Pregnancy
Resources
Style
Planning
View All
Pregnancy is a season when your body simply needs more—more rest, more support, and yes, more nutrients. During this time, demands for key nutrients like folate, iodine, choline, and vitamin D increase significantly. If these needs aren’t met, deficiencies can have long-term effects not only for you, but for your growing baby as well.
Nourishing your body during this incredibly important and transformative time isn’t optional—it’s foundational to supporting a healthy pregnancy.
Is a healthy diet enough?
Even when you’re eating a well-balanced, nutrient-dense diet, it can still be difficult to meet all of your increased nutrient needs during pregnancy through food alone. This is where a high-quality prenatal vitamin becomes an essential part of your pregnancy toolkit.
Let’s break down a few of the most important nutrients to look for—and why they matter.

Folate
Folate (vitamin B9) is a critical micronutrient for fetal brain and spinal cord development. In the very early weeks of pregnancy—often before someone even knows they’re pregnant—the neural tube forms and closes, eventually developing into the brain and spinal cord. This process typically happens within the first 3–4 weeks of pregnancy.
Folate plays a central role in this process by supporting rapid cell growth and division, as well as methylation—a biochemical process that is essential for proper neural tube closure and healthy brain and spinal cord development.
A quick (and gentle!) biochemistry moment—bear with us. Many supplements and fortified foods use folic acid, which is a synthetic form of vitamin B9. Folic acid must be converted in the body to its active form, methylfolate, before it can be fully utilized. Some individuals have a harder time completing this conversion, which can lead to less-than-optimal absorption.
To bypass this conversion step altogether and support optimal absorption, it’s ideal to choose a prenatal that contains methylfolate rather than folic acid.
Current Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) in the U.S. are:
- 400 mcg/day for women of childbearing age who are not pregnant
- 600 mcg/day for pregnant women
Iodine
Iodine is a crucial micronutrient for thyroid health and function. If you want a deeper dive into iodine’s role in fertility, thyroid health, reproductive health, and hormone balance, be sure to check out our earlier blog: Iodine and Women’s Health: What You Need to Know.
When it comes to pregnancy, iodine deserves special attention. It plays a key role in fetal brain and nervous system development, as well as in thyroid hormone production and regulation for both mom and baby.
The current RDAs in the U.S. are:
- 150 mcg/day for women of childbearing age who are not pregnant
- 220 mcg/day for pregnant women
Because iodine intake varies widely based on diet and food sourcing, it’s an especially important nutrient to confirm is included in your prenatal.

Vitamin D and Calcium
Calcium is essential for bone health, and during pregnancy, needs increase to support fetal skeletal development. At the same time, adequate calcium intake helps protect and maintain mom’s own calcium stores.
During breastfeeding, approximately 3–5% of a mother’s calcium stores can be depleted through breast milk production. While these losses haven’t been directly linked to an increased risk of osteoporosis later in life, ensuring adequate calcium intake before, during, and after pregnancy is still incredibly important.
One of the best ways to support calcium absorption? Vitamin D.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a role in fetal immune system development, overall fetal growth, and—importantly—calcium absorption.
Without getting too deep into the weeds, the active form of vitamin D (calcitriol) helps activate receptors in the intestines that increase the production of calcium-transporting proteins. These proteins work together to improve calcium absorption into the bloodstream—essentially helping your body actually use the calcium you’re consuming.
Current RDAs in the U.S.:
- Calcium: 1000–1300 mg/day (pregnant and non-pregnant women)
- Vitamin D: 15 mcg/day (pregnant and non-pregnant women)
Many perinatal practitioners recommend higher levels of vitamin D for optimal lab levels.
So… which prenatal should I choose?
Understanding nutrient needs is one thing—actually choosing a prenatal is another. With so many options on the market, it’s no wonder this step feels overwhelming.
One important thing to know: many prenatals still rely on outdated RDAs that were originally based on research conducted in men’s bodies—not women’s, and certainly not pregnant women’s.
This is where Needed stands out.
Needed recognized this gap and created prenatals that are science-backed and designed with women’s unique needs in mind—especially during preconception, pregnancy, and postpartum, when nutrient demands are higher across the board.
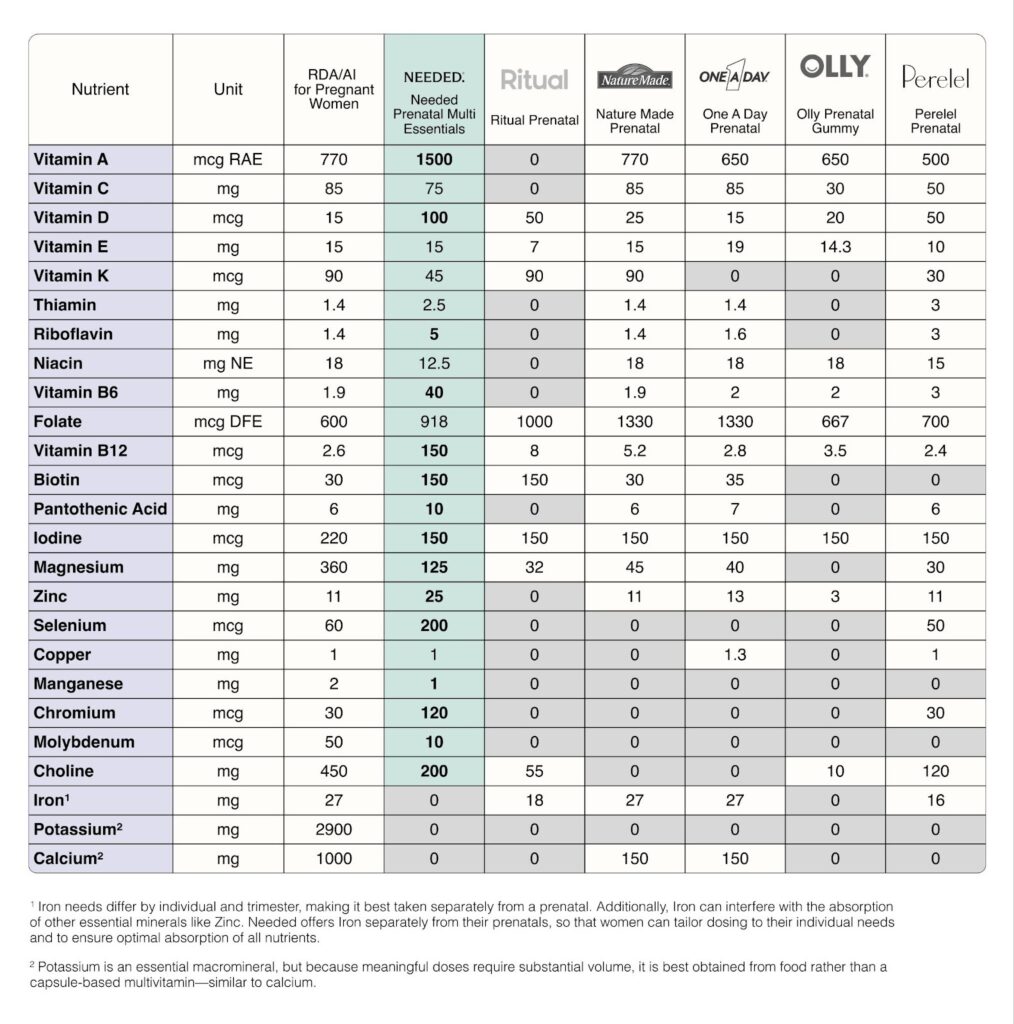
Needed Prenatal Multi provides 5x more nutrition than outdated RDAs, helping better meet the increased nutrient demands of pregnancy.*
How does Needed compare to other prenatals?

Needed Prenatal Multi Essentials delivers *8x more nutrition than other leading prenatals on the market.
It includes 551 mcg of folate in the methylated form, to support healthy neural tube development and methylation..
And yes—it really is that good.
Needed prenatals are third-party tested, meaning an independent, unbiased organization verifies the safety, quality, and accuracy of all label claims. In short: what’s on the label is exactly what’s in the product.
Needed offers multiple prenatal options: capsules and a vanilla powder, so you can choose what works best for you. I used the vanilla powder during my first pregnancy when I simply couldn’t swallow any pills and it was such a game changer for me personally.
You can easily purchase Needed prenatals directly through their website:
https://thisisneeded.com/products/prenatal-multi-essentials
Looking for More Support?
Navigating prenatal nutrition—and figuring out how to best support both you and your baby—can feel confusing. You don’t have to do this alone.
Using every tool available to you, including personalized nutrition guidance and high-quality supplementation, is one of the simplest ways to support a healthy pregnancy. Our 1:1 coaching services are designed to be that extra layer of support—someone firmly in your corner.
Let’s do this together. Reach out today to begin your journey toward nourishing and supporting your growing life with expert guidance every step of the way.
This post is sponsored by Needed, a brand I genuinely recommend to my patients and personally use.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
*Based on the total daily dosage of nutrients provided compared to leading prenatals as determined by IRI sales data as of December 2025
Sources:
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4933077/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iodine-HealthProfessional/
https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/pregnancy-breastfeeding-and-bone-health

Written by: Lauren Chamberlain
Edited and Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
Dealing with endometriosis is already a challenge—pain, fatigue, and the frustratingly long journey to diagnosis. But for many, one of the hardest realities to face is how this condition might impact fertility. Whether you’re actively trying to conceive or simply thinking about the future, it’s natural to wonder: Will I be able to get pregnant? Will it take longer? Am I at risk for complications?
Let’s break it down—why does endometriosis make conception more difficult? And what can be done to improve fertility outcomes?
Fertility and Endometriosis: The Numbers
Studies suggest that up to 50% of people with endometriosis may experience fertility challenges, and about half of those diagnosed with infertility have underlying endometriosis. However, a diagnosis doesn’t mean pregnancy is impossible! It may take longer, require medical support, or necessitate lifestyle adjustments—but many people with endometriosis go on to conceive and carry healthy pregnancies.
Now that we’ve covered the statistics, let’s explore why endometriosis affects fertility in the first place.
Understanding the Connection: Why Endometriosis Affects Fertility
Endometriosis is a complex condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, leading to inflammation, scarring, and hormonal imbalances. These factors can contribute to fertility struggles in multiple ways:
1. Chronic Inflammation and Hormonal Imbalances
Endometriosis is associated with chronic inflammation, which plays a key role in fertility challenges. The condition causes an increase in inflammatory cytokines—proteins that regulate immune responses. These cytokines can interfere with ovulation, fertilization, and implantation by creating a hostile uterine environment. Chronic inflammation may also impair the function of the corpus luteum, the structure responsible for producing progesterone after ovulation. Since progesterone is critical for preparing the uterine lining for implantation, low levels may result in implantation failure or early miscarriage.
Additionally, endometriosis is often linked to estrogen dominance. Excess estrogen can thicken the endometrial lining abnormally, disrupt the menstrual cycle, and contribute to a suboptimal hormonal balance for conception.
2. Reduced Egg Quality and Oxidative Stress
Endometriosis has been linked to oxidative stress, a condition where an excess of reactive oxygen species (ROS) damages cellular structures, including eggs. This oxidative damage can lead to:
- DNA fragmentation in eggs, reducing their ability to be fertilized.
- Lower embryo quality, decreasing the likelihood of successful implantation.
- Higher rates of aneuploidy (chromosomal abnormalities), which can lead to failed pregnancies or birth defects.
Research suggests that targeted nutritional strategies, such as increasing antioxidant intake (e.g., vitamin C, vitamin E, and CoQ10), can help mitigate oxidative stress and improve egg quality.
3. Decreased Ovarian Reserve and Endometriomas
Many individuals with endometriosis develop ovarian cysts known as endometriomas. These cysts, filled with old blood, can impact ovarian function in several ways:
- Damage to ovarian tissue: As endometriomas grow, they can infiltrate and compromise healthy ovarian tissue, reducing the number of viable eggs.
- Lower response to fertility treatments: Studies indicate that individuals with endometriomas often have a lower ovarian response to stimulation during assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like in vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Surgical risks: While surgical removal of endometriomas may relieve symptoms, it can also reduce ovarian reserve if healthy ovarian tissue is inadvertently removed during the procedure. Those considering surgery should discuss fertility preservation strategies, such as egg freezing, beforehand.
4. Blocked Fallopian Tubes and Pelvic Adhesions
Endometriosis can cause adhesions—bands of fibrous scar tissue that develop between organs. These adhesions may:
- Block or distort the fallopian tubes, preventing eggs from traveling to meet sperm.
- Interfere with ovulation, making it more difficult for the ovaries to release eggs effectively.
- Cause fluid buildup in the fallopian tubes (hydrosalpinx), which can create an inhospitable environment for embryos and decrease implantation success.
For those with significant tubal damage, natural conception may be challenging, and assisted reproductive technologies like IVF may be necessary.
5. Implantation Challenges and Uterine Dysfunction
Successful pregnancy depends on a fertilized egg implanting into a healthy uterine lining. Endometriosis can interfere with this process due to:
- Abnormal endometrial receptivity: The endometrium (uterine lining) may not develop properly due to chronic inflammation, hormonal imbalances, or scarring.
- Increased uterine contractility: The uterus may contract excessively, making it harder for an embryo to implant and remain stable.
- Altered immune response: Inflammatory and immune factors in the uterine environment may mistakenly attack the embryo, leading to implantation failure or early miscarriage.
Pregnancy with Endometriosis: Risks & Considerations
While many individuals with endometriosis achieve healthy pregnancies, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and considerations:
1. Increased Risk of Obstetrical Complications
Studies have identified a higher incidence of certain complications in pregnant individuals with endometriosis:
- Preterm Birth: There is an elevated risk of delivering before 37 weeks of gestation.
- Placenta Previa: The placenta may implant low in the uterus, covering the cervix, which can lead to bleeding and necessitate a cesarean section.
- Hypertensive Disorders: Conditions like preeclampsia, characterized by high blood pressure and potential damage to other organ systems, are more common.
- Gestational Diabetes: An increased likelihood of developing diabetes during pregnancy has been observed.
- Cesarean Delivery: The necessity for cesarean sections is higher among those with endometriosis.
These findings underscore the importance of vigilant prenatal care for individuals with endometriosis to monitor and manage potential complications effectively.
2. Impact of Surgical Treatment on Pregnancy Outcomes
Surgical interventions for endometriosis, such as laparoscopic excision, aim to alleviate symptoms and improve fertility. However, the effects of surgery on pregnancy outcomes are complex:
- Adhesion Formation: Post-surgical adhesions can lead to chronic pelvic pain and may impact fertility.
- Ovarian Reserve: Surgical removal of endometriomas (ovarian cysts associated with endometriosis) can reduce ovarian reserve, potentially affecting fertility.
Therefore, surgical decisions should be individualized, weighing the benefits against potential risks, and discussed thoroughly with a healthcare provider.
3. Importance of Preconception Counseling
Given the potential challenges associated with endometriosis and pregnancy, preconception counseling is highly recommended. This process involves:
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Assessing the extent of endometriosis and its impact on reproductive organs.
- Fertility Assessment: Evaluating ovarian reserve and tubal patency to determine the best conception strategies.
- Risk Discussion: Understanding the potential obstetrical risks and planning appropriate monitoring and interventions.
Engaging in preconception counseling allows for informed decision-making and the development of a tailored care plan to optimize pregnancy outcomes.
4. Nutritional and Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting specific dietary and lifestyle changes can positively influence fertility and pregnancy outcomes in individuals with endometriosis:
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Consuming foods rich in antioxidants can reduce oxidative stress and improve egg quality.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in moderate exercise can enhance overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Stress Management: Incorporating stress-reduction techniques like yoga or meditation may improve hormonal balance.
Implementing these modifications can support reproductive health and may increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy.
5. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
For those experiencing difficulty conceiving naturally, ART options such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be considered. While endometriosis can impact the success rates of ART, individualized treatment protocols and close monitoring can enhance outcomes. Consulting with a fertility specialist can provide personalized guidance on the most appropriate interventions.
Ultimately, while endometriosis can pose challenges to conception and pregnancy, understanding the potential risks and proactively managing them with a healthcare team can lead to successful outcomes.
What Can You Do?
If you have endometriosis and are concerned about your fertility, there are steps you can take to optimize your chances of conception:
- Adopt an anti-inflammatory diet: Eat foods rich in antioxidants, such as leafy greens, berries, turmeric, and omega-3 fatty acids, to combat oxidative stress and support egg quality.
- Consider medical treatment: Hormonal therapies like GnRH agonists, birth control pills, or progestin therapy may help manage symptoms and improve fertility outcomes.
- Support gut health: A balanced gut microbiome helps regulate inflammation. Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut, or consider a high-quality probiotic supplement.
- Optimize lifestyle factors: Engage in regular, low-impact exercise like yoga or walking to reduce inflammation and support reproductive health. Prioritize stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, and ensure you’re getting enough quality sleep.
- Work with a fertility specialist: A reproductive endocrinologist or fertility dietitian can assess your specific needs and create a personalized plan, whether you’re trying to conceive naturally or exploring medical interventions.
- Discuss fertility preservation: If you’re not trying to conceive yet but may want to in the future, options like egg freezing can help safeguard your reproductive potential.
Final Thoughts
Endometriosis may make conception more challenging, but it doesn’t mean it’s out of reach. Every fertility journey is different, and while endometriosis can present obstacles, there are many ways to take control of your reproductive health. Whether through lifestyle changes, medical treatments, or working with a specialist, you have options. If you’re struggling, reach out to a healthcare provider to explore the best path for you. Knowledge is power, and by understanding the impact of this condition, you can approach your fertility journey with confidence and clarity.

Sources
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9983692
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8224039
https://www.rbmojournal.com/article/S1472-6483(13)00007-2/fulltext
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8065992
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7226034
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9528818
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10058497/#sec5-life-13-00654
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10820275

Written by: Lauren Chamberlain
Edited and Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
If you’re trying to conceive, the food on your plate might be more important than you think! The link between diet and fertility is stronger than ever, with research showing that the right nutrition can make all the difference in hormone balance, egg and sperm quality, and overall reproductive health. Enter the Modified Mediterranean Diet – an upgraded version of one of the world’s healthiest eating patterns, tailored specifically for fertility support. Packed with antioxidants, healthy fats, and essential nutrients, this approach can help set the stage for a successful pregnancy. Let’s dive into how you can use food as a powerful tool to enhance fertility naturally!
The Role of Nutrition in Fertility
What you eat plays a direct role in shaping your reproductive health. A well-balanced diet provides the essential nutrients needed for hormone production, optimal egg and sperm quality, and a healthy reproductive system. Poor dietary choices, on the other hand, can lead to inflammation, oxidative stress, and metabolic imbalances, all of which can impair fertility.
One of the key factors in fertility is oxidative stress, which occurs when free radicals damage cells, including eggs and sperm. Antioxidant-rich foods such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts help neutralize these harmful compounds, protecting reproductive cells and improving their function. Research has shown that a diet high in antioxidants is linked to improved sperm motility and morphology, as well as better ovarian function in women.
Another crucial aspect is hormonal balance. Hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone rely on a steady supply of vitamins and minerals to function properly. Nutrients such as zinc, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids support hormone synthesis and regulation, helping to optimize fertility. Consuming high-quality protein sources, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbohydrates helps maintain stable hormone levels and reduces the risk of conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is a leading cause of infertility.
Additionally, mitochondrial health plays a significant role in reproductive success. Mitochondria, known as the powerhouses of the cell, provide the energy needed for fertilization and embryo development. Nutrients like CoQ10, found in fish, nuts, and organ meats, support mitochondrial function, ensuring that eggs and sperm have the energy required for optimal performance.
Finally, blood sugar stability is vital for fertility. High blood sugar levels can disrupt ovulation, impair egg quality, and contribute to insulin resistance, which is commonly associated with PCOS. A diet that prioritizes low-glycemic carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall reproductive health.
By focusing on nutrient-dense foods that combat oxidative stress, support hormone production, enhance mitochondrial function, and stabilize blood sugar, you can create the best possible environment for conception and a healthy pregnancy.
Why the Modified Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet has long been associated with numerous health benefits, including improved heart health, reduced inflammation, and better metabolic function. Studies have found that adherence to a Mediterranean diet is linked to increased fertility, improved assisted reproductive technology (ART) outcomes, and better pregnancy success rates.
However, for optimal fertility benefits, modifications to the traditional Mediterranean diet can enhance its effects. A modified Mediterranean diet prioritizes lower glycemic load foods, nutrient-dense proteins, and specific fertility-enhancing nutrients.
Understanding Glycemic Index vs. Glycemic Load
People often hear about glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) when discussing blood sugar management, but they are not the same. The glycemic index measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar on a scale from 0 to 100. However, it does not account for portion size. Glycemic load, on the other hand, considers both the GI and the amount of carbohydrates in a typical serving, giving a more accurate picture of a food’s impact on blood sugar. For fertility, focusing on low glycemic load foods is more beneficial for stabilizing blood sugar and hormone balance.
Read more about how to balance blood sugar through your meals here.
Key Components of the Modified Mediterranean Diet
1. Healthy Fats for Hormone Balance
Healthy fats play a vital role in hormone production and cell membrane integrity. The modified Mediterranean diet emphasizes:
- Extra virgin olive oil
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds (e.g., walnuts, flaxseeds, almonds)
- Omega-3-rich fatty fish (e.g., salmon, sardines, mackerel)
- Grass-fed animal fats in moderation
These fats support reproductive hormone function and reduce inflammation, benefiting egg and sperm quality.
2. High-Quality Protein Sources
Protein is essential for reproductive health, but the source matters. This diet focuses on:
- Grass-fed beef and pasture-raised poultry
- Wild-caught fish
- Eggs (rich in choline and vitamin B12)
- Legumes and lentils
- Full-fat dairy (linked to improved ovulation in women with PCOS)
Protein from high-quality sources supports mitochondrial function in eggs and sperm and provides key amino acids necessary for hormone production.
3. Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Oxidative stress is a significant contributor to poor egg and sperm quality. The modified Mediterranean diet is rich in antioxidants that combat free radical damage:
- Berries (blueberries, raspberries, strawberries)
- Dark leafy greens (spinach, kale, Swiss chard)
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, Brussels sprouts)
- Herbs and spices (turmeric, ginger, rosemary)
A diet high in antioxidants has been shown to improve sperm motility and morphology while enhancing egg quality.
4. Low-Glycemic Carbohydrates
Blood sugar imbalances can negatively impact fertility, particularly in individuals with insulin resistance or PCOS. This diet reduces refined grains and includes:
- Quinoa, farro, and barley in moderation
- Sweet potatoes, squash, and beets
- Legumes and lentils for fiber and protein
Stabilizing blood sugar through a low-glycemic diet helps regulate ovulation and improve egg quality.
5. Essential Micronutrients for Fertility
Several key vitamins and minerals are essential for reproductive health:
- Folate & B Vitamins: Support methylation and DNA synthesis (found in leafy greens, beans, and liver).
- Vitamin D: Linked to improved ovarian function and implantation (from sunlight, fatty fish, and fortified dairy).
- Zinc: Essential for sperm production and egg maturation (in nuts, seeds, and shellfish).
- CoQ10: Supports mitochondrial function in eggs and sperm (in grass-fed meat, fish, and supplements).
- Choline: Crucial for fetal brain development and egg quality (in eggs and liver).
Learn more about my recommendations for prenatal supplements here.
Practical Meal Ideas for Fertility Support
To make following this diet easier, here are additional meal ideas:
Breakfast:
- Greek yogurt parfait with walnuts, chia seeds, and fresh berries.
- Scrambled eggs with sautéed spinach, tomatoes, and feta cheese on whole-grain toast.
- Oatmeal with almond butter, flaxseeds, and a sprinkle of cinnamon.
Lunch:
- Grilled salmon with quinoa, steamed asparagus, and a drizzle of olive oil.
- Mediterranean chickpea salad with cucumbers, cherry tomatoes, red onion, feta cheese, and olive oil dressing.
- Lentil soup with a side of whole-grain bread and a mixed greens salad.
Dinner:
- Grass-fed steak with sweet potato mash and roasted Brussels sprouts.
- Baked cod with a side of roasted vegetables (zucchini, bell peppers, eggplant) and brown rice.
- Chicken and vegetable stir-fry with cauliflower rice and sesame ginger dressing.
Snacks:
- Hummus with carrot and celery sticks.
- A handful of almonds and dark chocolate.
- Cottage cheese with flaxseeds and sliced peaches.
- Hard-boiled eggs with a sprinkle of sea salt.
Lifestyle Considerations for Fertility
In addition to diet, lifestyle factors play a crucial role in optimizing fertility:
- Stress Management: Chronic stress disrupts hormonal balance. Incorporate mindfulness, yoga, or meditation.
- Sleep Hygiene: Poor sleep affects hormone regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Exercise: Moderate exercise improves fertility, but excessive exercise can have negative effects, particularly on ovulation.
- Reducing Toxins: Minimize exposure to endocrine disruptors such as BPA and phthalates found in plastics and personal care products.
Research Insights and Case Studies
Several studies highlight the success of dietary modifications in improving fertility:
- Women who adhered to a Mediterranean-style diet had a 65% higher chance of conception through IVF.
- A study found that men following a nutrient-rich diet improved their sperm parameters within just three months.
- Higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a 40% lower risk of ovulatory infertility in women.
- Couples undergoing fertility treatments who followed a Mediterranean-style diet had a 30% higher live birth rate compared to those who did not.
- A study on male fertility found that men with a diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids had 20% higher sperm motility and 15% better morphology than those consuming a Western-style diet.
- Women who consumed higher levels of folate and vitamin B12 had a 50% lower risk of miscarriage compared to those with lower intake.
Conclusion
A modified Mediterranean diet offers a comprehensive and evidence-based approach to improving fertility. By emphasizing nutrient-dense foods, balancing blood sugar, and supporting mitochondrial function, this dietary pattern can enhance reproductive health for both men and women. Coupled with a healthy lifestyle, these dietary modifications can significantly improve conception outcomes and pave the way for a healthy pregnancy.
Fertility is a complex journey, and while diet alone may not guarantee success, it plays a crucial role in creating the best possible conditions for conception. Every small change—whether it’s adding more antioxidant-rich foods, choosing high-quality proteins, or reducing processed carbohydrates—can have a profound impact on reproductive health.
If you’re trying to conceive, consider incorporating these dietary principles into your daily routine. Start by making simple swaps, such as using extra virgin olive oil instead of processed vegetable oils or choosing whole grains over refined grains. Focus on consuming a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Additionally, be mindful of lifestyle factors such as stress management, sleep quality, and physical activity, all of which influence fertility.
Now is the time to take charge of your fertility health! Whether you’re planning to conceive soon or in the future, these dietary and lifestyle changes can set the foundation for a healthier pregnancy and baby. If you need personalized guidance, consider working with a nutritionist or healthcare professional specializing in fertility nutrition to tailor a plan that meets your unique needs.
Start today—your future self (and baby) will thank you!

Sources
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8909876
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2846864
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4475051
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10005661

Written by: Lauren Chamberlain
Edited and Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
Thinking about starting a family? Have you ever wondered what you can do before trying to conceive to boost your chances of a healthy pregnancy? Your fertility journey starts long before a positive pregnancy test. Preparing for pregnancy isn’t just about tracking ovulation and taking prenatal vitamins—it’s about optimizing your entire body for conception and a healthy pregnancy. Scientific research increasingly shows that preconception health plays a crucial role in reproductive success and fetal development. Here are five key areas you can’t afford to skip when getting ready to grow your family.
1. Support Your Gut Health
Your digestive system isn’t just about breaking down food—it’s a complex ecosystem that plays a central role in your overall health, including fertility. A healthy gut microbiome, which refers to the trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microbes living in your digestive system, influences numerous physiological functions, from hormone regulation to immune function and even mood.
The connection between gut health and fertility is emerging as an important area of study. Research increasingly shows that an imbalanced gut microbiome, also known as dysbiosis, can have a significant impact on fertility. When the gut microbiome is out of balance, it can lead to inflammation, hormonal imbalances, and poor nutrient absorption—all of which can affect your ability to conceive.
The Gut Microbiome and Hormone Regulation
A healthy gut microbiome is essential for maintaining hormonal balance, which is crucial for fertility. The gut bacteria help metabolize estrogens, which are important for regulating the menstrual cycle and maintaining a healthy ovulation pattern. Dysbiosis has been linked to estrogen dominance, which can interfere with ovulation and lead to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a common cause of infertility.
The microbiome also plays a key role in detoxifying estrogen and other hormones, helping to prevent an overload of hormones that can disrupt your reproductive system. When the gut is not functioning optimally, it can lead to a build-up of excess estrogen in the body, a condition known as estrogen dominance, which can impact fertility and cause other reproductive health problems.
Gut Health and Immune Function
In addition to influencing hormones, the gut microbiome also affects your immune system. Around 70% of the body’s immune cells reside in the gut, and the microbiome plays a vital role in maintaining immune balance. A healthy immune system is essential for fertility because an overactive or dysfunctional immune response can interfere with embryo implantation and fetal development. Chronic inflammation in the gut can trigger an autoimmune response, leading to complications in fertility and pregnancy.
Studies have shown that women with autoimmune diseases, such as endometriosis or thyroid disorders, often have gut dysbiosis, which could be contributing to their fertility struggles. This means addressing gut health may also help reduce inflammation and autoimmune responses, creating a more favorable environment for conception and pregnancy.
The Role of Diet in Gut Health
Your diet plays a crucial role in shaping your gut microbiome. The foods you eat provide fuel for your gut bacteria, and by choosing nutrient-dense, whole foods, you can encourage the growth of beneficial microbes that support both gut and reproductive health.
To promote a healthy gut microbiome and support fertility:
- Eat fiber-rich foods: A diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes provides the necessary fiber to feed beneficial gut bacteria. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, helping to nourish the good bacteria in your gut that help regulate hormones and immune function.
- Include fermented foods: Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha contain probiotics, which are live beneficial bacteria that help restore balance to the gut microbiome. These foods support the growth of healthy bacteria, improve digestion, and reduce inflammation, all of which are essential for fertility.
- Limit processed foods and sugar: Processed foods, refined sugars, and artificial sweeteners can encourage the growth of harmful bacteria in the gut, leading to an imbalance in the microbiome. This imbalance can contribute to inflammation and poor immune function, both of which can hinder fertility.
Addressing Gut Dysbiosis for Fertility
If you suspect that gut dysbiosis may be affecting your fertility, it’s important to work with a healthcare professional, such as a dietitian or functional medicine practitioner, to assess and address the issue. Common signs of dysbiosis include digestive symptoms like bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea, and food intolerances. A professional can help guide you through dietary changes and supplements, such as probiotics or antimicrobial herbs, to support gut health and restore balance to your microbiome. Some studies have suggested that the use of probiotics and other gut-healing supplements may improve fertility outcomes, particularly in women with PCOS and other reproductive health conditions.
By supporting your gut health, you’re not just promoting better digestion and immune function—you’re creating a favorable environment for fertility.
Learn more about gut health and fertility
2. Balance Blood Sugar
Maintaining balanced blood sugar is crucial for overall health, especially when preparing for pregnancy. Blood sugar imbalances, such as insulin resistance and high blood glucose levels, can interfere with ovulation, hormone production, and overall fertility. In fact, managing blood sugar levels can be one of the most effective ways to optimize reproductive health and enhance fertility. Here’s why blood sugar balance matters and how you can achieve it.
How Blood Sugar Affects Fertility
Blood sugar imbalances, particularly insulin resistance, can have a significant impact on fertility. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, and when the body becomes resistant to insulin, it needs to produce more of it to maintain normal blood glucose levels. High insulin levels can disrupt the balance of other hormones that regulate reproductive function, such as estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. In addition to disrupting ovulation, high insulin levels can also impact the quality of the eggs and the ability to support a pregnancy.
The Link Between Blood Sugar and Hormone Imbalance
The relationship between blood sugar and hormone balance is intricate. Insulin not only regulates glucose levels but also interacts with other hormones like cortisol, leptin, and thyroid hormones, all of which play essential roles in fertility. High insulin levels can lead to an imbalance in these hormones, affecting reproductive function.
For example:
- Cortisol: Chronic stress and high blood sugar levels can elevate cortisol, a stress hormone that disrupts hormone production and reduces fertility. High cortisol levels can lead to irregular menstrual cycles and impair ovulation.
- Leptin: Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells that helps regulate appetite, metabolism, and reproductive function. Imbalances in leptin levels, often seen in individuals with insulin resistance, can interfere with ovulation and menstrual regularity.
- Insulin resistance can also disrupt thyroid function, which is crucial for fertility. Studies have shown that insulin resistance can lead to hypothyroidism (low thyroid function), which can cause menstrual irregularities, poor egg quality, and difficulty getting pregnant.
How to Balance Blood Sugar for Fertility
Achieving and maintaining stable blood sugar levels is a key factor in preparing for pregnancy. Here are some practical steps you can take to balance your blood sugar:
Prioritize Protein, Fiber, and Healthy Fats
Including a balance of protein, fiber, and healthy fats at each meal can help stabilize blood sugar levels. These nutrients slow the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar. Focus on lean protein sources (such as chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes), fiber-rich vegetables and whole grains, and healthy fats (like avocado, nuts, and olive oil).
Minimize Refined Carbs and Sugar
Refined carbohydrates (such as white bread, pasta, and baked goods) and sugary foods cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, followed by crashes that can lead to insulin resistance over time. Instead, opt for whole grains, vegetables, and fruits that release sugar more slowly into the bloodstream, providing a steady supply of energy.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise, especially strength training, helps improve insulin sensitivity, meaning your body uses insulin more effectively to regulate blood sugar. Studies have shown that regular physical activity, including moderate aerobic exercise and strength training, can improve metabolic function and support healthy hormone levels, thereby enhancing fertility.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels, which in turn disrupt blood sugar regulation and fertility. Incorporating stress-management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can help lower cortisol levels and improve overall hormonal balance.
Consider Supplements
Certain nutrients, such as magnesium, chromium, and omega-3 fatty acids, may help support healthy blood sugar metabolism. Magnesium, in particular, is important for insulin function, and research has shown that adequate magnesium levels are associated with better fertility outcomes.
Managing blood sugar not only supports fertility but also helps set the stage for a healthy pregnancy by lowering the risk of complications like gestational diabetes.
Explore blood sugar management strategies
3. Detox Your Environment
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), found in plastics, pesticides, pollution, and personal care products, can interfere with hormone balance and reproduction. Research shows that exposure to EDCs—such as BPA, phthalates, and pesticides—can affect fertility by disrupting hormone production and ovarian function.
The 4 P’s to Avoid:
- Plastics: Opt for glass or stainless steel for food storage and drink containers to reduce exposure to BPA and phthalates, which have been linked to reduced ovarian reserve and lower sperm quality.
- Pesticides: Choose organic produce when possible and thoroughly wash fruits and vegetables. Pesticides can disrupt estrogen and progesterone levels, hindering reproductive success.
- Pollution: Use air purifiers and avoid high-traffic areas to minimize exposure to air pollution, which can lower fertility rates and increase miscarriage risk.
- Personal Care Products: Swap conventional beauty, skincare, and cleaning products for non-toxic alternatives. Parabens and synthetic fragrances found in many products are linked to hormone disruption and reduced fertility.
Reducing your exposure to these toxins can help protect your hormones and reproductive health.
Learn more about reducing toxic exposure
4. Optimize Sleep & Manage Stress
Poor sleep and chronic stress can raise cortisol levels, negatively impacting reproductive hormones and fertility. Disrupted sleep patterns—such as waking up between 1-3 AM—may indicate liver detoxification issues, while difficulty staying asleep or waking up feeling unrested often correlates with low progesterone levels. Stress can lead to irregular cycles, making conception more difficult.
Studies show that sleep disturbances and high stress levels can disrupt menstrual cycle regularity, reduce ovarian function, and even affect early pregnancy outcomes.
To improve sleep and reduce stress:
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends.
- Avoid blue light exposure from screens at least an hour before bed.
- Create a calming nighttime routine—try magnesium, herbal teas, or journaling.
- Get sunlight exposure in the morning to regulate circadian rhythms.
Stress-reducing activities like meditation, breathwork, and yoga can support your fertility by lowering cortisol levels.
5. Assess Your Partner’s Health
Fertility is a team effort! Around 40% of infertility cases involve male factors, and sperm health plays a major role in conception. Changes in diet, lifestyle, and environmental exposure can improve sperm quality, motility, and count. Since sperm takes about 74 days to regenerate, it starts by making changes at least three months before conception.
To support male fertility:
- Nutrient-dense foods rich in zinc, selenium, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants are essential for sperm health. Zinc and selenium, in particular, play critical roles in sperm formation and motility.
- Limit alcohol and cannabis use, as both can reduce sperm concentration and motility.
- Avoid excessive heat—hot tubs, saunas, and even laptops on laps can lower sperm count. The testes require a cooler temperature for optimal sperm production.
- Reduce stress—high cortisol levels can lower testosterone and sperm quality.
The father’s lifestyle before conception can influence the baby’s long-term health through epigenetic changes, which may affect gene expression in both parents.
Learn more about understanding cortisol
The Bottom Line
Prepping for pregnancy isn’t just about waiting for a positive test—it’s about creating the healthiest possible environment for conception and beyond. By addressing gut health, blood sugar balance, environmental toxins, sleep, and both partners’ health, you’re laying the groundwork for a smoother fertility journey. Small, intentional choices today can make a big difference tomorrow. Take control of your health today!
Start your journey to optimal fertility

Sources
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9603966
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5052775
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S245196502030079X
https://www.cdc.gov/genomics-and-health/epigenetics/index.html
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/planning-a-pregnancy
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6075697
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4145858

The Preconception Playbook
This free playbook provides specific actionable tips to get started on your fertility journey, as well as what to avoid while you're trying to conceive.
Get the free playbook