Menstrual Cycle
Resources
Style
Planning
View All
If you’ve ever been told “everything looks normal”-yet nothing feels normal at all- you know how deeply frustrating those words can be.
You watch friends, coworkers, even strangers announce pregnancies that seemed to happen effortlessly. Meanwhile, you’re tracking, testing, timing and doing everything under the sun… and still, nothing. It’s exhausting. It’s isolating. It can make you feel like you’re somehow missing something obvious.
You’re not.
So many couples reach this same breaking point after hearing that familiar line, “everything looks fine.” It can feel like the end of the road- like the doctors have checked their boxes and moved on, even though your gut tells you something isn’t adding up. Because if everything were truly fine, this wouldn’t feel so hard.
Hormone testing can be incredibly helpful. It gives us a valuable snapshot of what’s happening beneath the surface, at the microscopic level. But here’s the truth, hormones don’t tell the whole story.
Fertility isn’t controlled by a single switch or dictated by hormones alone. It’s a complex, multi-factorial system influenced by far more than any one lab result can capture. When something feels off, it’s worth looking deeper- because “normal” doesn’t always mean optimal, and it certainly doesn’t mean your experience isn’t valid.
What does “normal” hormone blood work actually mean?
When it comes to fertility, hormones are the behind-the-scenes directors calling the shots. But which hormones actually matter- and when should they be tested? Let’s break it down.
Key players we look at for fertility include follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone
(LH), estradiol (E2), anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), and Progesterone. Together, these hormones
help paint a clear picture of ovarian reserve and overall reproductive function. Most of these labs are checked on day 3 of your menstrual cycle, and that timing isn’t random. Day 3 of your cycle is when many of these hormones are at their lowest, or most baseline, levels. Testing consistently on this day allows us to compare apples to apples each month. Without that consistency, hormone levels can jump all over the chart, making us compare apples to oranges

The “normal” reference ranges you see on lab reports aren’t always the same as optimal ranges for
fertility. Those reference ranges are designed to catch diseases or major deficiencies -not to tell us
whether your body is operating at peak reproductive potential. So yes, you can fall within the “normal” range and still have room for improvement when it comes to fertility.
In short: the right hormones, the right timing, and the right interpretation make all the difference when it comes to understanding your fertility.
Why can Standard labs miss fertility root causes?
As mentioned earlier, the cornerstone hormones assessed in routine fertility testing include
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estradiol (E2), anti-Müllerian
hormone (AMH), and Progesterone. These labs are undeniably important and offer valuable insight into reproductive function. But fertility is far more nuanced than a handful of numbers on a lab report- and there are critical factors these values simply can’t capture.
Blood sugar regulation plays a foundational role in fertility. When blood sugar is poorly controlled,
insulin levels can remain chronically elevated, disrupting hormonal balance. High insulin has been shown to impair egg maturation in women and reduce both sperm count and quality in men. In other words, stable blood sugar isn’t just about energy- it’s about creating the right hormonal environment for conception.
Another major, yet often overlooked, factor is chronic inflammation. Persistent inflammation interferes with hormone signaling, which can lead to irregular ovulation and compromised egg quality. Over time, it may even contribute to structural issues such as uterine scar tissue resulting from chronic pelvic inflammation. For men, chronic inflammation creates a hostile environment for sperm, increasing oxidative stress and impairing healthy sperm development.
Nutrient status is equally essential. Both undernutrition and overnutrition can negatively impact fertility. Undernutrition- often associated with calorie restriction and vitamin deficiencies- is typically more commonly recognized. However, overnutrition- frequently linked to obesity- can coexist with significant micronutrient deficiencies as well. Evaluating and correcting nutrient imbalances is critical not only for conception but also for supporting a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Then there’s gut health, a keystone in hormone balance and nutrient absorption. The gut is far more than just the stomach- it’s an intricate system extending from the mouth to the anus, housing trillions of beneficial bacteria. These microbes play a vital role in extracting, absorbing, and even synthesizing key nutrients. When the gut microbiome is out of balance, nutrient deficiencies and poor digestion often follow. Even more importantly, the gut actively interacts with sex hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and estradiol. When gut function is compromised, hormone imbalances- and fertility challenges- often follow.
By now, a clear theme may be emerging: fertility is deeply interconnected with nearly every aspect of our physiology. This is especially true when it comes to stress. Stress isn’t just an uncomfortable mental state-it triggers real, measurable physiological changes. Chronic stress activates the release of “fight or flight” hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These can disrupt our overall hormonal balance and negatively affect fertility. Stress can also impair gut health and increase unhealthful coping behaviors such as overeating, excessive alcohol consumption, or smoking-all of which further hinder reproductive health.
To make a long story short, optimizing fertility requires looking beyond hormone labs alone. It means supporting the body as a whole. Balancing blood sugar, calming inflammation, replenishing nutrient stores, healing the gut, and managing stress- so our sex hormones can have the space to do what they need to do.
Can you ovulate and still have hormone dysfunction?

While ovulation is a crucial milestone for fertility, it’s only one piece of a much larger hormonal puzzle. A healthy pregnancy depends not just on releasing an egg, but on creating the ideal environment for that egg to implant and thrive. One of the most critical factors here is the uterine lining. For an embryo to successfully implant, the uterine wall must be thick, nourished, and stable. The hormone responsible for maintaining this environment is progesterone. If progesterone isn’t operating in sufficient amounts, the uterine lining will not be thick enough to sustain a successful implantation.
Timing matters just as much as hormone levels themselves. A well-orchestrated menstrual cycle requires precise communication between hormones. It is critical that the luteal phase, the phase of the menstrual cycle after ovulation, is at least 10 days long. Any time shorter than this is not enough time for progesterone to thicken the uterine wall to sufficient amounts.
Conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) illustrate this clearly. Some women with PCOS do ovulate regularly, yet continue to experience hormonal imbalance with elevated testosterone levels. Symptoms like acne, excess hair growth, and weight gain can persist despite ovulation, signaling that the underlying hormonal landscape is still out of balance.
The same holds true for thyroid disorders. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt
menstrual cycles and make conception more challenging. And yet, regular ovulation can still occur in both conditions. Once again, ovulation alone doesn’t guarantee optimal fertility.
So in short, Yes- it’s absolutely possible to ovulate and still have hormonal imbalances.
What tests look deeper than standard OB labs?
To gain meaningful insight into fertility, we need to look beyond a single lab panel and take a more
comprehensive, whole-body approach. Utilizing a range of advanced and functional laboratory tests allows us to better understand what’s happening at the microscopic level.
These assessments may include functional blood work, gut testing, mineral analysis, and hormone
metabolism testing. Each test adds another layer of clarity which can help to reveal hidden imbalances that standard testing often misses.
What should I focus on if my labs are “normal”, but I’m not pregnant?
Sometimes all the tests come back “normal”, yet the outcome you’re hoping for still doesn’t happen. If you’ve been there, you know how deeply frustrating- and confusing- that can feel.
When this happens, the next step is often to return to the foundations of health. Supporting fertility starts with making sure your body has enough fuel to run a full, healthy menstrual cycle. That means eating enough- especially the nutrients your hormones rely on to function and communicate effectively.
Nutrition plays a powerful role here. Focusing on gut-supportive foods like fiber-rich beans, whole
grains, and produce. Alongside probiotics like fermented foods can help to nourish the beneficial bacteria within our GI tract. At the same time, reducing artificial sugars supports blood sugar balance and helps to prevent the overgrowth of less-than-healful gut microbes.

Stress management is another key piece of the puzzle. Finding healthy ways to cope during stressful seasons allows your body to spend less time stuck in “fight or flight” mode and more time in a calm, hormonally optimized state. Fertility thrives in an environment of safety and balance.
Finally, this is not a journey meant to be navigated alone. Working with a practitioner who looks at the entire picture, not just a single lab value or isolated symptom, makes all the difference. Fertility is complex, and having someone who understands how all the pieces connect is often the missing link.
Want to learn more?
If you like what you read here, want to know more, but don’t have the time to sit down and read through all our blogs, check out our free private podcast where we break down fertility root causes in more detail. Perfect for those who want to learn more about their hormones and bodies all while still keeping up their busy schedule.
Sources
https://www.stonybrookmedicine.edu/islandfertility/news/sugar
https://rep.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/rep/169/4/REP-24-0197.xml
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10097215/
https://azgyn.com/blog/fertility-gut-health

Written by: Lauren Chamberlain
Edited and Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
Your menstrual cycle isn’t just about fertility—it’s a vital sign of your overall health. A healthy cycle is often an indicator of wellness, while irregularities can be a red flag for potential health issues. Just like your heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate, your cycle provides valuable insights into your body’s well-being. Understanding and tracking it can help you detect potential health problems early and take proactive steps toward better health. Whether you’re looking to optimize your health or manage a condition, your menstrual cycle is a powerful tool for self-awareness. Let’s dive into why your menstrual cycle is the ultimate monthly report card for your body.
Why Your Menstrual Cycle Matters
Ovulation is more than just a reproductive function—it’s a key indicator of your overall health. A regular menstrual cycle means your body is producing hormones in a balanced way, supporting everything from bone density to cardiovascular health. When your cycle is off, it might be your body’s way of signaling an underlying issue like hormonal imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, or even chronic conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders.
The Menstrual Cycle as a Vital Sign
Medical professionals now recognize the menstrual cycle as the “fifth vital sign” because it reflects overall physiological health. A healthy cycle indicates that your hormones are functioning properly, while irregularities could signal potential concerns such as:
- Hormonal imbalances – Irregular periods can be a sign of PCOS, thyroid dysfunction, or estrogen dominance.
- Nutritional deficiencies – A lack of key nutrients like iron, zinc, and vitamin D can affect your cycle’s regularity and flow.
- Stress and lifestyle factors – High stress, poor sleep, or over-exercising can impact ovulation and menstrual health.
The Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
Understanding the four phases of the menstrual cycle can help you align your lifestyle, nutrition, and self-care routines with your body’s natural rhythm.
- Menstrual Phase (1-6 days)
- This phase begins with the shedding of the uterine lining.
- Energy levels may be low, and the body benefits from rest and nutrient-dense foods.
- Follicular Phase (7-21 days)
- The body starts preparing for ovulation by increasing estrogen production.
- This is an optimal time for creativity, social activities, and higher-intensity workouts.
- Ovulatory Phase (1 day)
- The body releases an egg, and estrogen peaks.
- Many women experience increased energy, confidence, and libido during this time.
- Luteal Phase (10-16 days)
- Progesterone rises, preparing the body for a potential pregnancy.
- PMS symptoms may appear, and the body may crave more rest and nourishing foods.
Aligning your activities with these phases can help you optimize performance, reduce stress, and support hormonal balance. Learn more about eating for your cycle here.
What a Healthy Menstrual Cycle Looks Like
A normal menstrual cycle varies from person to person, but generally:
- Cycle length: 21–35 days (consistently within an 8-day range)
- Menstruation duration: 3–7 days with a blood loss of about 25–80 mL
- Ovulation: Occurs between days 10–23, followed by a luteal phase of 12–14 days
- Cervical mucus changes: 2–7 days of cervical mucus with at least one day of peak mucus before ovulation
If your cycle frequently falls outside these parameters, it might be time to investigate further.
What Your Menstrual Cycle Can Reveal About Your Health
Your menstrual cycle is an important indicator of your overall health, and any changes or irregularities can signal underlying issues. Here are some signs to watch for:
- No cycle: This could indicate anovulation, amenorrhea, stress or trauma, or possibly PCOS.
- Skipped cycles: Anovulation, stress or trauma, or potentially PCOS.
- Cycles longer than 35 days: Anovulation or PCOS.
- Cycles shorter than 21 days: May point to a luteal phase defect (and see “Luteal Phase shorter than 10 days”).
- Luteal phase shorter than 10 days: Low progesterone due to inadequate follicle or corpus luteum development, which may be linked to egg quality issues, inflammation, thyroid dysfunction, insulin metabolism problems, or nutrient deficiencies (especially magnesium, B vitamins, Vitamin D, iodine, zinc, selenium).
- Heavy flow: This can indicate estrogen dominance, often accompanied by painful cramps, tender breasts, headaches, fluid retention, and mood swings.
- Light flow/Dark or brown color: This could suggest inadequate corpus luteum development or uterine lining thickening, with low estrogen, FSH, or LH levels.
- Menstrual fluid odor: A possible sign of infection or dysbiosis.
- Cramping: Often associated with estrogen dominance.
- Bleeding outside of menstruation: Spotting in the luteal phase could indicate low progesterone production, often due to issues with follicular or corpus luteum development.
- Vaginal discharge/cervical mucus changes: Typically, the pattern will progress from dry → sticky → creamy → egg white → sticky → dry.
If any of these signs are present, it may be time to seek medical advice and investigate further.
Learn more about how optimizing gut health can help manage PCOS here: Understanding PCOS and Gut Health
How Hormones Influence Your Cycle
Two primary hormones drive the menstrual cycle: estrogen and progesterone.
- Estrogen helps build up the uterine lining and triggers the release of an egg during ovulation.
- Progesterone stabilizes the uterine lining, supports pregnancy, and helps balance estrogen’s effects.
When these hormones are out of balance, it can lead to irregular periods, mood swings, fatigue, and other symptoms. Proper ovulation is essential not just for fertility but for long-term health, as it helps protect against conditions like osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and even certain cancers.
Natural Ways to Balance Female Sex Hormones
Balancing hormones naturally can improve menstrual health and overall well-being. Here are key strategies to support hormone balance:
- Nutrient-Dense Diet – Prioritize whole foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and essential vitamins. Foods like leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids help regulate estrogen levels.
- Gut Health Support – A healthy gut microbiome plays a crucial role in hormone metabolism. Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can aid digestion and hormone balance.
- Reducing Toxins – Environmental toxins found in the 4 P’s (plastics, pesticides, pollution and personal care products) can act as endocrine disruptors. Switching to natural alternatives can help minimize exposure to hormone-disrupting chemicals.
- Stress Management – Chronic stress increases cortisol levels, which can disrupt estrogen and progesterone balance. Practices like meditation, deep breathing, and regular movement can help lower stress levels.
- Common causes of stress:
- Chronic stressors → oxidative stress, inflammation, immune dysfunction, thyroid suppression (“rest and repair”)
- Common causes of stress:
- Sleep Optimization – Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night, as inadequate rest can negatively impact hormone regulation.
- Sleep signs that indicate something is “off”:
- Light sleeping/lack of deep sleep → low progesterone
- Waking frequently to urinate → sign of chronic stress
- Waking between 1-3am, night sweats → liver detoxification
- Sleep signs that indicate something is “off”:
Tracking Your Cycle: A Powerful Health Tool
Charting your cycle helps you understand your body’s unique rhythm and detect early signs of imbalance. Fertility awareness methods (FAM) focus on tracking:
- Basal body temperature (BBT) – A rise in temperature indicates ovulation has occurred.
- Cervical mucus patterns – Clear, stretchy mucus signals peak fertility.
- Cervical position – Changes throughout the cycle, helping identify fertility windows.
Tracking these signs can give you a clearer picture of your health, help you time conception (or avoid pregnancy naturally), and even provide clues about underlying health issues.
Lifestyle and Nutrition for a Healthy Cycle
Supporting your menstrual health involves more than just tracking—it’s about optimizing your lifestyle:
- Eat nutrient-dense foods: Include healthy fats, iron-rich foods, and plenty of fiber.
- Manage stress: High cortisol levels can disrupt ovulation.
- Get enough sleep: Poor sleep affects hormone production.
- Exercise wisely: Overtraining can negatively impact your cycle, while moderate movement supports hormone balance.
The Pill and Menstrual Health
Hormonal contraceptives suppress ovulation, meaning they override your body’s natural cycle. While effective for pregnancy prevention, long-term use can deplete essential nutrients like folate, vitamin B6, and zinc. Research also shows that hormonal contraceptives can impact cervical health, making women up to 85% less likely to clear HPV infections, which increases the risk of cervical cancer. Additionally, long-term pill use has been linked to folate deficiency, affecting cell repair and increasing the chances of abnormal cervical changes. Nutritional support, including adequate folate, vitamin A, and B vitamins, may help mitigate some of these effects. Understanding these potential impacts can help individuals make informed decisions about their contraceptive choices.
Learn more about the steps to take before getting off hormonal birth control here.
Take Charge of Your Cycle
Your menstrual cycle is a powerful health indicator that deserves attention. By tracking and understanding your cycle, you gain insights into your body’s needs, allowing you to make informed decisions about your health. If you notice irregularities, don’t ignore them—your cycle is your body’s way of communicating with you.
Want to start tracking? Use a simple journal, an app, or work with a fertility nutritionist to get a deeper understanding of your unique cycle. Your period isn’t just a monthly inconvenience—it’s a crucial barometer of your health!

Sources
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7643763
https://drbrighten.com/stopping-birth-control-side-effects

Written by: Lauren Chamberlain
Edited and Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
Hormonal contraceptives, including birth control pills, patches, injections, and intrauterine devices (IUDs), have transformed reproductive health, offering women reliable family planning options. However, many individuals experience symptoms after discontinuing hormonal contraception, a phenomenon sometimes referred to as post-birth control syndrome (PBCS). These symptoms can range from irregular cycles and acne to mood swings and digestive issues. Understanding the impact of hormonal contraceptives on the body and implementing strategies to support recovery can help ease this transition.
Understanding the Effects of Hormonal Contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives work by suppressing ovulation, altering cervical mucus, and changing the uterine lining to prevent pregnancy. While effective, these changes influence several body systems, including the endocrine, digestive, and immune systems. Long-term use can disrupt the body’s natural hormone production, leading to potential withdrawal effects when stopping contraception.
A recent study found that hormonal contraceptives impact the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which regulates stress response and hormone production. This may explain why some women experience mood disturbances and fatigue after discontinuation. Additionally, research suggests that birth control pills may alter gut microbiota composition, contributing to inflammation and digestive issues post-contraception.
The Role of the HPA Axis
The HPA axis plays a crucial role in regulating cortisol, a stress hormone that influences metabolism, immune function, and mood. Studies have shown that long-term contraceptive use can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to post-pill anxiety, fatigue, and even adrenal dysfunction. As the body readjusts, individuals may experience heightened stress sensitivity and emotional imbalances.
Additionally, research suggests that chronic hormonal suppression can contribute to reduced ovarian hormone production post-contraception, leading to symptoms like irregular cycles, low libido, and difficulty ovulating.
Common Symptoms After Stopping Hormonal Contraceptives
Post-birth control syndrome encompasses a variety of symptoms that may arise within weeks or months after stopping contraception.
Common symptoms include:
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles
- Acne and skin changes
- Hair loss or thinning
- Digestive disturbances, including bloating and constipation
- Fatigue and mood swings
- Low libido
- Headaches and joint pain
These symptoms occur as the body attempts to restore natural hormone balance. For some, this transition is seamless, while for others, it may take several months to regulate.
Life After Birth Control: What to Expect
The transition off hormonal contraceptives varies for each individual. Some experience a smooth adjustment, while others face lingering hormonal imbalances.
- Menstrual Cycle Irregularities: It may take several months for cycles to regulate. If cycles remain absent or irregular for more than six months, professional evaluation is recommended. Ovulatory dysfunction is common post-contraception, particularly after long-term use of hormonal birth control. Tracking basal body temperature (BBT) and cervical mucus can provide insight into ovulation status and cycle health
- Acne and Skin Changes: Hormonal shifts can temporarily worsen acne. Supporting detox pathways, reducing dairy and sugar intake, and using non-comedogenic skincare products can help. Elevated androgens post-pill can contribute to excess sebum production, leading to breakouts. Incorporating zinc, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants may promote clearer skin.
- Mood and Energy Levels: Some experience heightened anxiety or depression post-contraception. Prioritizing gut health, sleep, and stress reduction can ease this transition. The gut-brain axis plays a key role in mood regulation, making probiotics and a fiber-rich diet beneficial for mental well-being.
- Fertility Awareness: Some individuals regain fertility immediately, while others need time for ovulation to resume. Those trying to conceive may benefit from monitoring ovulation signs. If fertility does not return within six months, an evaluation for conditions like post-pill PCOS or hypothalamic amenorrhea may be necessary.
- Weight Fluctuations: Water retention and metabolism changes can impact weight. Focusing on whole foods, movement, and hydration supports a stable transition. Hormonal contraceptives can affect insulin sensitivity, and some women notice changes in blood sugar regulation post-pill. Balancing macronutrients and avoiding refined sugars can help stabilize weight.
- Increased Libido: Many report improved libido and natural cycle awareness after stopping hormonal contraceptives due to restored testosterone and estrogen levels.
Adjusting to life after birth control involves patience and self-care. Tracking symptoms, optimizing nutrition, and seeking support when needed can help individuals regain hormonal balance and overall well-being.
Supporting Hormonal Balance Post-Contraception
While post-birth control symptoms can be challenging, several strategies can support the body’s recovery and restore hormonal balance.
1. Nourishing Your Body with Key Nutrients
Hormonal contraceptives can deplete essential nutrients, including B vitamins, magnesium, zinc, and vitamin C. It has been found essential to replenish these nutrients to support metabolism, immune function, and hormone production.
Incorporating the following nutrient-dense foods can be beneficial:
- B Vitamins: Found in leafy greens, eggs, and whole grains
- Magnesium: Present in nuts, seeds, and dark chocolate
- Zinc: Found in oysters, beef, and lentils
- Vitamin C: Abundant in citrus fruits, bell peppers, and strawberries
Supplementing with a high-quality multivitamin or targeted nutrients may also help restore levels more efficiently.
2. Prioritizing Liver Health
The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing hormones and detoxifying excess estrogen. Supporting liver function can aid hormone clearance and balance. Key strategies include:
- Drinking plenty of water to support detoxification
- Eating cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, kale) to promote estrogen metabolism
- Avoiding alcohol and excessive caffeine, which can burden the liver
- Taking liver-supporting supplements such as milk thistle and dandelion root
3. Balancing Blood Sugar Levels
Insulin resistance and blood sugar imbalances can contribute to hormonal dysregulation post-contraception. Stabilizing blood sugar helps maintain steady energy levels and prevents cortisol spikes, which can further disrupt hormones. To support blood sugar balance:
- Consume protein and healthy fats with every meal
- Avoid refined carbohydrates and excessive sugar
- Incorporate fiber-rich foods, such as legumes, nuts, and vegetables
- Engage in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity
4. Restoring Gut Health
The gut microbiome influences hormone metabolism and immune function. Studies suggest that hormonal contraceptives may alter gut bacteria, leading to digestive issues and inflammation. Supporting gut health can enhance nutrient absorption and hormone clearance:
- Probiotic-Rich Foods: Yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kefir can replenish beneficial bacteria
- Prebiotic Fiber: Found in onions, garlic, bananas, and asparagus to support microbial diversity
- Bone Broth and Collagen: Aid in gut lining repair
- Limiting Processed Foods: Reducing inflammatory foods can alleviate digestive distress
- Fermented Foods and Fiber: Incorporating fermented foods like miso and fiber-rich foods such as flaxseeds can further support microbiome diversity
According to research, discontinuing birth control can cause shifts in the gut microbiome that affect estrogen metabolism and immune responses. A focus on gut healing post-contraception may accelerate hormonal recovery and reduce systemic inflammation.
5. Managing Stress and Prioritizing Sleep
Chronic stress and inadequate sleep can exacerbate hormonal imbalances. Since the HPA axis is affected by hormonal contraceptives, post-contraceptive recovery requires stress management techniques. Effective strategies include:
- Practicing mindfulness or meditation
- Engaging in gentle movement, such as yoga or walking
- Setting a consistent sleep schedule and avoiding blue light before bedtime
- Taking adaptogenic herbs, like ashwagandha or rhodiola, to support adrenal function
6. Tracking Your Menstrual Cycle
Monitoring menstrual patterns post-contraception provides insight into hormonal recovery. Using a cycle-tracking app or basal body temperature charting can help identify ovulation and cycle health.
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT): Measuring BBT each morning helps detect ovulation. A sustained temperature rise typically indicates ovulation has occurred.
- Cervical Mucus Changes: Observing cervical mucus consistency can signal fertility. Egg-white-like mucus usually indicates peak fertility.
- Cycle Length and Symptoms: Keeping track of cycle length, PMS symptoms, and flow characteristics provides valuable data about hormonal balance.
- Ovulation Predictor Kits: These kits measure luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, indicating the fertile window.
If menstruation does not return within three to six months, consulting a healthcare provider may be necessary to rule out underlying conditions like hypothalamic amenorrhea or PCOS.
7. Seeking Professional Support
If symptoms persist or become severe, working with a healthcare provider, such as a functional medicine/nutrition practitioner, can be beneficial. They can assess hormone levels, address underlying imbalances, and provide personalized recommendations for recovery.
Here are some issues you may need to address:
Prolonged Absence of Periods: If your period hasn’t returned after six months.
Persistent Acne or Severe Hair Loss: Significant changes in skin or hair health could indicate hormonal imbalances that require attention.
Excessive Mood Changes or Fatigue: If symptoms like mood swings, anxiety, or extreme tiredness persist.
Chronic Digestive Issues: Ongoing digestive disturbances such as bloating or constipation.
Conclusion
Recovering from hormonal contraceptives is a unique process for every individual. While some may transition smoothly, others may experience a range of symptoms as their body readjusts. By focusing on nutrient replenishment, liver and gut health, blood sugar balance, stress management, and cycle tracking, individuals can support their hormonal recovery more effectively. If challenges persist, seeking professional guidance can ensure a smoother transition and optimal long-term health.

Sources:
https://drbrighten.com/post-birth-control-syndrome
https://drbrighten.com/stopping-birth-control-side-effects
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0889159123003331?via%3Dihub
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6055351
https://drbrighten.com/the-contraception-guide/ https://www.kernodle.com/obgyn_blog/side-effects-of-stopping-the-pill-after-prolonged-use/

Hormonal fluctuations impact your energy levels, mood, and overall well-being throughout your menstrual cycle. By aligning your diet with these hormonal changes—a practice known as cycle syncing—you can optimize your energy, reduce PMS, and improve overall cycle health. This guide will help you understand the phases of the menstrual cycle and how nutrition can play a vital role in supporting hormonal balance.
Let’s begin by breaking down the menstrual cycle and understanding how your hormones fluctuate during each phase!
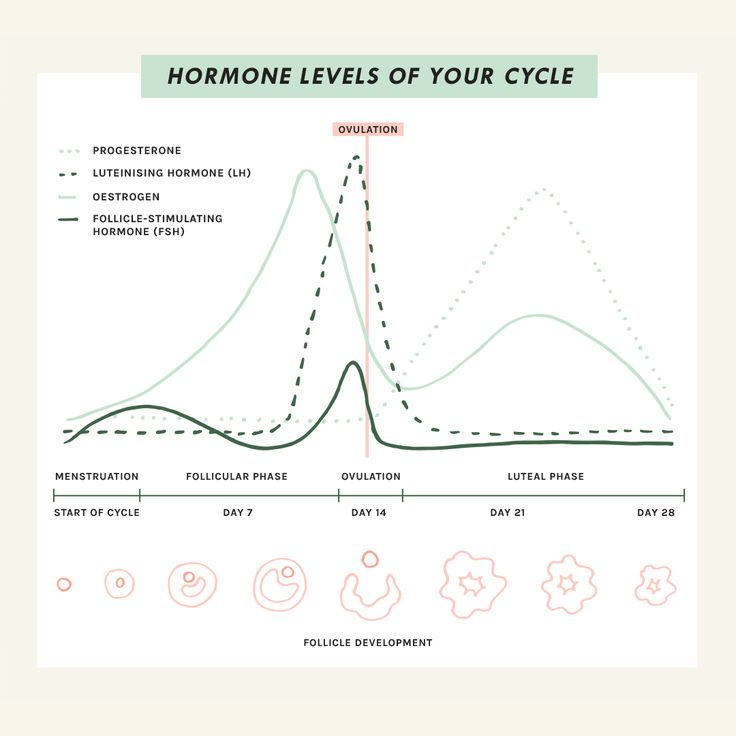
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle has four distinct phases: the menstrual phase, follicular phase, ovulatory phase, and luteal phase. Each phase brings unique hormonal shifts that influence your body’s nutritional needs and energy requirements.
1. Menstrual Phase
(Day 1-6)
- This phase begins with menstruation. Hormone levels of estrogen and progesterone are at their lowest.
- Symptoms may include fatigue, cramping, and low energy levels.
2. Follicular Phase
(Day 7-13)
- Estrogen levels begin to rise, stimulating the growth of follicles in the ovaries and increasing energy.
- This is often when women feel their best, with improved mood and vitality.
3. Ovulatory Phase
(Day 14-16)
- Estrogen peaks, and luteinizing hormone (LH) surges to trigger ovulation.
- Energy levels and libido are typically at their highest.
4. Luteal Phase
(Day 17-28)
- Progesterone rises to prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy, while estrogen levels dip. If fertilization does not occur, both hormones decrease, leading to PMS symptoms.
- Symptoms may include bloating, fatigue, and cravings.
Understanding these phases allows you to tailor your diet and lifestyle to support your body’s natural rhythms.
How Nutrition Supports Each Phase
Menstrual Phase: Focus on Iron and Hydration
During the menstrual phase, many individuals experience common symptoms such as cramping, fatigue, and irritability. While it may be tempting to indulge in comfort foods like sweets, pizza, and chips, these choices can disrupt hormonal balance and deplete important nutrients needed to support your body during this phase. Instead, focusing on nutrient-dense foods that support iron levels, reduce inflammation, and promote hydration. These all can help alleviate symptoms and maintain overall well-being.
- Foods to prioritize: One of the most important considerations during the menstrual phase is replenishing iron lost through bleeding. Incorporating iron-rich foods like lean red meat, spinach, lentils, beans, and beets can help restore iron levels. To optimize iron absorption, pair these foods with sources of vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, berries, broccoli, and bell peppers. Vitamin C enhances the bioavailability of iron, ensuring that your body can make the most of the iron you consume. Vitamin K is another key nutrient that can help reduce heavy bleeding. Leafy greens, blueberries, cheese, and eggs are excellent sources of vitamin K, which supports blood clotting and helps regulate menstrual flow. Omega-3 fatty acids are also beneficial during this phase, as they have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce cramping. Incorporate omega-3-rich foods like salmon, flaxseed, and tree nuts to support your body’s natural processes and ease discomfort.
- Hydration: This is particularly important during the menstrual phase, as it can help reduce bloating and prevent dehydration, which can exacerbate fatigue. Herbal teas such as ginger or chamomile are soothing options that can help alleviate cramps, reduce bloating, and promote relaxation.
- Avoid: Avoid high-sodium foods during your period, as they can exacerbate bloating and lead to water retention. Instead, focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins and minerals, as well as plenty of hydration, to help you feel your best during this time.
Follicular Phase: Build Energy with Nutrient-Dense Foods
As estrogen rises, focus on foods that provide sustained energy and promote gut health. Maintaining gut health is deeply connected to hormonal balance, playing a crucial role in maintaining a healthy menstrual cycle. A well-functioning gut microbiome, particularly the estrobolome, aids in estrogen metabolism, preventing hormonal imbalances that could lead to PMS or heavy periods. Incorporating fiber-rich foods, probiotics, and fermented options can support gut health. These choices not only benefit your cycle but also improve digestion, energy, and mood, contributing to overall well-being!
- Foods to prioritize: Incorporate fiber-rich foods such as quinoa, oats, fresh vegetables, and seeds, which aid in digestion and promote stable blood sugar levels. Fermented foods like kimchi, sauerkraut, and yogurt are excellent choices as they provide beneficial probiotics that support gut health. Omega-3-rich foods like walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are also important as they have anti-inflammatory properties that can help balance hormones during this phase.
- Key nutrients: Prioritize B vitamins which support energy production and help combat fatigue, and omega-3 fatty acids, which promote overall hormonal balance and reduce inflammation.
- Avoid: It’s crucial to avoid refined sugars, as they can cause blood sugar spikes that disrupt energy levels and hormone regulation.
Ovulatory Phase: Support Detoxification
During the ovulatory phase, estrogen levels peak, and the body enters a high-energy phase, making it important to support both hormonal balance and overall vitality. Since the liver plays a key role in breaking down and detoxifying excess estrogen, it’s crucial to include foods that promote liver function and aid in estrogen metabolism.
- Foods to prioritize: Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale, Brussels sprouts) are excellent choices, as they contain compounds such as sulforaphane that help the liver process estrogen more efficiently. Berries help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which can support overall hormonal health. Flaxseeds are also beneficial as they contain lignans that can bind to excess estrogen, helping to regulate levels in the body.
- Key nutrients: Zinc is a key nutrient for supporting ovulation, making it important to include zinc-rich foods like pumpkin seeds, shellfish, and legumes.
- Avoid: It’s important to avoid alcohol and excessive caffeine during this phase. Both substances can burden the liver, slowing down its detoxification processes and potentially causing hormonal imbalances. Drinking plenty of water and consuming foods rich in fiber will further support liver health and overall detoxification.
Luteal Phase: Balance Blood Sugar and Reduce Inflammation
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly increased progesterone, can contribute to common symptoms such as cravings, mood swings, fatigue, and bloating during this phase of your cycle. The key to managing these symptoms is balancing blood sugar levels, reducing inflammation, and nourishing your body with foods that support hormonal balance.
- Foods to prioritize: One effective strategy is to focus on complex carbohydrates, which provide steady energy and help stabilize blood sugar. Foods such as sweet potatoes, whole grains, and high-fiber vegetables, including cruciferous vegetables, can help curb hunger and keep blood sugar levels steady.
- Magnesium-rich foods are also important during this phase, as magnesium has been shown to alleviate PMS symptoms, including mood swings, irritability, and cramps. Magnesium-rich options like dark chocolate, almonds, and pumpkin seeds are excellent choices.
- Anti-inflammatory spices like turmeric and ginger can also be beneficial, as they help reduce inflammation, soothe cramps, and support overall well-being. These spices have natural properties that may help ease discomfort associated with PMS, including bloating and muscle tension.
- Key nutrients: Vitamin B6 is another important nutrient during the luteal phase, as it helps regulate mood and reduce irritability, which can be exacerbated by hormonal changes. Foods such as bananas, poultry, and potatoes are rich in vitamin B6 and can be incorporated into your meals to support emotional well-being during this time.
Avoid: If you’re craving something sweet or salty, opt for healthier alternatives such as dark chocolate, fruit, nuts, and seeds. These foods can satisfy cravings without causing the blood sugar spikes and crashes that processed snacks can induce. Additionally, staying hydrated is crucial during the luteal phase, as water helps reduce bloating, brain fog, and PMS-related discomfort.

Seed Cycling for Hormonal Balance
Seed cycling is a holistic dietary practice that involves eating specific seeds at different phases of the menstrual cycle to support hormone balance. The idea behind seed cycling is that different phases of the menstrual cycle require different hormone support, and specific seeds contain the nutrients necessary for this. This method is particularly beneficial for regulating irregular cycles and managing PMS symptoms.
Follicular Phase (Day 1-14)
During the follicular phase, estrogen is the dominant hormone. The goal is to support estrogen production and metabolism. The recommended seeds for this phase are raw, freshly ground flaxseeds and pumpkin seeds. Flaxseeds are rich in lignans, which have weak estrogenic properties and support elimination. Pumpkin seeds, on the other hand, provide zinc, an essential mineral for testosterone production and healthy hormone levels.
- Seeds: Flaxseeds and pumpkin seeds
- Benefits: Flaxseeds contain lignans that help balance estrogen levels. Pumpkin seeds provide zinc to support progesterone production later in the cycle.
Luteal Phase (Day 15-28)
After ovulation, progesterone becomes the dominant hormone. To support this, the recommended seeds are raw, freshly ground sunflower seeds and sesame seeds. Sunflower seeds are rich in vitamin E, which helps reduce PMS symptoms and supports estrogen detoxification. Sesame seeds are high in lignans and fatty acids, which help balance progesterone and reduce inflammation.
- Seeds: Sesame seeds and sunflower seeds
- Benefits: Sesame seeds contain lignans to modulate estrogen, and sunflower seeds provide selenium to support liver detoxification.
Can Seed Cycling Be Used Mid-Cycle? Yes, seed cycling can be started at any point in the cycle, depending on where you are in your menstrual phase. If you’re tracking your cycle closely, you can adjust your seed rotation accordingly to match your ovulation timing.
Seed Cycling’s Nutritional Basis The seeds used in seed cycling are rich in essential nutrients that support hormone production, including omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, magnesium, and antioxidants. These nutrients help optimize hormone balance by supporting estrogen and progesterone levels, promoting healthy testosterone levels, and reducing inflammation, which can lead to hormonal imbalances.
Seed Cycling Science Although the term “seed cycling” itself is not widely researched in scientific literature, the individual nutrients in the seeds have been extensively studied for their health benefits. For example, lignans in flaxseeds have been linked to improved estrogen and progesterone balance, and the zinc in pumpkin seeds supports testosterone production. Research has also shown that these seeds can benefit cardiovascular health, gut health, and even cancer prevention.
Does Seed Cycling Really Work? While more research is needed to fully validate seed cycling as a hormone-balancing practice, many women have reported positive changes in their menstrual health, including improved hormone balance, reduced PMS symptoms, and better skin health. The key is consistency and combining seed cycling with other healthy lifestyle practices, such as a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management.
Additional Benefits of Seed Cycling
- For Menopause: Seed cycling can be continued post-menopause by aligning the seed rotation with the moon cycle. This can help manage symptoms like hot flashes and mood swings.
- For PCOS: Seed cycling can help balance testosterone and estrogen levels in women with PCOS, potentially alleviating symptoms like acne and hirsutism.
- For Acne: Seed cycling may help improve acne by balancing hormones, particularly when coming off hormonal birth control, which can trigger an androgen rebound and worsen acne.
- For Painful Periods: Seed cycling may help reduce period pain by balancing estrogen and progesterone levels and supporting inflammation reduction.
How to Start Seed Cycling To begin seed cycling, it’s recommended to consume 1-2 tablespoons of freshly ground, raw seeds daily. You can add them to smoothies, salads, oatmeal, or even make homemade seed-based snacks! Consistency is key, and it’s best to give the practice at least one full cycle (about a month) to assess its effectiveness.
Exercise and Cycle Syncing
Adjusting your exercise routine to match your cycle phases can optimize performance and reduce hormonal stress.
- Menstrual Phase: Prioritize rest and gentle movements like yoga or walking.
- During your period, light activities like walking, stretching, or gentle movement can help ease discomfort and match your energy levels, especially if you’re dealing with cramps.
- While it’s natural to feel less active on the first day of your period, exercise can actually relieve cramps, boost energy, and improve your mood! Surprisingly, even in the early follicular phase, you might find you can lift heavier weights or handle more intense workouts. The key is to listen to your body and adjust your activity based on how you feel rather than sticking to rigid rules or expectations.
- Follicular Phase: Increase intensity with strength training and cardio as energy levels rise.
- During this phase of your cycle, rising estrogen and testosterone levels can enhance muscle-building potential, making cardio and strength training feel more effective. By as early as day three of your period, you might notice a boost in energy and exercise stamina as estrogen levels continue to climb!
- Ovulatory Phase: Engage in high-intensity workouts like HIIT or running.
- This typically occurs between the end of week two and the start of week three in your cycle and can leave you feeling more energized. During this time, many women notice they can handle higher levels of physical exertion compared to other phases.
- Luteal Phase: Shift to moderate-intensity exercises like Pilates or swimming to accommodate fatigue.
- After ovulation, some women notice a quick drop in exercise tolerance, while others experience this closer to their period. The week before your period can bring challenges like reduced tolerance, trouble cooling down, and water retention, which may affect workouts. Staying hydrated, focusing on electrolytes, wearing breathable clothing, and exercising in a cool space can help. This is a great time to prioritize recovery with activities like yoga or Pilates.
- Increased hunger is normal due to higher calorie needs, especially carbohydrates, as your body becomes less insulin sensitive. You can honor your cravings or increase your intake by 5–10%, choosing what works best for you!
This cyclical approach helps prevent overtraining and supports hormonal balance.
Lifestyle Tips for Cycle Health
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance. Incorporate mindfulness practices like meditation or journaling.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours per night to support hormone production and recovery.
- Track Your Cycle: Use apps or journals to monitor your symptoms and identify patterns.
Conclusion
Cycle syncing empowers you to take control of your health by aligning nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle with your menstrual cycle! By nourishing your body with the right foods at the right time, you can alleviate symptoms, enhance energy levels, and promote overall well-being. Implementing practices like seed cycling and phase-specific exercise further supports hormonal harmony.
Start small and make gradual changes to experience the benefits of cycle syncing. Your body will thank you for it!
Sources
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10251302
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/search/research-news/17857
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/nutrition-and-exercise-throughout-your-menstrual-cycle
https://drbrighten.com/how-to-exercise-with-your-cycle
https://drbrighten.com/seed-cycling-for-hormone-balance
https://drbrighten.com/seed-cycling-menopausal-hormones
https://drbrighten.com/gut-hormone-connection
Images
Female Cycle https://www.pinterest.com/pin/962222276632847842/

The Preconception Playbook
This free playbook provides specific actionable tips to get started on your fertility journey, as well as what to avoid while you're trying to conceive.
Get the free playbook