, it’s crucial to approach treatment on an individualized basis. In recent years, emerging studies have started to explore the connection between gut health and PCOS, revealing that a balanced gut microbiome might be an essential key to managing this disorder.

The Gut-Health Connection: Why It Matters
Your gut health doesn’t just affect your digestion; it has a profound impact on your overall well-being. The human gut microbiome, an ecosystem of trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, plays a crucial role in many bodily functions. Notably, it helps regulate metabolism, supports the immune system, and maintains the structural integrity of the gut lining.
But the relationship between gut health and conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is particularly interesting. The gut-brain axis, a complex communication network that links your gut and brain, further illustrates this connection. When your gut microbiota is in balance, it positively influences hormonal health, which is central to managing PCOS symptoms.
Emerging research highlights how an imbalance in the gut microbiota, also known as dysbiosis, can exacerbate PCOS symptoms. Dysbiosis has been linked to increased inflammation, insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalances—all of which are critical factors in PCOS. This makes maintaining a healthy gut not just a recommendation, but a necessity for those managing PCOS.
Moreover, factors like diet, sleep, and exercise play a significant role in shaping your gut microbiome. Consuming a diet rich in diverse, fiber-rich foods, getting quality sleep, limiting alcohol intake, and engaging in regular physical activity can all foster a healthier gut. By focusing on these areas, you can support your gut health and, in turn, help manage PCOS more effectively.
How Gut Bacteria Influence Hormonal Balance
In understanding gut health’s role in PCOS, it’s essential to dive into the relationship between gut bacteria and inflammation. Gut microbiota plays a crucial role in regulating hormones and metabolism. When your gut microbiota is unbalanced, it can lead to chronic inflammation, a common issue in those with PCOS. But how exactly does this happen?
Your gut lining serves as a barrier, preventing harmful substances from entering your bloodstream. However, an imbalanced gut microbiota can weaken this barrier, allowing toxins and bacteria to escape into your system. This phenomenon, known as “leaky gut,” triggers your immune system to react, leading to chronic inflammation.
This inflammation doesn’t just stay localized in your gut. It can spread throughout your body, affecting various organs and tissues, including your ovaries. Chronic inflammation can exacerbate the symptoms of PCOS by disrupting your hormonal balance. For example, inflammation can impair insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance – a hallmark of PCOS.
Moreover, hyperandrogenism, or elevated levels of male hormones, is closely linked to gut health. Research indicates that your gut microbiota can influence sex hormone production. In those with PCOS, an imbalanced gut microbiota may contribute to increased testosterone levels, worsening symptoms like excess hair growth, acne, and menstrual irregularities.
Addressing inflammation through gut health can be a powerful strategy. By focusing on a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, you can help restore balance to your gut microbiota. Probiotics, prebiotics, and other dietary supplements may also play a vital role in reducing inflammation and supporting a healthier hormonal balance.
The Role of Inflammation in PCOS and Gut Health
Chronic inflammation is a known factor in the development of PCOS. Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of PCOS, often linked to an imbalance in gut microbiota. When your gut bacteria are out of balance, it can lead to increased intestinal permeability, commonly known as “leaky gut.” This condition allows toxins and partially digested food particles to enter the bloodstream, triggering an immune response and chronic inflammation.
This persistent inflammation can exacerbate insulin resistance, a common feature in PCOS. Insulin resistance leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which in turn can cause the body to produce more insulin. High insulin levels stimulate the ovaries to produce more androgens, contributing to symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and hirsutism.
Moreover, chronic inflammation influences ovarian function and insulin sensitivity through various biochemical pathways. For instance, certain inflammatory markers like IL-22 have been shown to affect ovarian granulosa cells, which are crucial for hormone production and ovarian health. Inflammatory cytokines can also disrupt the normal functioning of the ovaries, potentially worsening PCOS symptoms.
It’s also worth noting that Vitamin D deficiency, commonly observed in PCOS patients, can further exacerbate inflammation. Vitamin D has anti-inflammatory properties, and its lack can lead to an increase in inflammatory responses, thereby worsening both gut health and PCOS symptoms. It is also known that Women with PCOS often have altered gut microbiota compared to those without PCOS.
Given this intricate relationship, addressing inflammation by improving gut health can be a promising approach to managing PCOS. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, probiotics, and dietary changes can help maintain a balanced gut microbiota, reduce intestinal permeability, and ultimately mitigate the inflammatory processes that contribute to PCOS.
Recognizing the Signs of Poor Gut Health
Recognizing the signs of poor gut health is crucial in managing PCOS effectively. You might wonder what symptoms to look out for. Here’s a quick guide to help you identify potential gut issues:
- Digestive discomfort: Frequent bloating, gas, diarrhea, or constipation could indicate an imbalance in your gut microbiota.
- Food intolerances: If you notice increased sensitivity to certain foods, it might be linked to gut health issues.
- Fatigue: Chronic tiredness can be a sign that your gut is not absorbing nutrients properly.
- Skin conditions: Issues like eczema or acne can be linked to gut health, as inflammation in the gut often manifests on the skin.
- Mood changes: An unbalanced gut microbiota can lead to abnormal hormone changes, potentially contributing to anxiety and mood swings.
- Unintentional weight changes: Both weight gain and loss without any obvious reason can indicate a gut health problem.
It’s important to be attentive to such signs because they can be early indicators of more significant issues. If you experience any of these symptoms consistently, it might be time to take a closer look at your gut health, especially if you have PCOS.
Dietary Changes to Boost Gut Health for PCOS
Making the right dietary choices can significantly influence your gut health and, by extension, help manage symptoms of PCOS. Let’s delve into some practical and effective changes you can implement.

1. Incorporate Fiber-Rich Foods
Fiber acts as fuel for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can support these bacteria, which in turn helps regulate hormones and reduce inflammation. Aim to include at least 25-30 grams of fiber daily.
2. Add Fermented Foods

Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha are brimming with probiotics. Regularly consuming these foods can help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiota, crucial for managing PCOS symptoms. Probiotics, like bifidobacterium lactis V9, in particular, have shown promising results in improving gut health for women with PCOS.
3. Focus on Prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. Foods like garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus, and oats are excellent prebiotic sources. Integrating these into your diet can help nurture a healthy gut environment. Probiotics and prebiotics can positively influence gut microbiota.
4. Opt for Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, particularly those from omega-3 fatty acids, can reduce inflammation and support overall gut health. Include sources such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts in your meals to reap their benefits.
5. Minimize Processed Foods and Sugars
Highly processed foods and sugary snacks can promote harmful bacteria growth and contribute to gut dysbiosis. Steering clear of these foods can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which is crucial for managing PCOS effectively.
By making these dietary adjustments, you can create a supportive environment for your gut health, potentially alleviating some of the hormonal and metabolic challenges associated with PCOS. Remember, small, consistent changes can lead to significant improvements over time.
Supplements That Support Gut Health in PCOS
Supplements can play a significant role in supporting gut health, particularly for women managing PCOS. Integrating the right supplements into your routine can help rebalance your gut microbiota, leading to improved overall health.

Probiotics
One of the most well-researched supplements for gut health is probiotics. Strains like Bifidobacterium lactis V9 have shown promise in improving gut health in women with PCOS. Probiotics can help restore the natural balance of gut bacteria, which in turn may enhance metabolic and reproductive functions. One of our favorites is Megaspore biotic – which you can find inside our supplement store right here.
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are another cornerstone of gut health. These are non-digestible fibers that fuel the growth of beneficial bacteria in your gut. Incorporating prebiotic supplements can create a more favorable environment for your gut microbiota, helping to improve hormonal balance and reduce inflammation, both crucial for managing PCOS.
Synbiotics
Combining probiotics and prebiotics, synbiotics offer dual benefits. By taking these supplements, you provide your gut with beneficial bacteria while ensuring they have the nutrients they need to thrive. This synergistic approach can be particularly effective for restoring gut microbiota diversity and improving PCOS symptoms.
Vitamin D
Emerging research suggests that Vitamin D might influence the occurrence of PCOS by affecting the composition of gut microbiota. Vitamin D supplementation could improve gut health and potentially alleviate some symptoms of PCOS by enhancing the microbiota balance. *It’s important to test vitamin D levels before supplementing, as you can go *too high* with this as well.
Getting Support with Your Gut Health and PCOS
If you’re looking for more support with managing your PCOS, improving your gut health, and preparing your body for a healthy pregnancy, reach out to our team of highly trained functional fertility nutritionists.
We utilize functional lab testing such as the GI MAP, to help uncover the root cause of your fertility struggles. We’ve worked with hundreds of women in our practice, and are here to support you!

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a condition that can significantly affect a woman’s health and fertility, but diet plays a crucial role in managing its symptoms. For many women, questions arise about the impact of dairy on their condition. Contrary to popular belief, consuming dairy may not be harmful and can even offer benefits. Recent studies suggest that incorporating certain types of dairy could support hormonal balance and improve fertility. Let’s explore how you can make dairy work for you if you’re navigating life with PCOS.
The Role of Diet in Managing PCOS
Your diet has a profound impact on managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet not only helps to alleviate symptoms but also supports overall well-being. One of the primary goals in managing PCOS through diet is stabilizing insulin levels, as insulin resistance is a common issue among women with this condition.
Dairy and Hormonal Balance: What You Need to Know
When discussing hormonal balance and PCOS, dairy often comes under scrutiny. However, it’s important to understand that no single dietary choice universally affects every woman in the same way. Dairy has gotten a bit of a bad rap in the realm of hormonal health, but recent research sheds a more nuanced light on its role, and probably let you to ask the question at some point: Can I eat dairy with PCOS?
The Hormonal Connection: Some studies suggest that dairy can influence hormone levels due to the presence of natural hormones in milk. Yet, this impact may not necessarily be negative. For instance, certain high-fat dairy products, like full-fat yogurt and cheese, contain beneficial nutrients that support hormonal balance. These include calcium, vitamin D, and various bioactive compounds that may aid in regulating your menstrual cycle and improving overall fertility. Dairy products provide essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein, which are beneficial for reproductive health.
Additionally, dairy is a valuable source of protein, which plays a key role in managing blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity – crucial aspects for women with PCOS. According to some findings, consuming high-fat dairy could enhance insulin sensitivity and promote more stable glucose levels, potentially mitigating some PCOS symptoms.
One study highlighted by Gunther et al. categorized 155 women by their dairy intake and observed lower fat accumulation in those with higher dairy consumption over a six-month follow-up period. This suggests that, for some, dairy might contribute to better weight management, another crucial factor for hormonal health.
To maximize the benefits, it’s advisable to opt for organic, pasture-raised, and whole-fat dairy products. These options minimize exposure to synthetic hormones and preservatives, offering a cleaner source of nutrition.
While dairy’s effects can vary based on individual tolerance and physiology, incorporating it mindfully might just provide the hormonal harmony you need for better fertility outcomes.
Recent Studies on Dairy and Fertility in Women with PCOS

Recent research has highlighted the potential benefits of dairy consumption for women with PCOS, especially concerning fertility. A study conducted at Shahid Beheshti hospital clinic in 2013 involving 400 women explored the relationship between dairy intake and PCOS. The results were intriguing, suggesting that women who consume dairy products may experience fewer PCOS symptoms and improved fertility outcomes. High-fat dairy consumption is actually associated with a 27% lower risk of ovulatory infertility
Historically, the influence of dairy products on female fertility and ovulation has drawn considerable interest. Numerous studies have pointed toward a positive correlation, particularly with full-fat dairy products. These products, laden with healthy fats, can help regulate blood sugar levels, which is crucial for women with PCOS.
Interestingly, a prospective study examining dairy food intake and anovulatory infertility found that incorporating full-fat dairy into the diet may reduce the risk of this type of infertility. This is a significant finding, as anovulatory infertility is one of the primary reproductive challenges women with PCOS face. (Article: Women who consume full-fat dairy products have a 25% lower risk of infertility due to anovulation)
However, the existing body of research is not without its inconsistencies. While several studies suggest beneficial effects, others call for more comprehensive, randomized clinical trials to conclusively determine the impact of dairy on PCOS and related conditions like Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). Despite these inconsistencies, the overall trend appears promising.
Including dairy products in your diet could indeed be advantageous if you have PCOS. Many experts now advocate for the integration of milk and dairy products into the dietary plans of women with PCOS due to their beneficial effects on diabetes risk and their neutral or positive effects on ovulation and fertility.
Types of Dairy That May Boost Fertility
If you’re considering adding dairy to your diet to potentially boost fertility, it’s essential to choose the right types. According to research, full-fat dairy products may provide more benefits compared to their low-fat and fat-free counterparts. The higher fat content in full-fat dairy aids in better blood sugar regulation, a crucial factor for women with PCOS.
For starters, whole milk is an excellent option. Studies have indicated that consuming whole milk, rather than skim or low-fat versions, can significantly reduce the risk of ovulatory infertility. This is due to the presence of beneficial fatty acids that may enhance ovarian function.
Next, consider incorporating whole milk yogurt. Not only does it offer probiotic benefits for gut health, but it’s also packed with essential nutrients that support hormonal balance, such as calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D.
Organic full-fat cheese is another dairy product that may be beneficial. Rich in essential fats, vitamins, and protein, organic cheese can be a delicious and nutritious way to support your fertility journey. Remember to opt for organic versions to avoid potential hormonal disruptors found in non-organic dairy products.
Don’t forget about butter and cream. These often-overlooked dairy products can be healthful additions to your diet in moderation. They provide high-quality fats that are essential for maintaining hormonal health and improving the body’s insulin sensitivity, which is particularly important for managing PCOS symptoms.
Additionally, raw milk has been a subject of interest in various health and nutrition studies. One of the primary benefits often cited is its rich content of natural enzymes and probiotics. These enzymes, such as lactase, can aid in the digestion of lactose, potentially making raw milk easier to digest for some individuals who are lactose intolerant.
In summary, focusing on full-fat, organic dairy products like whole milk, yogurt, cheese, butter, and cream could be a strategic move in improving fertility outcomes for women with PCOS. However, always remember to monitor your body’s response and consult with a healthcare professional to tailor dietary choices to your specific needs.
How Much Dairy Should You Eat?
Determining the right amount of dairy can be a balancing act, especially when managing PCOS. Research suggests that moderate dairy consumption may benefit women with PCOS. For example, studies have indicated that consuming around 2.6 servings of dairy per day could lower the risk of type 2 diabetes by 21%. Additionally, another study reported a 30% lower risk when consuming 1.9 servings of low-fat dairy products daily.
But how do you translate this into your daily diet? A serving of dairy can be one cup of milk, one cup of yogurt, or around 1.5 ounces of cheese. Integrating these servings into your meals can be simple and enjoyable. Imagine starting your day with a yogurt parfait, using milk in your morning coffee, or adding a slice of cheese as a snack.
It’s crucial to choose the right type of dairy. Opt for organic, pasture-raised, and whole-fat products whenever possible, as these tend to have higher nutritional value. However, balance is key. Overconsumption of any food group can lead to unintended consequences, so moderation is essential. Aim to observe how your body responds to different amounts of dairy and adjust accordingly.
Lastly, while these guidelines can help you get started, remember to personalize your diet. Consulting with a dietitian or healthcare provider can provide tailored advice that aligns with your unique health profile and fertility goals. Regular check-ins will also help you monitor any changes or improvements, ensuring that your diet supports your overall well-being.
Myths and Facts About Dairy Consumption with PCOS

When it comes to dairy and PCOS, there is a whirlwind of myths that can leave you feeling confused. It’s important to separate fact from fiction to make informed choices that best support your health and fertility.
Myth: Dairy should be completely avoided if you have PCOS.
Fact: While some women may find that dairy exacerbates their symptoms, it is not a universal rule. Many women with PCOS can consume dairy without adverse effects. In fact, some studies suggest that full-fat dairy can be beneficial for hormonal balance and fertility.
Myth: Low-fat dairy is always the healthier choice.
Fact: Research indicates that full-fat dairy products may actually be more favorable for women with PCOS. The higher fat content helps with blood sugar regulation and may support overall hormonal balance, which can positively impact fertility.
Myth: All dairy products affect insulin resistance the same way.
Fact: Different types of dairy can have varying impacts on insulin resistance. While some studies suggest that low-fat dairy might exacerbate insulin resistance, other research shows that fermented dairy products like yogurt may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes in women with PCOS. It’s essential to consider the type of dairy you’re consuming.
Myth: Dairy alternatives are always better than traditional dairy.
Fact: Dairy-free alternatives may not always be the healthier option. Some of these products can contain high amounts of added sugars or artificial sweeteners, which could worsen PCOS symptoms. Reading labels and choosing products with minimal additives is crucial.
By distinguishing facts from myths, you can craft a more effective dietary plan that aligns with your health goals and supports your journey with PCOS.
Monitoring Your Body’s Response to Dairy
Monitoring how your body responds to dairy is crucial when managing PCOS. Start by paying close attention to any immediate physical changes post-consumption. Symptoms like bloating, gas, and changes in bowel habits can be telltale signs of how your body is reacting. Additionally, a thorough self-check for skin issues, such as acne or rashes, can provide valuable insights.
Remember, everyone’s body responds differently to food. Finding the right balance takes time and patience, but understanding your individual response to dairy can play a significant role in managing PCOS effectively and potentially improving fertility outcomes.
Key Takeaways:
- Dairy can be beneficial: Emerging research suggests that consuming dairy may have positive effects on fertility for women with PCOS.
- Types of dairy matter: Opt for low-fat or fermented dairy products such as yogurt and kefir, which may offer more benefits.
- Monitor your intake: While dairy can help, moderation is key. Aim for balanced portions that fit into your overall dietary plan.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to how your body reacts to different types of dairy. What works for one person may not work for another.

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects millions of women worldwide, often making the journey to conception a challenging one. If you’re navigating the complexities of PCOS, understanding the role of insulin resistance is crucial not just for managing symptoms but also for enhancing your fertility naturally. This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the connection between PCOS and insulin resistance, offering practical dietary and lifestyle tips to help you take control of your health.
A journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step. Let’s start with understanding how insulin resistance impacts PCOS.
- Types of PCOS
- What is Insulin Resistance?
- Causes of Insulin Resistance in PCOS
- Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
- Dietary Tips for Managing Insulin Resistance
- Which Labs to Request when you have PCOS
- Conclusion
Types of PCOS
There are four different types of PCOS. Each type comes with its own set of challenges and requires tailored management strategies.
- Insulin-Resistant PCOS: This is the most common type and is characterized by significant insulin resistance, leading to high insulin levels. Managing this type involves focusing on improving insulin sensitivity through diet and lifestyle changes.
- Inflammatory PCOS: Women with this type often experience symptoms like unexplained fatigue, skin issues like eczema or psoriasis, and elevated levels of inflammation markers. Anti-inflammatory diets and stress management techniques can be particularly beneficial.
- Adrenal PCOS: This type is linked to an abnormal stress response, leading to elevated levels of DHEA-S, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Stress reduction techniques and targeted dietary changes are crucial for managing this type.
- Post-Pill PCOS: Some women experience PCOS-like symptoms after discontinuing birth control pills. This type often resolves on its own, but meanwhile, focusing on hormonal balance and liver health can help.
Understanding which type or combination of types of PCOS you have can significantly impact your fertility treatment plan. It’s essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine your specific type and develop a personalized strategy.
Okay, so let’s dive into the first one: insulin-resistant PCOS. Up to 70% of women with PCOS have insulin resistance, so this tends to be the one we focus on the most in our practice. But really, all women should be concerned with blood sugar management when trying to conceive.
What is insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance is a condition where your body’s cells become less responsive to the hormone insulin. This means that the glucose in your blood isn’t efficiently absorbed into your cells, leading to higher blood sugar levels. For women with PCOS, this can be particularly problematic, as insulin resistance can exacerbate many of the symptoms associated with the syndrome.

In simple terms, when you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is the main source of energy for your cells. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, helps transport this glucose into your cells. When you have insulin resistance, your cells don’t respond effectively to insulin, so your pancreas produces more insulin to compensate. This can lead to a myriad of issues, including weight gain and difficulty losing weight, two common problems associated with PCOS.
The relationship between PCOS and insulin resistance is complex. Though insulin resistance is commonly linked to obesity, it can also occur in women with PCOS who are lean. Research has shown that the mechanism of insulin resistance in PCOS differs from that seen in individuals with type 2 diabetes, suggesting unique cellular and receptor abnormalities.
It’s crucial to address insulin resistance not only to improve your fertility but also to reduce the risk of developing other long-term health issues like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, understanding and managing insulin resistance through diet, exercise, and possibly medications such as metformin is vital for anyone dealing with PCOS.
Causes of Insulin Resistance in PCOS:
This debilitating condition isn’t only limited to those struggling with weight issues; it affects lean women as well. Insulin resistance in PCOS involves a complex interplay between hormones and metabolic processes.
In many cases, the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, forcing the pancreas to produce more of this hormone to compensate. This condition, known as compensatory hyperinsulinemia, exacerbates the hormonal imbalances already present in PCOS, contributing to an increase in androgen levels. Elevated androgens can lead to several of the symptoms associated with PCOS, such as irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and excessive hair growth.
Understanding the underlying causes and identifying symptoms can help you take targeted steps to manage them effectively. Research has shown that regardless of body mass index, the unique cellular mechanisms and insulin receptor functions in women with PCOS are inherently different.
It’s essential to recognize these differences to tailor appropriate lifestyle and dietary modifications that can help regain control over your insulin levels and improve your overall reproductive health. Taking proactive steps can make a significant difference in managing both PCOS and insulin resistance.
Symptoms of Insulin Resistance:
Recognizing the symptoms of insulin resistance can be a crucial step in managing PCOS effectively. Often, these symptoms overlap with those of PCOS, making it essential to pay close attention to your body and how it responds to different situations and dietary choices.
Common symptoms of insulin resistance include:
- Increased hunger and cravings, particularly for sugary or carbohydrate-rich foods
- Weight gain, especially around the abdomen, despite no significant changes in diet or lifestyle
- Fatigue or feeling overly tired, even after adequate rest
- Difficulty losing weight, even with diet and exercise efforts
- Dark, velvety patches of skin, often found on the neck, armpits, or groin area, known as acanthosis nigricans
- Frequent or increased need to urinate
- Increased thirst
If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and management can help mitigate the risk of associated conditions, such as type 2 diabetes. Testing for insulin resistance typically involves blood tests to measure fasting blood glucose and insulin levels. Other tests, like the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), may also be utilized to get a comprehensive understanding of your body’s insulin response.
Understanding these symptoms and seeking timely medical advice can empower you to take control of your health and make informed decisions about your lifestyle and dietary choices.
Dietary Tips for Managing Insulin Resistance
In our private practice, we work with many women with PCOS. In fact PCOS is the leading cause of fertility struggles among women. 70-80% of women with PCOS experience infertility. Luckily, there are ways to manage PCOS and insulin resistance, and still go on to have a healthy pregnancy.
One of the cornerstones of managing PCOS and improving fertility is understanding and addressing insulin resistance. Insulin resistance plays a significant role in how PCOS affects your body, contributing to issues like weight gain, irregular menstrual cycles, and difficulty with ovulation. By focusing on lifestyle and dietary changes, you can effectively reduce insulin resistance and enhance your chances of conception.

Firstly, adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods is crucial. Emphasize low glycemic index (GI) foods, which help manage blood sugar levels more effectively. Think whole grains, legumes, lean proteins, and plenty of vegetables. Incorporating these into your daily meals can stabilize insulin levels and support overall health. Dietary changes can improve insulin sensitivity by 25-30%
To further optimize your diet for managing insulin resistance, follow these specific tips:
- Balance Your Carbs: Avoid eating carbohydrates on their own. Pair them with proteins or healthy fats to slow down digestion and prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar levels. Low glycemic index diets can improve menstrual regularity in women with PCOS by 50%
- Protein Intake: Aim for 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight each day. Quality sources include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, and plant-based options like beans and lentils.
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Include plenty of fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management. Aim for 30-40g of fiber per day. Using an app to track your food can be helpful here!
Implementing these tips can promote better blood sugar control and overall health, making it easier to manage symptoms of PCOS and insulin resistance.
Regular physical activity is another essential component. Exercise not only aids in weight management but also improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling, along with strength training to build muscle mass, which helps your body use insulin more efficiently. Regular physical activity can reduce insulin resistance by up to 60% – so it’s a good idea to find an activity you really enjoy doing!
Stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation can also play a critical role. Chronic stress can exacerbate insulin resistance and disrupt your hormonal balance, so finding ways to relax and manage stress is vital.
Lastly, working closely with a healthcare provider to monitor your condition and perhaps incorporating medications like Metformin can further assist in managing insulin resistance. A comprehensive approach that combines diet, exercise, stress management, and medical guidance offers the best chance for improving fertility and achieving a healthy pregnancy with PCOS.
If you’ve recently been diagnosed with PCOS, here are some labs you can ask your doctor to run for you:

- B12
- Vitamin D
- Fasting Insulin
- Fasting Glucose
- A1c
- CRP
- Lipid Profile
- Thyroid Panel
- Liver Function Tests
Understanding the importance of specific lab tests can illuminate how best to manage PCOS and its associated insulin resistance.
B12: Vitamin B12 is crucial for energy production and neurological function. Deficiencies, often found in those with PCOS, can exacerbate fatigue and other metabolic issues. Women who are prescribed Metformin should be especially concerned with their vitamin B12 levels as this medication will lower B12 over time.
Vitamin D: This vitamin plays a significant role in insulin sensitivity and hormone regulation. Low levels, common in PCOS, can impair glucose metabolism and worsen insulin resistance.
Fasting Insulin: Measuring fasting insulin helps assess insulin resistance, a key factor in PCOS. Elevated fasting insulin levels can indicate that your body is struggling to manage blood sugar effectively.
Fasting Glucose: This test checks for impaired fasting glucose, which can signify prediabetes. It’s a straightforward way to gauge how well your body is handling blood sugar regulation.
A1c: Hemoglobin A1c provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past three months, offering a comprehensive picture of glucose control. High levels suggest chronic insulin resistance or diabetes.
CRP: C-reactive protein is a marker for inflammation, which is often elevated in PCOS. High levels can indicate chronic low-grade inflammation contributing to insulin resistance.
Lipid Profile: This panel measures cholesterol and triglycerides, vital for understanding cardiovascular risk. PCOS often correlates with unfavorable lipid profiles, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Thyroid Panel: Hypothyroidism is common in women with PCOS and can exacerbate symptoms like weight gain and irregular periods. A thyroid panel ensures that thyroid function is not contributing to metabolic issues.
Liver Function Tests: These tests evaluate liver health, critical in PCOS management. Elevated liver enzymes can signal fatty liver, a condition frequently associated with insulin resistance.
Navigating the complexities of PCOS and insulin resistance can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can take control of your health. By understanding the relationship between diet, lifestyle, and hormone balance, you can naturally improve your fertility and overall well-being. However, every journey is unique. If you’re looking for personalized guidance, our 1-1 coaching services are here to help.
Our expert coaches specialize in tailoring advice to meet your specific needs, helping you to implement effective changes seamlessly. From customized meal plans to stress management techniques, we offer comprehensive support to ensure you achieve your health goals.
Ready to take the next step? Contact us today and start your journey towards a healthier, more balanced life with our dedicated 1-1 fertility nutrition coaching services.

By: Anabelle Harari Clebaner MS, RDN
Diet impacts everything
Want to boost fertility? 🌟 Start with what’s on your plate. Yep, your diet can make a HUGE difference.
When it comes to fertility, adequate nutrition plays a pivotal role. The right nutrients can significantly influence your reproductive health, improving your chances of conception and a healthy pregnancy.
As a fertility dietitian, I know firsthand just how much nutrition makes an impact on your reproductive health, after working with hundreds of women in my private practice, Wellspring Nutrition.
Think of it this way – you have three opportunities every single day to make a healthy choice that nourishes your body for fertility and pregnancy.
So let’s get right into it – here are 5 foods you can start to incorporate or increase in your diet to start to see positive changes in your fertility.
Leafy greens: The superstars 🌿
Spinach, kale, and their leafy friends are packed with folate, iron, and antioxidants.
Folate is essential for: DNA synthesis and repair, embryonic development, and preventing neural tube defects.
Folic acid is crucial for both men and women. For women, it helps create a healthy environment for egg fertilization and early embryonic growth. For men, it supports healthy sperm production.
Iron is essential for: Hemoglobin production and oxygen transport.
Adequate iron levels prevent anemia, which can affect ovulation and overall energy levels, making your body more conducive to conception.
These nutrients are your fertility BFFs. Add them to salads, smoothies, or soups. Easy peasy!
Fatty fish: Omega-3 magic 🐟
We can’t have a conversation about Omega-3 fats without also talking about Omega-6 fats.
Both Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fats, meaning your body cannot produce them, and they must be obtained through your diet. Despite being in the same family of fats, they have different roles and effects on the body.
The three most important types are:
– **EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)**: Found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. – **DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)**: Also found in fatty fish and is a crucial component of brain and eye health.
– **ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid)**: Found in plant sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
ALA can be converted to EPA and DHA in the body, but this process is relatively inefficient.

Health Benefits
**Anti-Inflammatory**: Omega-3s help reduce inflammation in the body, which can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and arthritis. – **Cardiovascular Health**: They are known for their heart-protective effects, reducing blood pressure, and improving cholesterol levels. – **Mental Health**: Omega-3s play a crucial role in brain health and have been linked to reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety. – **Fertility**: As mentioned earlier, they improve egg quality, regulate ovulation, and reduce the risk of endometriosis.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Types
The most common type is: – **LA (Linoleic Acid)**: Found in vegetable oils like sunflower, soybean, and corn oil. – **AA (Arachidonic Acid)**: Found in meat and eggs; it is derived from LA. – **GLA (Gamma-Linolenic Acid)**: Found in evening primrose oil and blackcurrant seed oil; it’s a less common omega-6.
Health Benefits
**Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory**: Omega-6 fats can produce both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory compounds. The body’s balance of omega-6 to omega-3 determines the effect. – **Skin Health**: Omega-6 fatty acids can help support skin barrier function and hydration. – **Growth and Development**: Essential for normal growth and brain function, particularly in children.
Key Differences
**Balance and Ratio** – **Ideal Ratio**: Historically, humans consumed Omega-3 and Omega-6 fats in a balanced ratio of about 1:1 to 1:4. However, modern diets tend to have a ratio closer to 1:20 or 1:30, significantly skewed towards Omega-6, leading to an imbalance.
**Health Impact**: An imbalanced ratio (high in Omega-6 and low in Omega-3) can promote inflammation and contribute to chronic diseases. Ensuring an adequate intake of Omega-3s while reducing excessive Omega-6s can optimize health.
Sources
**Omega-3s**: Primarily found in fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and algae.
**Omega-6s**: Found mostly in vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, and processed foods. They are more prevalent in the typical Western diet.
While both Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are essential for health, maintaining a proper balance between them is crucial. Increasing your Omega-3 intake and being mindful of Omega-6 consumption can help in achieving better overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids are Essential for: Reducing inflammation, hormone production, and cell membrane function.
Omega-3 fatty acids are known to improve egg quality, regulate ovulation, and reduce the risk of endometriosis. For men, they improve sperm quality and mobility.
So where do you find Omega-3 fatty acids? Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are where it’s at. These fatty fish are fertility wonders. Grill ’em, bake ’em, or toss ’em in a salad. Your future self will thank you.
Nuts and seeds: Tiny powerhouses 🥜
Pumpkin seeds, walnuts, and almonds are considered tiny powerhouses because they are bursting with zinc and selenium. When it comes to fertility, both zinc and selenium play critical roles in ensuring optimal reproductive health. These essential trace minerals are involved in numerous bodily functions, specifically those related to reproductive health for both men and women.

Zinc
Zinc is vital for:
- Hormone Regulation: Zinc helps in regulating hormone levels, particularly testosterone in men and estrogen and progesterone in women. Balanced hormone levels are crucial for a healthy reproductive system.
- Sperm Production and Quality: In men, zinc is essential for spermatogenesis, the process of sperm production. It also enhances sperm motility and morphology, crucial factors for successful fertilization.
- Ovulation: For women, zinc supports the maturation of eggs and ensures regular ovulation, which is essential for conception.
- DNA Synthesis: Zinc is involved in DNA synthesis and cell division, processes that are fundamental during the early stages of fetal development once conception occurs.
Selenium
Selenium contributes to fertility by:
- Antioxidant Support: Selenium acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting reproductive cells from oxidative stress, which can damage sperm and eggs.
- Thyroid Function: Proper thyroid function, supported by selenium, is crucial for fertility. The thyroid gland regulates many metabolic processes, including those that affect reproductive health.
- Sperm Quality: In men, selenium is essential for the formation and motility of sperm. It helps in maintaining the integrity and function of sperm cells.
- Development: Selenium plays a role in the early stages of embryo development by ensuring proper DNA synthesis and protecting against cellular damage.
Snack on them, throw them in your oatmeal, or mix them in a trail mix – there’s no way to go wrong here! And if you want to learn more about seed cycling, check out this blog right here.
Berries: Antioxidant champs 🍓
Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are loaded with antioxidants. These little champs keep your reproductive system in top shape. Enjoy them fresh, frozen, or in a smoothie. Yum!
Antioxidants are compounds that help protect the body from oxidative stress, which is caused by an excess of free radicals—unstable molecules that can damage cells.
Free radicals are naturally produced during metabolism, but environmental factors like pollution, UV exposure, and poor diet can increase their levels.

Berries Images – Free Download on Freepik
Importance of Antioxidants for Fertility
1. **Protecting Reproductive Cells**: Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress on reproductive cells like sperm and eggs. This protection is crucial for maintaining the health and viability of these cells.
2. **Improving Egg Quality**: Oxidative stress can negatively affect egg quality, leading to issues like chromosomal abnormalities. Antioxidants can improve the quality and viability of eggs by reducing this stress.
3. **Enhancing Sperm Health**: In men, antioxidants play a vital role in protecting sperm from oxidative damage, which can affect sperm count, motility, and overall fertility.
4. **Supporting Hormonal Balance**: Certain antioxidants, like vitamin E and Coenzyme Q10, are involved in hormone production and regulation, which is essential for fertility.
5. **Reducing Inflammation**: Antioxidants like vitamin C, E, and selenium have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the reproductive organs, supporting overall fertility.
Including a variety of antioxidant-rich foods like berries, nuts, seeds, leafy greens, and colorful vegetables can be beneficial for those looking to optimize their fertility.
Eggs: The complete package 🍳
Eggs—especially organic, free-range ones—are amazing. They’re packed with choline and protein, both super important for fertility. Scramble them, poach them, or make a frittata. So versatile!
Eggs are an excellent food for fertility, and one of the key reasons is their high content of choline, an essential nutrient that plays a significant role in reproductive health.

Eggs Pictures [HD] | Download Free Images on Unsplash
Choline and Fertility
1. **Cell Membrane Formation**: Choline is crucial for the formation and maintenance of cell membranes. This is particularly important during pregnancy, as it supports the development of the baby’s brain and nervous system. In the context of fertility, choline ensures the health and integrity of reproductive cells, such as eggs and sperm.
2. **Gene Expression**: Choline is involved in methylation, a process that regulates gene expression. Proper methylation is essential for DNA synthesis and repair, which is vital for healthy cell division and the development of a viable embryo.
3. **Reducing Neural Tube Defects**: Adequate choline intake during pregnancy is associated with a lower risk of neural tube defects in the developing baby. For those trying to conceive, ensuring sufficient choline intake can help prepare the body for a healthy pregnancy.
4. **Supporting Hormone Production**: Choline is a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in muscle control and memory but also supports hormone production and regulation. Balanced hormone levels are crucial for ovulation and overall reproductive health.
Other Nutrients in Eggs
In addition to choline, eggs are packed with other nutrients that support fertility:
– **Protein**: Eggs are an excellent source of high-quality protein, essential for the growth and repair of tissues, including reproductive tissues.
– **Healthy Fats**: The healthy fats in eggs, including omega-3 fatty acids, support hormone production and reduce inflammation.
– **Vitamins and Minerals**: Eggs are rich in vitamins like B12, D, and A, as well as minerals like selenium and zinc, all of which play important roles in reproductive health.
Practical Tips
– **Whole Eggs**: Most of the choline in eggs is found in the yolk, so it’s important to consume whole eggs rather than just egg whites.
– **Balanced Diet**: Including eggs as part of a balanced diet can provide a variety of essential nutrients that collectively support fertility. Pairing eggs with other fertility-boosting foods like leafy greens, avocados, and whole grains can further enhance their benefits.
Incorporating eggs into your diet, especially for those looking to boost fertility, is a simple and effective way to ensure you’re getting enough choline and other vital nutrients.
Conclusion: Make it a habit
So, there you have it—the top 15 fertility-boosting foods – phew! That was a lot. Start adding these to your daily meals to reap all the benefits!
And if you’re looking for a super easy way to incorporate these foods, and so many others that are vital for fertility, check out my four-week fertility meal plan.
It was designed to take all of the nutrients important for fertility and translate it into delicious, healthy, and simple recipes to naturally nourish your fertility.
Whether you’re planning your next IUI cycle or are just getting started on your preconception journey, investing in your health is always worth it!

“At no point in human nutrition is it more critical to ensure adequate nutrient intake than during the state of pregnancy”
– Bruce Hollis, PhD
Studies show 95 percent of pregnant women are nutritionally depleted.
Fertility, pregnancy, and postpartum are some of the most physically and mentally demanding times in a woman’s life. Unfortunately, the prenatal vitamin industry is failing women, leaving 95% depleted when nutrition for body and mind is needed most.
Why?
Because most supplement companies follow the current RDAs.
RDAs are based on outdated research methods and studies conducted mainly on white men. In fact, pregnant and breastfeeding women were intentionally excluded from 83% of the studies chosen as the basis for the current perinatal RDAs. Including pregnant and breastfeeding women in clinical research was considered too risky and so these groups were excluded from clinical research under the guise of “protection”.
Ironically, their exclusion ultimately led to misinformed recommendations and a major gap in our collective understanding of women’s bodies, which had a devastating impact on millions of women and their families not set to support the mother in addition to the baby.
Over 630 nutrition studies support the finding that for many nutrients, the current nutritional guidelines for pregnancy and lactation are set well below optimal levels. Take choline as an example. More and more research is showing that the RDA for choline consumption should be much higher than it is to support a baby’s brain development.
Yet 90% or more women aren’t even reaching the current RDA level and most prenatals don’t even include choline in their formulation at all!
Why isn’t this research making its way into the official perinatal nutrition guidelines? On average it takes 17 years for new research to be incorporated. The lag between research and RDAs means women aren’t receiving the optimal support that they so desperately need.
So which 5 key components should you focus on when looking for a prenatal?
- Methylated B Vitamins
- Activate form of vitamin A
- Vitamin D in adequate amounts
- Adequate amount of Choline
- Third-party testing
Methylated Folate and B-Vitamins
When it comes to prenatal supplements, one critical factor to keep in mind is the form of B vitamins they contain, particularly folate. While folic acid is the synthetic form commonly found in many supplements, methylated folate is often the preferred choice. This is because a significant percentage of people have a mutation in the MTHFR gene, which affects their ability to convert folic acid into its active form, folate, that the body can readily use.
Having methylated B vitamins, including methylated folate, in your prenatal supplements ensures that your body gets the essential nutrients it needs without needing to convert them first. This can be incredibly important for preventing neural tube defects and supporting your baby’s growth and development. Moreover, B vitamins in their active, bioavailable forms are more easily absorbed and utilized by the body, providing better overall support during pregnancy.
Therefore, opting for a prenatal vitamin that includes methylated folate rather than standard folic acid can be a game-changer, especially if you have concerns about the MTHFR gene mutation. Always consult with your healthcare provider to choose the prenatal supplement that best meets your individual needs.
Active Vitamin A
When it comes to choosing the right form of Vitamin A in prenatal supplements, you might come across two common forms: retinyl palmitate and beta carotene. Retinyl palmitate is often considered more effective as it is a preformed version of Vitamin A, meaning it is readily usable by your body without the need for conversion. On the other hand, beta carotene, a pro-vitamin A, requires conversion by your body to be utilized. This conversion process can sometimes be less efficient, especially for individuals with certain genetic variations or dietary restrictions. Therefore, retinyl palmitate can offer more reliable and immediate benefits, ensuring that you and your baby receive the requisite amounts of this crucial nutrient.
Activated vitamin A:
- boosts brain development
- enhances immune function
- supports bone formation
Vitamin D and Pregnancy
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin and hormone. Its major functions include maintaining calcium and phosphorus in the body, regulating 3% of the genome, bone mineralization, blood pressure, mental health, cardiovascular health, neurodevelopment, immune health, and regulating cell growth and differentiation.
How is it made?
When UVB light in the sun interacts with 7-dehydrocholesterol, turning it into vitamin D3. You need adequate sun, and the time of day and year, latitude, sunscreen, clothing, and skin color can all affect vitamin D production.
If you have pale skin, have moderate exposure to sun in a bathing suit can give you 10-25000 IU/day.
Vitamin D3 is metabolized in the liver and converted to 25 (OH)D which is then converted to 1,25 OHD = calcitriol, which is the active form of vitamin D
- 25OH D has a half-life of 2-3 weeks and is an indicator of vitamin D status
- 1,25 OH D has a half-life of 4-16 hours
In pregnancy, the production of calcitriol increases dramatically. The placenta converts vitamin D to its active form (1,25OHD). By 12 weeks, 1,25 OHD serum levels are 2x the level before pregnancy, and it continues to rise reaching 700+ pmol/L (non-pregnant range is 48-120 pmol/L). These levels would be toxic (due to hypercalcemia) normally, but essential during pregnancy.
Over 30 tissues express the vitamin D receptor and are able to respond to 1,25OH D. Adequate 25 OH D directly affects 1,25 OH D levels in pregnancy.
Role of vitamin D in pregnancy:
- Aids in implantation
- Supports fetal growth through the delivery of calcium
- Regulates placental function and placental hormone levels
- Limits production of proinflammatory cytokines (which can impact preeclampsia)
- Involved in the maturation of fetal lungs
- Maintains endothelial integrity/membrane stability
Vitamin D Requirements (highly debated):
IOM: 600 IU /day
RDA: 600 IU/ day
UL: 4000 IU/ day
Endocrine Society: 1500-200 IU/day and UL 10,000 IU
It’s estimated that 20-85% of pregnant women are deficient in vitamin D worldwide. Women of color are at greatest risk because of the melanin – black women 6x more deficient/at risk than white women.
Vitamin D Deficiency:
- Deficiency is even common at latitudes where year-round UVB exposure is expected to be adequate
- Dark skin women in northern latitudes are at higher risk because you need even more time in the sun
- Study of 40 healthy moms in Michigan (42 latitude) took 600 IU daily + 2 cups milk (100 IU/cup)
- Found that at birth 76% of mothers were deficient (>20 ng/ml) and 81% of newborns were deficient
- 600 IU is not enough!
What happens when you’re deficient?
- Increases odds for gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and preterm birth
- Associated with periodontal disease, postpartum depression, prolonged obstructive labor, recurrent pregnancy loss, C-section
*Always optimal to get levels high before pregnancy!
- Stores of vitamin D in the infant is dependent on maternal vitamin D status.
- 25 OH D passes from the placenta to the fetus
- Maternal 1,25 OH D does NOT cross the placenta, however, the placenta can synthesize 1,25 OHD directly from 25 OHD
- Mother typically maintains higher vitamin D than the baby
Choline
Most women do not consume enough choline in their daily diets and supplementation is high beneficial. Most prenatal vitamins contain too little to be supportive (55mg of Choline or less) as it’s a bulky nutrient that can be difficult to formulate with. Our dose is optimally supportive and safe.
How it supports baby:
- Normal neural tube development
- Optimal brain development, including cognitive performance
- Proper DNA synthesis
- Help mitigate some of the adverse effects of prenatal stress
- Transporting Omega-3 DHA from mom to baby
Third Party Testing
In addition to the forms and amounts of nutrients, we recommend seeking out a prenatal that has third-party testing and is medical grade. When a product is third-party tested, it means it undergoes independent testing by accredited laboratories to verify its purity, potency, and overall quality.
This additional layer of scrutiny provides peace of mind, knowing that your products meet the highest standards of safety and efficacy. Third-party testing is not only important to confirm that what you would expect from the label is actually in your supplement, but also to ensure that there is nothing you would not expect.
Testing for microcontaminants and heavy metals ensures that the product is safe and of the highest quality. We recommend looking for reputable independent third-party certifications such as Clean Label Project, NSF, or USP to help verify product quality.
Additionally, when choosing prenatal supplements, it’s crucial to scrutinize the ingredient list. Opt for products that are free of common allergens like gluten, dairy, and soy, to minimize the risk of adverse reactions. Checking the expiration date on the bottle ensures you’re not consuming a product past its prime, which could compromise its effectiveness.
What’s more, some supplements include herbal ingredients designed to alleviate pregnancy-related ailments. While these can be beneficial, they should be used with caution. Always consult your healthcare provider before adding any herbal supplements to your routine to ensure they are safe for you and your baby.
Remember, a well-rounded prenatal supplement should contain essential nutrients like folate, B12, and chelated minerals in their active, bioavailable forms. These nutrients are crucial for fertility and pregnancy health. For instance, an iron-free formula offers customizability and may be easier on your digestive system, as iron needs can vary among pregnant individuals.
Finally, always keep your doctor informed about any changes to your diet or supplements. This will help them give you the best advice tailored to your specific needs, ensuring a healthy pregnancy journey.

By: Josie Mangano
Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
It’s commonplace for women to are trying to conceive to track their menstrual phases. However,
did you know that whether or not you’re trying to conceive, tracking the phases of your
menstrual cycle can be a valuable tool for assessing overall health and wellbeing? If you have
PCOS or are experiencing symptoms related to hormone imbalance, fertility awareness may
help you understand the cues your body is giving you in order to address the root causes.
Irregular menstrual cycles are linked to nutritional deficiencies, energy deficits, hormonal acne,
and even loss of bone density in the long-term. Put simply, your hormone health is important
even before you are trying to conceive.
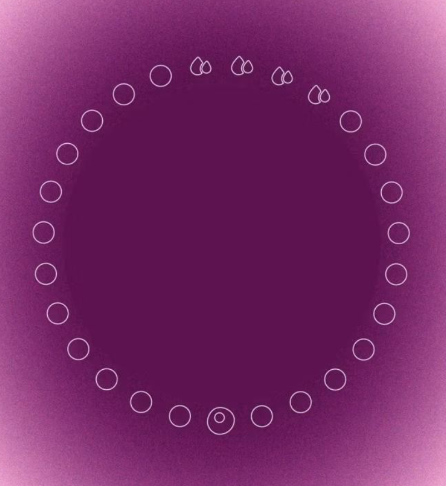
What is Fertility Awareness?
Fertility awareness — is a set of practices that are used to determine the fertile and infertile
phases of your menstrual cycle.
The techniques used to track menstruation and ovulation are known as Fertility Awareness
Methods (FAMs). But first, let’s review what you should know about the menstrual cycle, the
fertile window, and what the patterns of a normal cycle look like.
What You Need to Know About the Menstrual Cycle
A normal menstrual cycle lasts anywhere between 24-35 days. The first day of your period
(when flow begins) is always considered day 1 of your cycle. Normal menstruation lasts
between 3-7 days.
In the days following menstruation, your ovaries release an egg into the fallopian tubes — this
process is called ovulation. This egg stays in your fallopian tubes and, if not fertilized by a
sperm, will dissolve after 12-24 hours. Contrary to the myth that ovulation occurs 14 days after
your period starts, ovulation typically happens between days 10-23, depending on the length of
your cycle. It is essential to note that sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to
5 days. Therefore, your fertile window is classified as the 5 days before ovulation, the day of
ovulation, and the following day (7 days total).
During the fertile window, the sperm present in the female reproductive tract may fertilize an egg
and implant itself in the uterine lining, thus marking the beginning of pregnancy. If the egg is not
fertilized and the egg is reabsorbed, hormones drop, and menstruation occurs, marking the
beginning of a new cycle. After the fertile window passes, pregnancy is not possible because
the egg is no longer present for fertilization. The days after ovulation and before menstruation
are referred to as the post-ovulatory phase.
With that covered, we can dive into the science-backed tools we use for fertility awareness cycle
tracking.

The 3 main fertile signs to pay attention to are:
1. Cervical mucus
2. Basal body temperature (BBT)
3. Cervical position
Let’s review each of these signs more closely and learn how they may be related to underlying
causes such as hormone imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, and/or underlying health conditions.
Cervical Mucus
The presence of cervical mucus (CM) is indicative of your fertile window. CM plays an essential
role in natural conception by matching the pH of sperm, creating the perfect environment for it to
stay alive for up to 5 days in the otherwise hostile female reproductive tract.
There are two kinds of cervical mucus that are often referred to when it comes to reproductive
health. The first is “peak mucus” which is an optimal environment for sperm and is also an
indicator of a healthy cycle when present in the fertile window. Peak mucus is clear, stretchy,
and is comparable to egg whites. There is also “non-peak mucus” which is cloudy, white, and similar to creamy hand lotion. Non-peak mucus is not as optimal because it is hostile to sperm.
It is usually present shortly after menstruation and later in the menstrual cycle (luteal phase).
However, it is important to note that all mucus is fertile in the pre-ovulatory phase! Pregnancy
can occur in the presence of either kinds of CM in the fertile window

If your experience with CM differs, there are some red flags we can look for to assess
underlying hormonal imbalances and/or health conditions.
Cervical Mucus Red Flags
Limited or no mucus — can indicate an issue with hormone production, the cervix, or other
related issues including HPV, cervical dysplasia, or use of medications like hormonal birth
control, fertility drugs, or antihistamines. Can indicate inadequate nutrient intake of cholesterol
(to support estrogen and progesterone production), vitamin A, and B vitamins (folate). Can
indicate endocrine issues such as thyroid disorder, HPA axis dysregulation, hypothalamic
amenorrhea, etc.
Continuous mucus — can indicate an issue in the cervix, or presence of infection,
inflammation, or hormone imbalance.
Continuous creamy/lotiony (non-peak) mucus — may indicate an overgrowth of
yeast/bacteria. During the luteal phase, low progesterone production may contribute to
continuous non-peak mucus.
Continuous clear/stretchy (peak) mucus — seen in women with PCOS and/or women
experiencing food sensitivities, IBS, and other gut-related issues in the pre-ovulatory phase.
Yellow-tinged mucus – can be indicative of infection.
Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
Basal Body Temperature can be measured by taking your temperature first thing in the morning,
before getting. It is important that you do this immediately after waking up for an accurate
reading, before eating or drinking.
Tracking these temperatures provides us with the information we need to confirm when
ovulation occurs, but keep in mind that there is no way to predict when ovulation will occur due
to extraneous factors like travel and stress which may delay ovulation. You can keep track of
your BBTs by either logging them manually on a BBT chart or by using a fertility tracking app.
Normal pre-ovulatory temperatures should consistently be above 97.5° F ranging up to about
98.2 °F. Normal post-ovulatory temperatures should be higher than the pre-ovulatory range with
at least one temperature higher than 98.6 °F. Temperatures that fall consistently lower than this
range indicate potential health issues and nutrient deficiencies.
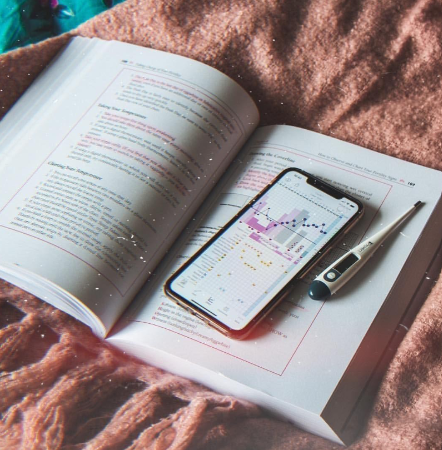

What are Some Possible Causes of Low Basal Body Temperatures?
Possible causes of low BBT include nutrient deficiencies of nutrients involved in thyroid function
such as zinc, iron, selenium, and iodine. Iron deficiency may also contribute to low BBTs since
iron is highly involved in body temperature regulation. Zinc and iron supplementation have
independently been shown to improve thyroid hormone levels and thus increase BBTs in
deficient women.
Low BBTs may also result from inadequate calorie consumption from skipping meals or failing
to consume enough calories to offset exercise levels. Poor sleep may also contribute to low
BBTs by offsetting natural circadian rhythms. Finally, thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism
and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis play a role in lowering BBTs.
Cervical Position
The final indicator of fertility is cervical position, which changes throughout the menstrual cycle.
By regularly checking cervical position we can better understand our bodies through common
patterns that we notice throughout our cycles.
But what is the cervix and how can we use it to track our cycles?
The cervix is the small, muscular organ that connects the vagina to the uterus. It’s a round,
prominent structure with a hole in the middle that’s roughly an inch in diameter. It produces
cervical mucus, expels menstrual flow, allows sperm to pass through during ovulation, and acts
as a barrier against infections.
During ovulation, high estrogen levels cause the cervix to rise closer to the top of the vagina.
The cervix often feels softer during the fertile window. As mentioned previously, the cervix is
responsible for producing peak CM during this time.
After ovulation (luteal phase), the position of the cervix lowers to prepare for menstruation. This
cervix tends to lower or “drop” on average a week to 10 days before menstruation begins.
During menstruation, the cervix remains low and opens slightly to release the menstrual blood
flow. The cervix feels firm to the touch during this time and will continue to feel this way until
after your period ends.
In early pregnancy, the position of this cervix is high in the vagina, similar to its position during
ovulation. The cervix is known to feel soft during this time, however it is important to use a
pregnancy test to confirm pregnancy as cervical position is not a guarantee in confirming early
pregnancy.
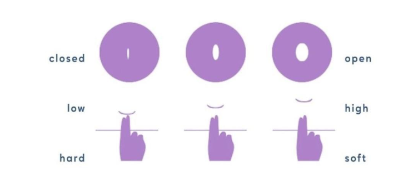
For more information on how to check your cervical position, click here.
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork of cycle tracking, let’s discuss some specific nutrients and
how they uniquely benefit cervical health!
Key Nutrients to Support Cervical Health
1. Folate — has been shown to reverse abnormal (precancerous) cervical cells and reverse
cervical dysplasia. Folate plays a key role in supporting healthy cell division, most notably
during early pregnancy in the formation of the spinal cord.
2. Vitamin A (retinol) — has been shown to reverse abnormal cervical cells when applied
topically to the cervix. Vitamin A is critical for fertility and plays a role in preparing the uterine
lining for implantation. Pregnant women should avoid all forms of vitamin A supplementation.
Dark leafy greens, red/orange vegetables, beef, eggs, and dairy products are rich in vitamin A.
3. Indole-3-Carbinol – has been shown to reverse abnormal cervical cells in clinical trials.
I3C plays a role in modulating estrogen metabolism and is a compound found in cruciferous
vegetables like broccoli, brussels sprouts, kale, and cauliflower

There you have it — the 3 main fertile signs to pay attention to and related cues that can give us
powerful insights into our hormonal and reproductive health. If you feel passionate about using
fertility awareness as a guide to managing hormonal imbalances, managing PCOS, or preparing
your body for the healthiest pregnancy possible, consider reaching out to our team at Wellspring
Nutrition for 1:1 functional nutrition counseling and a personalized plan to achieve your unique
health goals.
References
Hendrickson-Jack L. Women’s Health Nutrition Academy (WHNA). “Unlocking the Secrets of the
Menstrual Cycle: How Fertility Awareness Cycle Tracking Can Help Your Nutrition Practice”.
Sumner C. Cervix positions: What they mean & how to check them. Natural Cycles. Published
June 28, 2022. https://www.naturalcycles.com/cyclematters/cervix-positions-explained

If you’ve ever been told “everything looks normal”-yet nothing feels normal at all- you know how deeply frustrating those words can be.
You watch friends, coworkers, even strangers announce pregnancies that seemed to happen effortlessly. Meanwhile, you’re tracking, testing, timing and doing everything under the sun… and still, nothing. It’s exhausting. It’s isolating. It can make you feel like you’re somehow missing something obvious.
You’re not.
So many couples reach this same breaking point after hearing that familiar line, “everything looks fine.” It can feel like the end of the road- like the doctors have checked their boxes and moved on, even though your gut tells you something isn’t adding up. Because if everything were truly fine, this wouldn’t feel so hard.
Hormone testing can be incredibly helpful. It gives us a valuable snapshot of what’s happening beneath the surface, at the microscopic level. But here’s the truth, hormones don’t tell the whole story.
Fertility isn’t controlled by a single switch or dictated by hormones alone. It’s a complex, multi-factorial system influenced by far more than any one lab result can capture. When something feels off, it’s worth looking deeper- because “normal” doesn’t always mean optimal, and it certainly doesn’t mean your experience isn’t valid.
What does “normal” hormone blood work actually mean?
When it comes to fertility, hormones are the behind-the-scenes directors calling the shots. But which hormones actually matter- and when should they be tested? Let’s break it down.
Key players we look at for fertility include follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone
(LH), estradiol (E2), anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), and Progesterone. Together, these hormones
help paint a clear picture of ovarian reserve and overall reproductive function. Most of these labs are checked on day 3 of your menstrual cycle, and that timing isn’t random. Day 3 of your cycle is when many of these hormones are at their lowest, or most baseline, levels. Testing consistently on this day allows us to compare apples to apples each month. Without that consistency, hormone levels can jump all over the chart, making us compare apples to oranges

The “normal” reference ranges you see on lab reports aren’t always the same as optimal ranges for
fertility. Those reference ranges are designed to catch diseases or major deficiencies -not to tell us
whether your body is operating at peak reproductive potential. So yes, you can fall within the “normal” range and still have room for improvement when it comes to fertility.
In short: the right hormones, the right timing, and the right interpretation make all the difference when it comes to understanding your fertility.
Why can Standard labs miss fertility root causes?
As mentioned earlier, the cornerstone hormones assessed in routine fertility testing include
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estradiol (E2), anti-Müllerian
hormone (AMH), and Progesterone. These labs are undeniably important and offer valuable insight into reproductive function. But fertility is far more nuanced than a handful of numbers on a lab report- and there are critical factors these values simply can’t capture.
Blood sugar regulation plays a foundational role in fertility. When blood sugar is poorly controlled,
insulin levels can remain chronically elevated, disrupting hormonal balance. High insulin has been shown to impair egg maturation in women and reduce both sperm count and quality in men. In other words, stable blood sugar isn’t just about energy- it’s about creating the right hormonal environment for conception.
Another major, yet often overlooked, factor is chronic inflammation. Persistent inflammation interferes with hormone signaling, which can lead to irregular ovulation and compromised egg quality. Over time, it may even contribute to structural issues such as uterine scar tissue resulting from chronic pelvic inflammation. For men, chronic inflammation creates a hostile environment for sperm, increasing oxidative stress and impairing healthy sperm development.
Nutrient status is equally essential. Both undernutrition and overnutrition can negatively impact fertility. Undernutrition- often associated with calorie restriction and vitamin deficiencies- is typically more commonly recognized. However, overnutrition- frequently linked to obesity- can coexist with significant micronutrient deficiencies as well. Evaluating and correcting nutrient imbalances is critical not only for conception but also for supporting a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Then there’s gut health, a keystone in hormone balance and nutrient absorption. The gut is far more than just the stomach- it’s an intricate system extending from the mouth to the anus, housing trillions of beneficial bacteria. These microbes play a vital role in extracting, absorbing, and even synthesizing key nutrients. When the gut microbiome is out of balance, nutrient deficiencies and poor digestion often follow. Even more importantly, the gut actively interacts with sex hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and estradiol. When gut function is compromised, hormone imbalances- and fertility challenges- often follow.
By now, a clear theme may be emerging: fertility is deeply interconnected with nearly every aspect of our physiology. This is especially true when it comes to stress. Stress isn’t just an uncomfortable mental state-it triggers real, measurable physiological changes. Chronic stress activates the release of “fight or flight” hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These can disrupt our overall hormonal balance and negatively affect fertility. Stress can also impair gut health and increase unhealthful coping behaviors such as overeating, excessive alcohol consumption, or smoking-all of which further hinder reproductive health.
To make a long story short, optimizing fertility requires looking beyond hormone labs alone. It means supporting the body as a whole. Balancing blood sugar, calming inflammation, replenishing nutrient stores, healing the gut, and managing stress- so our sex hormones can have the space to do what they need to do.
Can you ovulate and still have hormone dysfunction?

While ovulation is a crucial milestone for fertility, it’s only one piece of a much larger hormonal puzzle. A healthy pregnancy depends not just on releasing an egg, but on creating the ideal environment for that egg to implant and thrive. One of the most critical factors here is the uterine lining. For an embryo to successfully implant, the uterine wall must be thick, nourished, and stable. The hormone responsible for maintaining this environment is progesterone. If progesterone isn’t operating in sufficient amounts, the uterine lining will not be thick enough to sustain a successful implantation.
Timing matters just as much as hormone levels themselves. A well-orchestrated menstrual cycle requires precise communication between hormones. It is critical that the luteal phase, the phase of the menstrual cycle after ovulation, is at least 10 days long. Any time shorter than this is not enough time for progesterone to thicken the uterine wall to sufficient amounts.
Conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) illustrate this clearly. Some women with PCOS do ovulate regularly, yet continue to experience hormonal imbalance with elevated testosterone levels. Symptoms like acne, excess hair growth, and weight gain can persist despite ovulation, signaling that the underlying hormonal landscape is still out of balance.
The same holds true for thyroid disorders. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt
menstrual cycles and make conception more challenging. And yet, regular ovulation can still occur in both conditions. Once again, ovulation alone doesn’t guarantee optimal fertility.
So in short, Yes- it’s absolutely possible to ovulate and still have hormonal imbalances.
What tests look deeper than standard OB labs?
To gain meaningful insight into fertility, we need to look beyond a single lab panel and take a more
comprehensive, whole-body approach. Utilizing a range of advanced and functional laboratory tests allows us to better understand what’s happening at the microscopic level.
These assessments may include functional blood work, gut testing, mineral analysis, and hormone
metabolism testing. Each test adds another layer of clarity which can help to reveal hidden imbalances that standard testing often misses.
What should I focus on if my labs are “normal”, but I’m not pregnant?
Sometimes all the tests come back “normal”, yet the outcome you’re hoping for still doesn’t happen. If you’ve been there, you know how deeply frustrating- and confusing- that can feel.
When this happens, the next step is often to return to the foundations of health. Supporting fertility starts with making sure your body has enough fuel to run a full, healthy menstrual cycle. That means eating enough- especially the nutrients your hormones rely on to function and communicate effectively.
Nutrition plays a powerful role here. Focusing on gut-supportive foods like fiber-rich beans, whole
grains, and produce. Alongside probiotics like fermented foods can help to nourish the beneficial bacteria within our GI tract. At the same time, reducing artificial sugars supports blood sugar balance and helps to prevent the overgrowth of less-than-healful gut microbes.

Stress management is another key piece of the puzzle. Finding healthy ways to cope during stressful seasons allows your body to spend less time stuck in “fight or flight” mode and more time in a calm, hormonally optimized state. Fertility thrives in an environment of safety and balance.
Finally, this is not a journey meant to be navigated alone. Working with a practitioner who looks at the entire picture, not just a single lab value or isolated symptom, makes all the difference. Fertility is complex, and having someone who understands how all the pieces connect is often the missing link.
Want to learn more?
If you like what you read here, want to know more, but don’t have the time to sit down and read through all our blogs, check out our free private podcast where we break down fertility root causes in more detail. Perfect for those who want to learn more about their hormones and bodies all while still keeping up their busy schedule.
Sources
https://www.stonybrookmedicine.edu/islandfertility/news/sugar
https://rep.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/rep/169/4/REP-24-0197.xml
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10097215/
https://azgyn.com/blog/fertility-gut-health

Pregnancy is a season when your body simply needs more—more rest, more support, and yes, more nutrients. During this time, demands for key nutrients like folate, iodine, choline, and vitamin D increase significantly. If these needs aren’t met, deficiencies can have long-term effects not only for you, but for your growing baby as well.
Nourishing your body during this incredibly important and transformative time isn’t optional—it’s foundational to supporting a healthy pregnancy.
Is a healthy diet enough?
Even when you’re eating a well-balanced, nutrient-dense diet, it can still be difficult to meet all of your increased nutrient needs during pregnancy through food alone. This is where a high-quality prenatal vitamin becomes an essential part of your pregnancy toolkit.
Let’s break down a few of the most important nutrients to look for—and why they matter.

Folate
Folate (vitamin B9) is a critical micronutrient for fetal brain and spinal cord development. In the very early weeks of pregnancy—often before someone even knows they’re pregnant—the neural tube forms and closes, eventually developing into the brain and spinal cord. This process typically happens within the first 3–4 weeks of pregnancy.
Folate plays a central role in this process by supporting rapid cell growth and division, as well as methylation—a biochemical process that is essential for proper neural tube closure and healthy brain and spinal cord development.
A quick (and gentle!) biochemistry moment—bear with us. Many supplements and fortified foods use folic acid, which is a synthetic form of vitamin B9. Folic acid must be converted in the body to its active form, methylfolate, before it can be fully utilized. Some individuals have a harder time completing this conversion, which can lead to less-than-optimal absorption.
To bypass this conversion step altogether and support optimal absorption, it’s ideal to choose a prenatal that contains methylfolate rather than folic acid.
Current Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) in the U.S. are:
- 400 mcg/day for women of childbearing age who are not pregnant
- 600 mcg/day for pregnant women
Iodine
Iodine is a crucial micronutrient for thyroid health and function. If you want a deeper dive into iodine’s role in fertility, thyroid health, reproductive health, and hormone balance, be sure to check out our earlier blog: Iodine and Women’s Health: What You Need to Know.
When it comes to pregnancy, iodine deserves special attention. It plays a key role in fetal brain and nervous system development, as well as in thyroid hormone production and regulation for both mom and baby.
The current RDAs in the U.S. are:
- 150 mcg/day for women of childbearing age who are not pregnant
- 220 mcg/day for pregnant women
Because iodine intake varies widely based on diet and food sourcing, it’s an especially important nutrient to confirm is included in your prenatal.

Vitamin D and Calcium
Calcium is essential for bone health, and during pregnancy, needs increase to support fetal skeletal development. At the same time, adequate calcium intake helps protect and maintain mom’s own calcium stores.
During breastfeeding, approximately 3–5% of a mother’s calcium stores can be depleted through breast milk production. While these losses haven’t been directly linked to an increased risk of osteoporosis later in life, ensuring adequate calcium intake before, during, and after pregnancy is still incredibly important.
One of the best ways to support calcium absorption? Vitamin D.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a role in fetal immune system development, overall fetal growth, and—importantly—calcium absorption.
Without getting too deep into the weeds, the active form of vitamin D (calcitriol) helps activate receptors in the intestines that increase the production of calcium-transporting proteins. These proteins work together to improve calcium absorption into the bloodstream—essentially helping your body actually use the calcium you’re consuming.
Current RDAs in the U.S.:
- Calcium: 1000–1300 mg/day (pregnant and non-pregnant women)
- Vitamin D: 15 mcg/day (pregnant and non-pregnant women)
Many perinatal practitioners recommend higher levels of vitamin D for optimal lab levels.
So… which prenatal should I choose?
Understanding nutrient needs is one thing—actually choosing a prenatal is another. With so many options on the market, it’s no wonder this step feels overwhelming.
One important thing to know: many prenatals still rely on outdated RDAs that were originally based on research conducted in men’s bodies—not women’s, and certainly not pregnant women’s.
This is where Needed stands out.
Needed recognized this gap and created prenatals that are science-backed and designed with women’s unique needs in mind—especially during preconception, pregnancy, and postpartum, when nutrient demands are higher across the board.
Needed Prenatal Multi provides 5x more nutrition than outdated RDAs, helping better meet the increased nutrient demands of pregnancy.*
How does Needed compare to other prenatals?

Needed Prenatal Multi Essentials delivers *8x more nutrition than other leading prenatals on the market.
It includes 551 mcg of folate in the methylated form, to support healthy neural tube development and methylation..
And yes—it really is that good.
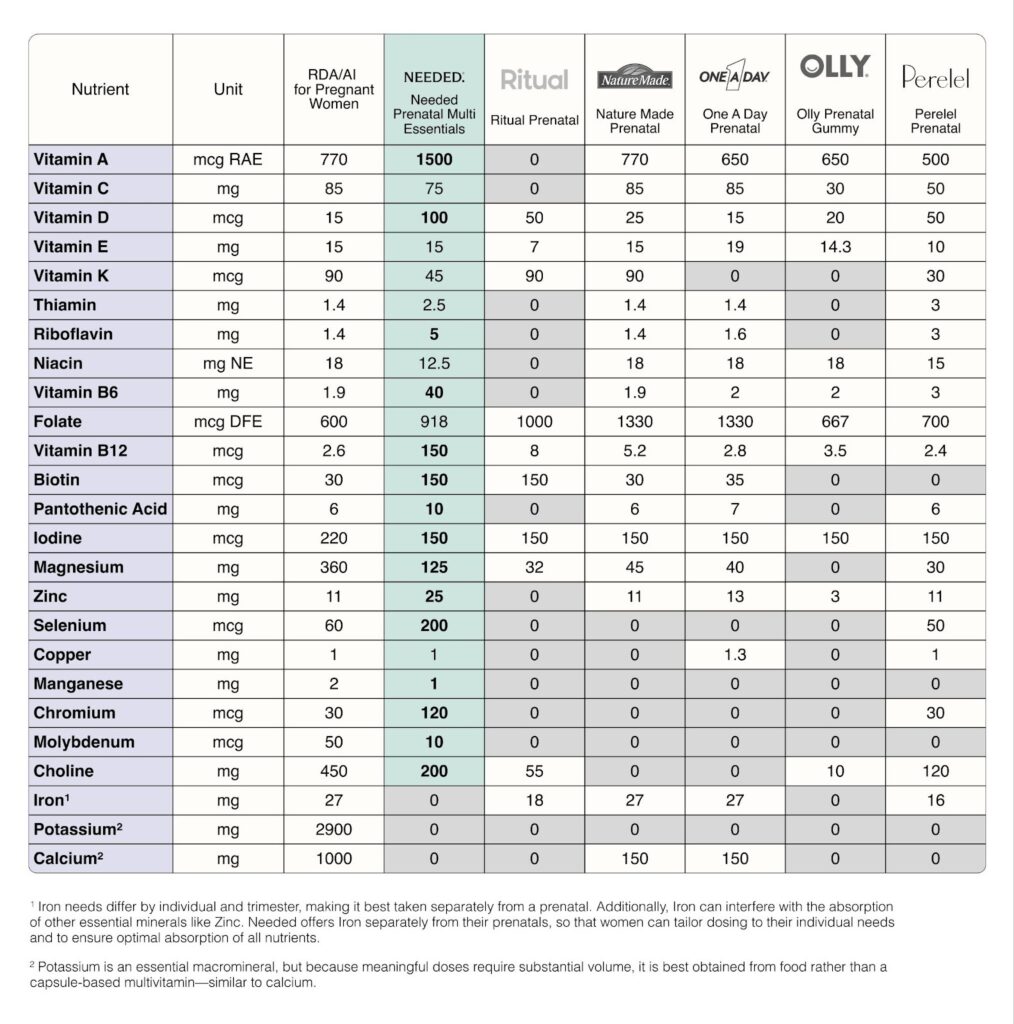
Needed prenatals are third-party tested, meaning an independent, unbiased organization verifies the safety, quality, and accuracy of all label claims. In short: what’s on the label is exactly what’s in the product.
Needed offers multiple prenatal options: capsules and a vanilla powder, so you can choose what works best for you. I used the vanilla powder during my first pregnancy when I simply couldn’t swallow any pills and it was such a game changer for me personally.
You can easily purchase Needed prenatals directly through their website:
https://thisisneeded.com/products/prenatal-multi-essentials
Looking for More Support?
Navigating prenatal nutrition—and figuring out how to best support both you and your baby—can feel confusing. You don’t have to do this alone.
Using every tool available to you, including personalized nutrition guidance and high-quality supplementation, is one of the simplest ways to support a healthy pregnancy. Our 1:1 coaching services are designed to be that extra layer of support—someone firmly in your corner.
Let’s do this together. Reach out today to begin your journey toward nourishing and supporting your growing life with expert guidance every step of the way.
This post is sponsored by Needed, a brand I genuinely recommend to my patients and personally use.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
*Based on the total daily dosage of nutrients provided compared to leading prenatals as determined by IRI sales data as of December 2025
Sources:
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4933077/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iodine-HealthProfessional/
https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/pregnancy-breastfeeding-and-bone-health

Menopause is often discussed in whispers and framed through negative stereotypes, yet it is one of the most significant and transformative stages of life. Understanding what’s happening in the body—and how to support it through nutrition and lifestyle—can help dismantle stigma and reframe menopause for what it truly is: a period of reflection, strength, and renewed autonomy.
To understand how functional nutrition supports menopause, it helps to briefly revisit how the menstrual cycle works before this transition. While this biology may feel basic, it provides essential context for understanding why symptoms arise and how targeted support can help.

Why Do Hormones Change So Much During Menopause?
Before menopause, the menstrual cycle is regulated by a tightly coordinated hormonal feedback system between the brain and ovaries.
The hypothalamus releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which signals the pituitary gland to secrete luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones stimulate the ovaries to develop follicles, each containing an immature egg (ova).
As follicles mature, they release estrogen along with inhibin A and inhibin B. These hormones create a negative feedback loop, signaling the brain to slow the release of GnRH, LH, and FSH. After ovulation, the follicle becomes the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone to support the uterine lining. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone levels fall and menstruation begins.
This predictable hormonal rhythm is what allows for regular cycles—and it’s this system that gradually shifts as menopause approaches.

What Happens to Hormones During Menopause?
Menopause typically begins around age 45, though timing varies widely and there is no “correct” age. Rather than a single event, menopause is a gradual process defined by the STRAW (Stages of Reproductive Aging Workshop) staging model.
Late Reproductive Stage (Stages −3A and −3B)
Cycles are usually regular, and pregnancy is still possible. However, ovarian reserve declines as fewer eggs remain available.
Early Menopause Transition (Stage −2)
This stage marks the beginning of perimenopause. Hormonal signaling from the brain increases, progesterone production becomes less consistent, and menstrual cycles often become unpredictable.
Late Menopause Transition (Stage −1)
Periods become very irregular, with gaps of 60 days or more between cycles. Hormonal fluctuations intensify, often leading to symptoms such as hot flashes, sleep disruption, mood changes, and weight gain. This phase can last up to three years, though duration varies.
Menopause (Stage 0)
Menopause is defined as the final menstrual period.
Early Postmenopause (Stages 1A and 1B)
These stages begin after 12 consecutive months without a period. Hormones continue to stabilize, but symptoms are often most pronounced during this time. Early postmenopause typically lasts two to six years as the endocrine system adjusts to a new baseline.
How Does Functional Nutrition Support Menopause?
Functional nutrition focuses on supporting the body’s changing hormonal, metabolic, and inflammatory needs during menopause rather than simply managing symptoms.
Nutrition for Hormone and Metabolic Health
A Mediterranean-style diet—rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats—has been shown to reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular and metabolic health during menopause.
Soy-based foods may also help alleviate menopausal symptoms. Soy contains phytoestrogens, plant compounds that interact with estrogen receptors in the body. While phytoestrogens cannot replace estrogen, they can provide mild estrogen-like activity that may help ease symptoms associated with estrogen decline.
Flaxseeds are another valuable dietary tool. Rich in fiber, healthy fats, and lignans, flaxseeds have been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes and night sweats. For best results, flaxseeds should be consumed consistently at approximately 2–3 tablespoons per day for at least 12 weeks.
Why Meal Timing Matters in Menopause
When we eat is just as important as what we eat. Late or irregular eating patterns are associated with weight gain and disruption of circadian rhythms that regulate sleep, stress hormones, and appetite. Consuming the majority of daily calories earlier in the day may support improved metabolic health, reduced inflammation, and more restorative sleep.
Movement and Nervous System Support
Regular physical activity—especially walking—has powerful benefits for both physical and mental health during menopause. Walking as little as 12.5 miles per week has been associated with reductions in anxiety and depression, along with improvements in sleep quality and insomnia symptoms.
Can Functional Nutrition Make Menopause Easier?
Menopause doesn’t have to be something you “just get through.” With the right nutritional and lifestyle support, it can be a time of empowerment, clarity, and renewed wellbeing.
Functional nutrition helps identify what your body needs during this transition—whether that’s blood sugar support, inflammation reduction, nutrient repletion, or nervous system regulation.
We’re Here to Support You
Navigating menopause can feel overwhelming, but you don’t have to do it alone. Our 1:1 coaching services provide personalized, functional nutrition support to help you feel informed, confident, and supported through every stage of menopause.
If you’re ready to invest in your health and wellbeing, we’d love to support you. Reach out today to begin your journey.
Sources:
Dr. Haylee Nye, Managing Menopausal Symptoms Naturally: Where to Begin (webinar)
Image Sources:
Organicauthority.com
Freepik.com

Why Routine Blood Work Matters for Women’s Health
Routine blood work is one of the most powerful ways to check in with your body and understand what’s really going on beneath the surface.
Your body can’t exactly tap you on the shoulder and say, “Hey, your vitamin D is low,” or “Your blood sugar is creeping up.” Instead, it communicates through subtle (and sometimes not-so-subtle) signs—fatigue, mood changes, stubborn weight, poor sleep, irregular cycles. While those symptoms are important clues, the most direct way to get answers is through routine blood work.
As a dietitian, I’m a big believer in using data to guide decisions—and I also believe it should be easy and accessible. That’s one of the reasons I personally decided to use Superpower for my own labs.
What Does “Routine Blood Work” Usually Include?
The term routine blood work is broad, but it typically includes several key tests that give a high-level snapshot of your health:
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A CBC looks at red blood cells, white blood cells, hemoglobin, and platelets. These markers tell us how well your body is transporting oxygen, fighting infections, and clotting blood. Suboptimal levels can point to issues like anemia, inflammation, or underlying infections.
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
A CMP evaluates 14 different markers related to kidney function, liver function, electrolytes, blood sugar, proteins, and acid–base balance. This panel gives valuable insight into digestion, nutrient absorption, mineral status, and overall organ health.
Lipid Panel
This test measures LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, HDL (“good”) cholesterol, VLDL, and triglycerides. These markers reflect long-term dietary patterns, metabolic health, and cardiovascular risk. Elevated triglycerides or LDL can increase the risk of heart disease, while HDL plays a protective role by helping remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Thyroid Panel
A standard thyroid panel usually includes TSH, T4, and T3. These hormones regulate metabolism, energy, temperature, and growth. Imbalances here can show up as fatigue, weight changes, hair loss, or cycle irregularities—symptoms many women are told are “normal,” but often aren’t.
HbA1c
HbA1c reflects your average blood sugar over the past 2–3 months. It’s one of the most important markers for identifying insulin resistance, prediabetes, and diabetes.
- Below 5.7%: typical
- 5.7–6.4%: prediabetes
- 6.5% or higher: diabetes
My Personal Experience with Superpower
One of the biggest barriers I see—both personally and with clients—is logistics. Scheduling labs, remembering appointments, waiting weeks for results…it’s enough to make routine testing feel overwhelming.
That’s where Superpower really stood out to me.
The sign-up process was incredibly easy, and my blood work came back much faster than I expected. I also loved receiving text updates along the way—no guessing, no wondering when results would arrive.
Once I had my labs, the value really clicked. Having everything clearly laid out made it obvious where things were improving and where I needed support. I could see, for example, that my HbA1c had come down, which was incredibly validating, and that my vitamin D levels were lower than optimal, giving me clear direction on what to address next.
As someone who works with labs every day, I can confidently say: having this kind of insight makes it so much easier to make informed, proactive health decisions instead of guessing.
Making Blood Work Fit Into Your Life
If going to a doctor’s office or lab feels like one more thing on an already full to-do list, Superpower simplifies the process.
Superpower offers blood testing either at home or through one of their 2,000+ partner labs and assesses 100+ biomarkers—far more than what’s typically included in standard annual labs.
Beyond the testing itself, Superpower provides:
- A personalized plan based on your results
- Easy-to-understand data through their member portal
- Ongoing updates as your health evolves
- 24/7 chat access to their team if questions come up
Instead of just handing you numbers and sending you on your way, they help you understand what those numbers actually mean.
The Bottom Line
Routine blood work isn’t about finding something “wrong”—it’s about listening to your body before small imbalances turn into bigger issues. When testing is accessible, clear, and actionable, it becomes one of the most empowering tools for long-term health.
If you’ve been putting off labs because of time, logistics, or confusion around results, Superpower is absolutely worth checking out.
Learn more at: https://superpower.com
Superhero doesn’t stop there though, based on your bloodwork result a personalized plan is created that evolves with you. All of this data is easy for you to check and access through their website and member portal.

What’s Blocking Your Fertility? Root Cause Quiz Development
Growing my nutrition practice taught me that most women struggling with fertility don’t just need another meal plan or supplement. They need help uncovering the underlying issues that are making conception so difficult. Clients often come to me feeling exhausted, bloated, anxious, or inflamed, yet they can’t connect the dots between these symptoms and their reproductive health. When I discovered Interact, a quiz‑building platform, I realized that an interactive diagnostic quiz could meet people right where they are—online—and guide them toward identifying possible root causes of their fertility challenges.

Interactive quizzes aren’t just fun; they’re powerful marketing tools. The Blogsmith notes that on average a quiz is shared 1,600 times, and in January 2015 nine out of ten of the most‑shared Facebook posts were quizzestheblogsmith.com. 70 % of marketers say interactive content is effective at converting visitors, and 88 % say it differentiates their brandtheblogsmith.com. The average lead‑capture rate for quizzes is 31.6 %, far above the 1–5 % typical for email opt‑instheblogsmith.com. Leveraging these statistics, I set out to build a quiz that wasn’t just entertaining—it needed to deliver meaningful, actionable information while capturing leads for my practice.
The Idea: A Diagnostic Quiz for Fertility Root Causes
My program, The Root Cause Fertility Method, focuses on helping women improve fertility through a holistic lens. Many clients experience sugar cravings, energy crashes, bloating, headaches, acne, insomnia, or chronic stress, yet don’t realize these are often connected to hormonal imbalances, digestive dysfunction, or nutrient deficiencies. I wanted a simple tool to help women start connecting these symptoms to possible underlying causes before they even book a consultation.
Choosing a point‑based system
To do this, I created a 25‑question quiz called “What’s Blocking Your Fertility?” Each question offers two answers—a symptom is either “yes” or “no.” Here’s a sample:
| Symptom category | Sample question | Answer A (points) | Answer B (points) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood‑sugar/insulin | Do you experience intense sugar or carb cravings, especially in the afternoon? | “Yep! Feel this all the time” (1 point) | “No, not really” (0 points) |
| Digestion/gut health | Do you often feel bloated even when eating healthy foods? | “Yes, I’m constantly unbuttoning my pants” (1 point) | “No, I rarely feel bloated” (0 points) |
| Inflammation/autoimmunity | Do you feel stiff or achy in the morning? | “Yes, I feel like I’m twenty years older” (1 point) | “No, I’m a spring chicken” (0 points) |
| Nutrient deficiencies | Do you notice brittle nails or hair thinning? | “Yes, I’m constantly finding hair everywhere” (1 point) | “No, my hair and nails are healthy” (0 points) |
| Adrenal/stress | Do you feel wired but tired at night? | “Yes, I’m tired all day and scrolling at night” (1 point) | “No, I have a solid bedtime routine” (0 points) |
Each “yes” answer in a category adds one point to that root‑cause bucket. At the end of the quiz, the category with the highest score indicates the user’s most likely area of imbalance—blood sugar/insulin, digestion/gut health, inflammation/autoimmunity, nutrient deficiencies, or adrenal/stress dysfunction. Every result page offers targeted suggestions (for example, balancing blood sugar with protein and fiber at meals, supporting digestion with probiotics and mindful eating, addressing inflammation through anti‑inflammatory foods, or prioritizing sleep and stress management). This point‑based design makes the quiz feel personalized and diagnostic without overstepping into medical diagnosis.
Building the quiz with Interact
Why Interact?
After researching quiz platforms, I chose Interact because the software is intuitive and flexible. The Blogsmith review highlights that Interact’s user interface is “ridiculously easy to use and navigate,” with a clean design that makes quiz creation straightforward. It allows you to add your branding basics, customize a quiz cover, create result pages, and then jump back and forth between sections as you refine questions (theblogsmith.com). I knew I wanted to design a quiz that looked polished and aligned with my brand, but I also needed the flexibility to adjust questions and scoring logic on the fly.

Customizing my quiz
- Branding and cover – I started by uploading my logo and choosing colors consistent with the Wellspring Nutrition brand. Interact prompts you to set up your quiz cover first, which ensures a cohesive look.
- Result pages – Before drafting questions, I defined five result types corresponding to the root‑cause categories above. Interact lets you add as many result pages as you need and edit them at any time. Each result page includes an explanation of the likely imbalance and a call to action directing readers to schedule a consultation or download a free fertility guide.
- Question & answer creation – Interact allows text‑based or image‑based questions, so I selected images of happy families and healthy food to make the quiz visually appealing. Adding questions is simple: you type your question, write the answer options, and use the points feature to assign values. The platform makes it easy to edit correlations so that one answer can map to multiple results.
- Scoring logic – I enabled the “scored quiz” option. For each answer, I assigned points to the appropriate categories. Interact automatically tallies points as users progress and displays the result page with the highest score when they finish. The platform supports multiple quiz types—including personality, knowledge tests and scored quizzes—so you can choose what fits your goals.
- Lead‑capture form and segmentation – Interact’s integrations with email service providers allow you to add an opt‑in form before revealing results. I connected the quiz to my email service and mapped each result to a segmented list. For example, someone with high blood‑sugar points receives a follow‑up email with tips for balancing insulin and information about my blood‑sugar reset program. Personalized segmentation like this automates nurture sequences without manual tagging.
- Embedding the quiz – Once the quiz was finalized, Interact generated an embed code that I inserted into a dedicated landing page on my website. It also offers a WordPress plugin, but I opted for the code to ensure full control over the page design. I added share buttons because social media is crucial for quiz success.
Following best practices
Interact’s internal data from over 40 k quizzes and 5 million leads has shaped a list of best practices, which was so helpful when creating the quiz. Here are some guidelines I followed:
- Keep it short: Aim for about 2 minutes or 7 questions to maintain engagement. My quiz has 25 questions but each is a quick yes/no, so completion time averages under three minutes.
- Use 3–6 answer options: I limited each question to two choices to reduce decision fatigue
- Offer an opt‑out: I allow users to skip the opt‑in if they just want to see their results, which avoids capturing unqualified leads.
- Call to action: Each result page directs users to book a free discovery call or download my fertility checklist.
Insights from quiz data
In its first month, the quiz attracted seven participants with an 87 % completion rate on early questions. Interestingly, the highest “yes” rates corresponded to symptoms of poor blood‑sugar control: sugar cravings, energy crashes after eating, and waking up between 2–4 a.m. Many respondents also reported digestive issues like bloating and irregular bowel movements, suggesting that gut health is a significant blocker for fertility in my audience. This data is incredibly valuable; it confirms patterns I see in one‑on‑one consultations and helps me tailor my content and offers to address the most common root causes.
The quiz also acts as a conversation starter. Women who score high in the adrenal/stress category often share stories about feeling overwhelmed and emotionally exhausted, and we talk about creating sustainable self‑care routines. Those who score high for nutrient deficiencies are often surprised when we connect brittle nails and hair loss to minerals like iron and magnesium. I always remind users that this quiz is a starting point, not a medical diagnosis. Nevertheless, it invites them into a coaching relationship where we can run functional lab tests and design personalized protocols.
Why interactive quizzes matter
Interactive quizzes drive engagement and segmentation more effectively than static content. Statistics show they convert visitors into leads at a higher rate than traditional email sign‑ups and are widely shared across social platforms. They also help automate personalization; Interact’s integrations let you segment users based on their answers and trigger tailored follow‑up sequences. For practitioners like me, quizzes are not just marketing tools; they’re educational resources that empower people to take the next step on their health journey.
Final thoughts
Creating my root‑cause fertility quiz with Interact was both fun and strategic. The platform’s intuitive interface, customizable design and flexible scoring system allowed me to build a diagnostic‑style quiz that engages visitors and delivers personalized results. The data I’ve collected so far confirms that blood sugar and gut health are the most common blockers for fertility in my audience, which helps me refine my services and content. For example, in my Root Cause Fertility Method program we include a continuous glucose monitor AND the GIMAP stool test because we know that blood sugar and gut health are the top two root causes our audience is working on.
If you’re a health professional or coach looking to generate leads while genuinely serving your audience, I highly recommend experimenting with interactive quizzes. They can be designed for personality‑based insights, knowledge tests, or scored diagnostics, and you’ll gain invaluable insights along the way. To see how my quiz works and discover what could be blocking your fertility, head over to my website and take the quiz yourself! And let me know what you think! 🙂

The Preconception Playbook
This free playbook provides specific actionable tips to get started on your fertility journey, as well as what to avoid while you're trying to conceive.
Get the free playbook