Hormone Health
Resources
Style
Planning
View All
If you’ve ever been told “everything looks normal”-yet nothing feels normal at all- you know how deeply frustrating those words can be.
You watch friends, coworkers, even strangers announce pregnancies that seemed to happen effortlessly. Meanwhile, you’re tracking, testing, timing and doing everything under the sun… and still, nothing. It’s exhausting. It’s isolating. It can make you feel like you’re somehow missing something obvious.
You’re not.
So many couples reach this same breaking point after hearing that familiar line, “everything looks fine.” It can feel like the end of the road- like the doctors have checked their boxes and moved on, even though your gut tells you something isn’t adding up. Because if everything were truly fine, this wouldn’t feel so hard.
Hormone testing can be incredibly helpful. It gives us a valuable snapshot of what’s happening beneath the surface, at the microscopic level. But here’s the truth, hormones don’t tell the whole story.
Fertility isn’t controlled by a single switch or dictated by hormones alone. It’s a complex, multi-factorial system influenced by far more than any one lab result can capture. When something feels off, it’s worth looking deeper- because “normal” doesn’t always mean optimal, and it certainly doesn’t mean your experience isn’t valid.
What does “normal” hormone blood work actually mean?
When it comes to fertility, hormones are the behind-the-scenes directors calling the shots. But which hormones actually matter- and when should they be tested? Let’s break it down.
Key players we look at for fertility include follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone
(LH), estradiol (E2), anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), and Progesterone. Together, these hormones
help paint a clear picture of ovarian reserve and overall reproductive function. Most of these labs are checked on day 3 of your menstrual cycle, and that timing isn’t random. Day 3 of your cycle is when many of these hormones are at their lowest, or most baseline, levels. Testing consistently on this day allows us to compare apples to apples each month. Without that consistency, hormone levels can jump all over the chart, making us compare apples to oranges

The “normal” reference ranges you see on lab reports aren’t always the same as optimal ranges for
fertility. Those reference ranges are designed to catch diseases or major deficiencies -not to tell us
whether your body is operating at peak reproductive potential. So yes, you can fall within the “normal” range and still have room for improvement when it comes to fertility.
In short: the right hormones, the right timing, and the right interpretation make all the difference when it comes to understanding your fertility.
Why can Standard labs miss fertility root causes?
As mentioned earlier, the cornerstone hormones assessed in routine fertility testing include
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estradiol (E2), anti-Müllerian
hormone (AMH), and Progesterone. These labs are undeniably important and offer valuable insight into reproductive function. But fertility is far more nuanced than a handful of numbers on a lab report- and there are critical factors these values simply can’t capture.
Blood sugar regulation plays a foundational role in fertility. When blood sugar is poorly controlled,
insulin levels can remain chronically elevated, disrupting hormonal balance. High insulin has been shown to impair egg maturation in women and reduce both sperm count and quality in men. In other words, stable blood sugar isn’t just about energy- it’s about creating the right hormonal environment for conception.
Another major, yet often overlooked, factor is chronic inflammation. Persistent inflammation interferes with hormone signaling, which can lead to irregular ovulation and compromised egg quality. Over time, it may even contribute to structural issues such as uterine scar tissue resulting from chronic pelvic inflammation. For men, chronic inflammation creates a hostile environment for sperm, increasing oxidative stress and impairing healthy sperm development.
Nutrient status is equally essential. Both undernutrition and overnutrition can negatively impact fertility. Undernutrition- often associated with calorie restriction and vitamin deficiencies- is typically more commonly recognized. However, overnutrition- frequently linked to obesity- can coexist with significant micronutrient deficiencies as well. Evaluating and correcting nutrient imbalances is critical not only for conception but also for supporting a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Then there’s gut health, a keystone in hormone balance and nutrient absorption. The gut is far more than just the stomach- it’s an intricate system extending from the mouth to the anus, housing trillions of beneficial bacteria. These microbes play a vital role in extracting, absorbing, and even synthesizing key nutrients. When the gut microbiome is out of balance, nutrient deficiencies and poor digestion often follow. Even more importantly, the gut actively interacts with sex hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and estradiol. When gut function is compromised, hormone imbalances- and fertility challenges- often follow.
By now, a clear theme may be emerging: fertility is deeply interconnected with nearly every aspect of our physiology. This is especially true when it comes to stress. Stress isn’t just an uncomfortable mental state-it triggers real, measurable physiological changes. Chronic stress activates the release of “fight or flight” hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These can disrupt our overall hormonal balance and negatively affect fertility. Stress can also impair gut health and increase unhealthful coping behaviors such as overeating, excessive alcohol consumption, or smoking-all of which further hinder reproductive health.
To make a long story short, optimizing fertility requires looking beyond hormone labs alone. It means supporting the body as a whole. Balancing blood sugar, calming inflammation, replenishing nutrient stores, healing the gut, and managing stress- so our sex hormones can have the space to do what they need to do.
Can you ovulate and still have hormone dysfunction?

While ovulation is a crucial milestone for fertility, it’s only one piece of a much larger hormonal puzzle. A healthy pregnancy depends not just on releasing an egg, but on creating the ideal environment for that egg to implant and thrive. One of the most critical factors here is the uterine lining. For an embryo to successfully implant, the uterine wall must be thick, nourished, and stable. The hormone responsible for maintaining this environment is progesterone. If progesterone isn’t operating in sufficient amounts, the uterine lining will not be thick enough to sustain a successful implantation.
Timing matters just as much as hormone levels themselves. A well-orchestrated menstrual cycle requires precise communication between hormones. It is critical that the luteal phase, the phase of the menstrual cycle after ovulation, is at least 10 days long. Any time shorter than this is not enough time for progesterone to thicken the uterine wall to sufficient amounts.
Conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) illustrate this clearly. Some women with PCOS do ovulate regularly, yet continue to experience hormonal imbalance with elevated testosterone levels. Symptoms like acne, excess hair growth, and weight gain can persist despite ovulation, signaling that the underlying hormonal landscape is still out of balance.
The same holds true for thyroid disorders. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt
menstrual cycles and make conception more challenging. And yet, regular ovulation can still occur in both conditions. Once again, ovulation alone doesn’t guarantee optimal fertility.
So in short, Yes- it’s absolutely possible to ovulate and still have hormonal imbalances.
What tests look deeper than standard OB labs?
To gain meaningful insight into fertility, we need to look beyond a single lab panel and take a more
comprehensive, whole-body approach. Utilizing a range of advanced and functional laboratory tests allows us to better understand what’s happening at the microscopic level.
These assessments may include functional blood work, gut testing, mineral analysis, and hormone
metabolism testing. Each test adds another layer of clarity which can help to reveal hidden imbalances that standard testing often misses.
What should I focus on if my labs are “normal”, but I’m not pregnant?
Sometimes all the tests come back “normal”, yet the outcome you’re hoping for still doesn’t happen. If you’ve been there, you know how deeply frustrating- and confusing- that can feel.
When this happens, the next step is often to return to the foundations of health. Supporting fertility starts with making sure your body has enough fuel to run a full, healthy menstrual cycle. That means eating enough- especially the nutrients your hormones rely on to function and communicate effectively.
Nutrition plays a powerful role here. Focusing on gut-supportive foods like fiber-rich beans, whole
grains, and produce. Alongside probiotics like fermented foods can help to nourish the beneficial bacteria within our GI tract. At the same time, reducing artificial sugars supports blood sugar balance and helps to prevent the overgrowth of less-than-healful gut microbes.

Stress management is another key piece of the puzzle. Finding healthy ways to cope during stressful seasons allows your body to spend less time stuck in “fight or flight” mode and more time in a calm, hormonally optimized state. Fertility thrives in an environment of safety and balance.
Finally, this is not a journey meant to be navigated alone. Working with a practitioner who looks at the entire picture, not just a single lab value or isolated symptom, makes all the difference. Fertility is complex, and having someone who understands how all the pieces connect is often the missing link.
Want to learn more?
If you like what you read here, want to know more, but don’t have the time to sit down and read through all our blogs, check out our free private podcast where we break down fertility root causes in more detail. Perfect for those who want to learn more about their hormones and bodies all while still keeping up their busy schedule.
Sources
https://www.stonybrookmedicine.edu/islandfertility/news/sugar
https://rep.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/rep/169/4/REP-24-0197.xml
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10097215/
https://azgyn.com/blog/fertility-gut-health

Pregnancy is a season when your body simply needs more—more rest, more support, and yes, more nutrients. During this time, demands for key nutrients like folate, iodine, choline, and vitamin D increase significantly. If these needs aren’t met, deficiencies can have long-term effects not only for you, but for your growing baby as well.
Nourishing your body during this incredibly important and transformative time isn’t optional—it’s foundational to supporting a healthy pregnancy.
Is a healthy diet enough?
Even when you’re eating a well-balanced, nutrient-dense diet, it can still be difficult to meet all of your increased nutrient needs during pregnancy through food alone. This is where a high-quality prenatal vitamin becomes an essential part of your pregnancy toolkit.
Let’s break down a few of the most important nutrients to look for—and why they matter.

Folate
Folate (vitamin B9) is a critical micronutrient for fetal brain and spinal cord development. In the very early weeks of pregnancy—often before someone even knows they’re pregnant—the neural tube forms and closes, eventually developing into the brain and spinal cord. This process typically happens within the first 3–4 weeks of pregnancy.
Folate plays a central role in this process by supporting rapid cell growth and division, as well as methylation—a biochemical process that is essential for proper neural tube closure and healthy brain and spinal cord development.
A quick (and gentle!) biochemistry moment—bear with us. Many supplements and fortified foods use folic acid, which is a synthetic form of vitamin B9. Folic acid must be converted in the body to its active form, methylfolate, before it can be fully utilized. Some individuals have a harder time completing this conversion, which can lead to less-than-optimal absorption.
To bypass this conversion step altogether and support optimal absorption, it’s ideal to choose a prenatal that contains methylfolate rather than folic acid.
Current Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) in the U.S. are:
- 400 mcg/day for women of childbearing age who are not pregnant
- 600 mcg/day for pregnant women
Iodine
Iodine is a crucial micronutrient for thyroid health and function. If you want a deeper dive into iodine’s role in fertility, thyroid health, reproductive health, and hormone balance, be sure to check out our earlier blog: Iodine and Women’s Health: What You Need to Know.
When it comes to pregnancy, iodine deserves special attention. It plays a key role in fetal brain and nervous system development, as well as in thyroid hormone production and regulation for both mom and baby.
The current RDAs in the U.S. are:
- 150 mcg/day for women of childbearing age who are not pregnant
- 220 mcg/day for pregnant women
Because iodine intake varies widely based on diet and food sourcing, it’s an especially important nutrient to confirm is included in your prenatal.

Vitamin D and Calcium
Calcium is essential for bone health, and during pregnancy, needs increase to support fetal skeletal development. At the same time, adequate calcium intake helps protect and maintain mom’s own calcium stores.
During breastfeeding, approximately 3–5% of a mother’s calcium stores can be depleted through breast milk production. While these losses haven’t been directly linked to an increased risk of osteoporosis later in life, ensuring adequate calcium intake before, during, and after pregnancy is still incredibly important.
One of the best ways to support calcium absorption? Vitamin D.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a role in fetal immune system development, overall fetal growth, and—importantly—calcium absorption.
Without getting too deep into the weeds, the active form of vitamin D (calcitriol) helps activate receptors in the intestines that increase the production of calcium-transporting proteins. These proteins work together to improve calcium absorption into the bloodstream—essentially helping your body actually use the calcium you’re consuming.
Current RDAs in the U.S.:
- Calcium: 1000–1300 mg/day (pregnant and non-pregnant women)
- Vitamin D: 15 mcg/day (pregnant and non-pregnant women)
Many perinatal practitioners recommend higher levels of vitamin D for optimal lab levels.
So… which prenatal should I choose?
Understanding nutrient needs is one thing—actually choosing a prenatal is another. With so many options on the market, it’s no wonder this step feels overwhelming.
One important thing to know: many prenatals still rely on outdated RDAs that were originally based on research conducted in men’s bodies—not women’s, and certainly not pregnant women’s.
This is where Needed stands out.
Needed recognized this gap and created prenatals that are science-backed and designed with women’s unique needs in mind—especially during preconception, pregnancy, and postpartum, when nutrient demands are higher across the board.
Needed Prenatal Multi provides 5x more nutrition than outdated RDAs, helping better meet the increased nutrient demands of pregnancy.*
How does Needed compare to other prenatals?
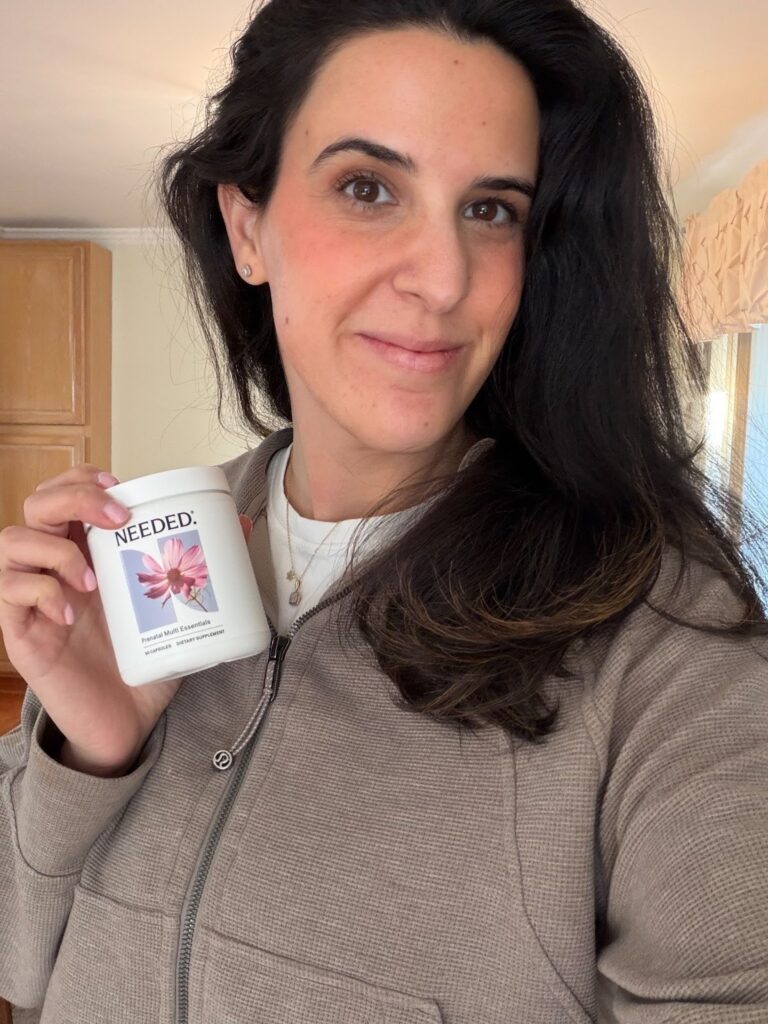

Needed Prenatal Multi Essentials delivers *8x more nutrition than other leading prenatals on the market.
It includes 551 mcg of folate in the methylated form, to support healthy neural tube development and methylation..
And yes—it really is that good.
Needed prenatals are third-party tested, meaning an independent, unbiased organization verifies the safety, quality, and accuracy of all label claims. In short: what’s on the label is exactly what’s in the product.
Needed offers multiple prenatal options: capsules and a vanilla powder, so you can choose what works best for you. I used the vanilla powder during my first pregnancy when I simply couldn’t swallow any pills and it was such a game changer for me personally.
You can easily purchase Needed prenatals directly through their website:
https://thisisneeded.com/products/prenatal-multi-essentials
Looking for More Support?
Navigating prenatal nutrition—and figuring out how to best support both you and your baby—can feel confusing. You don’t have to do this alone.
Using every tool available to you, including personalized nutrition guidance and high-quality supplementation, is one of the simplest ways to support a healthy pregnancy. Our 1:1 coaching services are designed to be that extra layer of support—someone firmly in your corner.
Let’s do this together. Reach out today to begin your journey toward nourishing and supporting your growing life with expert guidance every step of the way.
This post is sponsored by Needed, a brand I genuinely recommend to my patients and personally use.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
*Based on the total daily dosage of nutrients provided compared to leading prenatals as determined by IRI sales data as of December 2025
Sources:
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4933077/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iodine-HealthProfessional/
https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/pregnancy-breastfeeding-and-bone-health

Menopause is often discussed in whispers and framed through negative stereotypes, yet it is one of the most significant and transformative stages of life. Understanding what’s happening in the body—and how to support it through nutrition and lifestyle—can help dismantle stigma and reframe menopause for what it truly is: a period of reflection, strength, and renewed autonomy.
To understand how functional nutrition supports menopause, it helps to briefly revisit how the menstrual cycle works before this transition. While this biology may feel basic, it provides essential context for understanding why symptoms arise and how targeted support can help.

Why Do Hormones Change So Much During Menopause?
Before menopause, the menstrual cycle is regulated by a tightly coordinated hormonal feedback system between the brain and ovaries.
The hypothalamus releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which signals the pituitary gland to secrete luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones stimulate the ovaries to develop follicles, each containing an immature egg (ova).
As follicles mature, they release estrogen along with inhibin A and inhibin B. These hormones create a negative feedback loop, signaling the brain to slow the release of GnRH, LH, and FSH. After ovulation, the follicle becomes the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone to support the uterine lining. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone levels fall and menstruation begins.
This predictable hormonal rhythm is what allows for regular cycles—and it’s this system that gradually shifts as menopause approaches.

What Happens to Hormones During Menopause?
Menopause typically begins around age 45, though timing varies widely and there is no “correct” age. Rather than a single event, menopause is a gradual process defined by the STRAW (Stages of Reproductive Aging Workshop) staging model.
Late Reproductive Stage (Stages −3A and −3B)
Cycles are usually regular, and pregnancy is still possible. However, ovarian reserve declines as fewer eggs remain available.
Early Menopause Transition (Stage −2)
This stage marks the beginning of perimenopause. Hormonal signaling from the brain increases, progesterone production becomes less consistent, and menstrual cycles often become unpredictable.
Late Menopause Transition (Stage −1)
Periods become very irregular, with gaps of 60 days or more between cycles. Hormonal fluctuations intensify, often leading to symptoms such as hot flashes, sleep disruption, mood changes, and weight gain. This phase can last up to three years, though duration varies.
Menopause (Stage 0)
Menopause is defined as the final menstrual period.
Early Postmenopause (Stages 1A and 1B)
These stages begin after 12 consecutive months without a period. Hormones continue to stabilize, but symptoms are often most pronounced during this time. Early postmenopause typically lasts two to six years as the endocrine system adjusts to a new baseline.
How Does Functional Nutrition Support Menopause?
Functional nutrition focuses on supporting the body’s changing hormonal, metabolic, and inflammatory needs during menopause rather than simply managing symptoms.
Nutrition for Hormone and Metabolic Health
A Mediterranean-style diet—rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats—has been shown to reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular and metabolic health during menopause.
Soy-based foods may also help alleviate menopausal symptoms. Soy contains phytoestrogens, plant compounds that interact with estrogen receptors in the body. While phytoestrogens cannot replace estrogen, they can provide mild estrogen-like activity that may help ease symptoms associated with estrogen decline.
Flaxseeds are another valuable dietary tool. Rich in fiber, healthy fats, and lignans, flaxseeds have been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes and night sweats. For best results, flaxseeds should be consumed consistently at approximately 2–3 tablespoons per day for at least 12 weeks.
Why Meal Timing Matters in Menopause
When we eat is just as important as what we eat. Late or irregular eating patterns are associated with weight gain and disruption of circadian rhythms that regulate sleep, stress hormones, and appetite. Consuming the majority of daily calories earlier in the day may support improved metabolic health, reduced inflammation, and more restorative sleep.
Movement and Nervous System Support
Regular physical activity—especially walking—has powerful benefits for both physical and mental health during menopause. Walking as little as 12.5 miles per week has been associated with reductions in anxiety and depression, along with improvements in sleep quality and insomnia symptoms.
Can Functional Nutrition Make Menopause Easier?
Menopause doesn’t have to be something you “just get through.” With the right nutritional and lifestyle support, it can be a time of empowerment, clarity, and renewed wellbeing.
Functional nutrition helps identify what your body needs during this transition—whether that’s blood sugar support, inflammation reduction, nutrient repletion, or nervous system regulation.
We’re Here to Support You
Navigating menopause can feel overwhelming, but you don’t have to do it alone. Our 1:1 coaching services provide personalized, functional nutrition support to help you feel informed, confident, and supported through every stage of menopause.
If you’re ready to invest in your health and wellbeing, we’d love to support you. Reach out today to begin your journey.
Sources:
Dr. Haylee Nye, Managing Menopausal Symptoms Naturally: Where to Begin (webinar)
Image Sources:
Organicauthority.com
Freepik.com

Why Routine Blood Work Matters for Women’s Health
Routine blood work is one of the most powerful ways to check in with your body and understand what’s really going on beneath the surface.
Your body can’t exactly tap you on the shoulder and say, “Hey, your vitamin D is low,” or “Your blood sugar is creeping up.” Instead, it communicates through subtle (and sometimes not-so-subtle) signs—fatigue, mood changes, stubborn weight, poor sleep, irregular cycles. While those symptoms are important clues, the most direct way to get answers is through routine blood work.
As a dietitian, I’m a big believer in using data to guide decisions—and I also believe it should be easy and accessible. That’s one of the reasons I personally decided to use Superpower for my own labs.
What Does “Routine Blood Work” Usually Include?
The term routine blood work is broad, but it typically includes several key tests that give a high-level snapshot of your health:
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A CBC looks at red blood cells, white blood cells, hemoglobin, and platelets. These markers tell us how well your body is transporting oxygen, fighting infections, and clotting blood. Suboptimal levels can point to issues like anemia, inflammation, or underlying infections.
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
A CMP evaluates 14 different markers related to kidney function, liver function, electrolytes, blood sugar, proteins, and acid–base balance. This panel gives valuable insight into digestion, nutrient absorption, mineral status, and overall organ health.
Lipid Panel
This test measures LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, HDL (“good”) cholesterol, VLDL, and triglycerides. These markers reflect long-term dietary patterns, metabolic health, and cardiovascular risk. Elevated triglycerides or LDL can increase the risk of heart disease, while HDL plays a protective role by helping remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Thyroid Panel
A standard thyroid panel usually includes TSH, T4, and T3. These hormones regulate metabolism, energy, temperature, and growth. Imbalances here can show up as fatigue, weight changes, hair loss, or cycle irregularities—symptoms many women are told are “normal,” but often aren’t.
HbA1c
HbA1c reflects your average blood sugar over the past 2–3 months. It’s one of the most important markers for identifying insulin resistance, prediabetes, and diabetes.
- Below 5.7%: typical
- 5.7–6.4%: prediabetes
- 6.5% or higher: diabetes
My Personal Experience with Superpower
One of the biggest barriers I see—both personally and with clients—is logistics. Scheduling labs, remembering appointments, waiting weeks for results…it’s enough to make routine testing feel overwhelming.
That’s where Superpower really stood out to me.
The sign-up process was incredibly easy, and my blood work came back much faster than I expected. I also loved receiving text updates along the way—no guessing, no wondering when results would arrive.
Once I had my labs, the value really clicked. Having everything clearly laid out made it obvious where things were improving and where I needed support. I could see, for example, that my HbA1c had come down, which was incredibly validating, and that my vitamin D levels were lower than optimal, giving me clear direction on what to address next.
As someone who works with labs every day, I can confidently say: having this kind of insight makes it so much easier to make informed, proactive health decisions instead of guessing.
Making Blood Work Fit Into Your Life
If going to a doctor’s office or lab feels like one more thing on an already full to-do list, Superpower simplifies the process.
Superpower offers blood testing either at home or through one of their 2,000+ partner labs and assesses 100+ biomarkers—far more than what’s typically included in standard annual labs.
Beyond the testing itself, Superpower provides:
- A personalized plan based on your results
- Easy-to-understand data through their member portal
- Ongoing updates as your health evolves
- 24/7 chat access to their team if questions come up
Instead of just handing you numbers and sending you on your way, they help you understand what those numbers actually mean.
The Bottom Line
Routine blood work isn’t about finding something “wrong”—it’s about listening to your body before small imbalances turn into bigger issues. When testing is accessible, clear, and actionable, it becomes one of the most empowering tools for long-term health.
If you’ve been putting off labs because of time, logistics, or confusion around results, Superpower is absolutely worth checking out.
Learn more at: https://superpower.com
Superhero doesn’t stop there though, based on your bloodwork result a personalized plan is created that evolves with you. All of this data is easy for you to check and access through their website and member portal.

Written by: Lauren Chamberlain
Edited and Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
Iodine is a powerhouse nutrient that plays a vital role in thyroid function, hormone balance, and reproductive health. Despite its importance, many people—especially women—don’t get enough of it, leading to potential health complications. Beyond its well-known effects on thyroid function, recent research suggests that iodine plays a role in glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and fertility. In this post, we’ll explore iodine’s impact on the body, its connection to thyroid and reproductive health, and why you should consider testing your iodine levels!
Iodine and the Thyroid: A Critical Connection

The thyroid gland depends on iodine to produce hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and overall endocrine balance. Here’s how it works:
- Thyroxine (T4): Contains four iodine molecules and serves as a storage form of thyroid hormone.
- Triiodothyronine (T3): Contains three iodine molecules and is the active thyroid hormone that influences metabolism and energy levels.
When you consume iodine, it gets absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and transported to the thyroid via the sodium-iodide symporter (NIS). If your body detects low thyroid hormone levels, the pituitary gland releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to prompt the thyroid to absorb iodine and produce more T4, which then converts into the active T3.
Why Does TSH Increase with Iodine Supplementation?
A rise in TSH after starting iodine supplements is often misunderstood. TSH stimulates more NIS molecules, helping transport iodine into thyroid cells. A temporary increase in TSH is a normal response, not necessarily a sign of thyroid dysfunction. However, excessive iodine intake can paradoxically impair thyroid function by triggering hypothyroidism or autoimmune thyroiditis. This is why careful monitoring through the use of a health professional is essential.
Iodine’s Role in Women’s Health

Beyond the thyroid, iodine plays a crucial role in reproductive health, hormone balance, and even breast tissue integrity. Here’s how:
Ovulation & Progesterone Production
Iodine is essential for ovarian function because the ovaries store a lot of iodine because our growing follicles take up iodine to grow properly. Studies suggest that iodine deficiency may contribute to menstrual irregularities and impaired ovulation, potentially affecting fertility.
Endometriosis & Estrogen Dominance
Iodine helps regulate estrogen metabolism by promoting the breakdown of estrogen into more favorable metabolites. This may help reduce inflammation, fibrocystic breast changes, and the risk of estrogen-dominant conditions like endometriosis.
Breast & Uterine Health
Iodine accumulates in breast and uterine tissues, where it supports cellular integrity and may protect against fibrocystic breast disease. A deficiency in iodine has been linked to an increased risk of breast cancer due to impaired estrogen metabolism and oxidative stress.
Pregnancy & Fetal Development
Iodine is crucial during pregnancy, as it supports fetal brain development, prevents cretinism, and reduces the risk of miscarriage and low birth weight. A deficiency in pregnancy can lead to intellectual disabilities, developmental delays, and even maternal hypothyroidism, which can have long-term effects on the child.
Iodine Absorption & Halogens: A Competitive Battle

Iodine belongs to the halogen family, which includes fluorine, chlorine, and bromine. Unfortunately, these elements have similar chemical makeups so they compete with iodine for absorption and can erroneously bind to iodine receptors, potentially leading to deficiency:
- Fluoride (found in tap water and toothpaste)
- Bromine (found in baked goods and flame retardants)
- Chlorine (found in drinking water and pools)
This means that even if you consume iodine-rich foods, environmental exposure to these halogens could impact absorption.
Iodine’s Role in Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity
Emerging research suggests that iodine may play a crucial role in glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. One potential mechanism involves iodine’s interaction with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ), a nuclear receptor that regulates lipid and glucose metabolism. PPAR-γ activation has been associated with improved insulin sensitivity by enhancing glucose uptake in peripheral tissues and modulating adipocyte differentiation. This suggests that iodine may contribute to metabolic health by influencing pathways that regulate insulin signaling.
However, the relationship between iodine and glucose metabolism is complex. While adequate iodine intake may support insulin function, excessive iodine consumption has been linked to cytotoxic effects on pancreatic beta cells, which are responsible for insulin secretion. High iodine levels can induce oxidative stress and apoptosis (cell death) in these cells, potentially impairing insulin production and increasing the risk of glucose dysregulation. Additionally, iodine excess has been associated with thyroid dysfunction, which can indirectly affect insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis through alterations in thyroid hormone levels.
These findings highlight the need to maintain optimal iodine intake, as both deficiency and excess can have metabolic consequences. Further research is needed to clarify the precise mechanisms by which iodine influences insulin function and to determine safe and effective dietary recommendations for individuals at risk of metabolic disorders.
Who Might Need More Iodine?
While iodine deficiency can affect anyone, certain populations are at higher risk:
- Women with hormonal imbalances, endometriosis, or estrogen dominance
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women (who require higher iodine intake)
- Individuals with frequent exposure to fluoride, chlorine, and bromine
- People with thyroid dysfunction or subclinical hypothyroidism
- Those with blood sugar imbalances or insulin resistance
If you suspect iodine deficiency, a urinary iodine clearance test can help assess your levels. We only absorb 10% of iodine in the gut when levels are sufficient, so we want 90% excreted in the urine.
Key Thyroid Markers to Test

Relying on TSH alone isn’t enough to evaluate thyroid function. If you’re experiencing fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, or brain fog, consider testing:
- Free T3 (FT3): The active thyroid hormone–shows how much thyroid hormone is being converted
- Free T4 (FT4): The inactive form of thyroid hormone–shows how much thyroid hormone your thyroid is producing
- Reverse T3 (rT3): Puts the breaks on thyroid hormone conversion–indicates stress or inflammation
- Thyroid Antibodies (TPOAb, TgAb): Markers for autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto’s or Graves’ Disease
Before Increasing Iodine Intake

Before making changes to your iodine intake—whether through food sources or supplements—it’s essential to establish a strong foundation for overall health. Iodine metabolism is influenced by multiple factors, including stress, sleep, and nutrient status, so addressing these areas first can help your body utilize iodine more effectively. Consulting with a healthcare professional is also key to ensuring that supplementation is appropriate for your individual needs.
Consider these important questions before increasing iodine intake:
Am I eating enough?
- Chronic under-eating can contribute to nutrient deficiencies, including iodine.
Am I under high stress?
- Elevated stress levels increase cortisol, which can interfere with thyroid function and iodine metabolism.
Am I getting proper light exposure and balancing my circadian rhythm?
- Sunlight helps regulate hormone production, including thyroid hormones, which depend on iodine.
Am I getting quality sleep?
- Poor sleep can disrupt endocrine function, making it harder for your body to utilize iodine efficiently.
Am I going through a particularly demanding or stressful season of life?
- Major life changes, illness, or intense physical demands can impact overall nutrient needs.
Am I deficient in other key minerals?
- Iodine works in synergy with selenium, zinc, magnesium, and iron. Deficiencies in these minerals can impair iodine’s role in thyroid function and metabolism.
Since iodine is just one piece of the puzzle, it’s crucial to build a strong nutritional and lifestyle foundation before increasing intake. Addressing these factors first will help your body better absorb and utilize iodine while minimizing potential risks associated with excess or imbalance.
Safe Iodine Supplementation: What to Consider
Iodine supplementation isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach. Here are some key factors:
- Start Low and Go Slow: Gradually increase iodine intake to allow your body to adjust.
- Pair with Selenium: Selenium helps balance iodine metabolism and prevents thyroid inflammation.
- Ensure Adequate Sodium Intake: Unrefined salt supports iodine transport.
- Get Tested First: Urinary iodine testing and hair tissue mineral analysis (HTMA) can provide insights into your iodine status.
Symptoms of Iodine Deficiency
Signs of iodine deficiency can be subtle but may include:
- Fatigue and sluggishness
- Weight gain and slow metabolism
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin and brittle nails
- Hair thinning
- Brain fog and poor concentration
- Depression and mood swings
- Irregular menstrual cycles
Best Dietary Sources of Iodine

To maintain healthy iodine levels, include these foods in your diet:
- Seaweed (kelp, nori, wakame, dulse): The richest natural source of iodine.
- Fish and shellfish (cod, tuna, shrimp, oysters): Packed with iodine and essential minerals.
- Dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese): Often fortified with iodine.
- Eggs: A good source, especially from pasture-raised hens.
Final Thoughts
Iodine is an essential yet often overlooked nutrient that plays a pivotal role in thyroid function, hormone balance, metabolic health, and reproductive function. If you struggle with fatigue, hormonal imbalances, insulin resistance, or fertility concerns, it may be worth assessing your iodine levels and ensuring you’re getting enough from your diet or supplements. However, balance is key—too much iodine can be just as harmful as too little.
By understanding how iodine influences your health, you can take proactive steps to optimize your intake and support overall well-being.

Sources:
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6373336/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8709459/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3063534/#:~:text=Iodine%20is%20mostly%20concentrated%20in,stored%20in%20the%20thyroid%20gland
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10813031/#:~:text=Conclusions:%20Iodine%20could%20influence%20glucose%20metabolism%20in,cause%20cytotoxic%20damage%20to%20pancreatic%20beta%20cells
- https://www.news-medical.net/news/20240321/Exploring-the-role-of-iodine-in-obesity-diabetes-and-other-metabolic-conditions.aspx#:~:text=Iodine%20also%20interacts%20with%20peroxisome%20proliferator%2Dactivated%20receptor%2D%CE%B3,and%20glucose%20metabolism%20by%20improving%20insulin%20sensitivity
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7511676/
- https://academic.oup.com/humrep/article/36/2/265/6025913?login=false
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29340704/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0739724005000433
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3063534/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5327366/
- https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/3/1228#:~:text=Our%20group%20has%20found%20similar,tissues%20that%20take%20up%20iodine
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31284874

Written by: Lauren Chamberlain
Edited and Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
Dealing with endometriosis is already a challenge—pain, fatigue, and the frustratingly long journey to diagnosis. But for many, one of the hardest realities to face is how this condition might impact fertility. Whether you’re actively trying to conceive or simply thinking about the future, it’s natural to wonder: Will I be able to get pregnant? Will it take longer? Am I at risk for complications?
Let’s break it down—why does endometriosis make conception more difficult? And what can be done to improve fertility outcomes?
Fertility and Endometriosis: The Numbers
Studies suggest that up to 50% of people with endometriosis may experience fertility challenges, and about half of those diagnosed with infertility have underlying endometriosis. However, a diagnosis doesn’t mean pregnancy is impossible! It may take longer, require medical support, or necessitate lifestyle adjustments—but many people with endometriosis go on to conceive and carry healthy pregnancies.
Now that we’ve covered the statistics, let’s explore why endometriosis affects fertility in the first place.
Understanding the Connection: Why Endometriosis Affects Fertility
Endometriosis is a complex condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, leading to inflammation, scarring, and hormonal imbalances. These factors can contribute to fertility struggles in multiple ways:
1. Chronic Inflammation and Hormonal Imbalances
Endometriosis is associated with chronic inflammation, which plays a key role in fertility challenges. The condition causes an increase in inflammatory cytokines—proteins that regulate immune responses. These cytokines can interfere with ovulation, fertilization, and implantation by creating a hostile uterine environment. Chronic inflammation may also impair the function of the corpus luteum, the structure responsible for producing progesterone after ovulation. Since progesterone is critical for preparing the uterine lining for implantation, low levels may result in implantation failure or early miscarriage.
Additionally, endometriosis is often linked to estrogen dominance. Excess estrogen can thicken the endometrial lining abnormally, disrupt the menstrual cycle, and contribute to a suboptimal hormonal balance for conception.
2. Reduced Egg Quality and Oxidative Stress
Endometriosis has been linked to oxidative stress, a condition where an excess of reactive oxygen species (ROS) damages cellular structures, including eggs. This oxidative damage can lead to:
- DNA fragmentation in eggs, reducing their ability to be fertilized.
- Lower embryo quality, decreasing the likelihood of successful implantation.
- Higher rates of aneuploidy (chromosomal abnormalities), which can lead to failed pregnancies or birth defects.
Research suggests that targeted nutritional strategies, such as increasing antioxidant intake (e.g., vitamin C, vitamin E, and CoQ10), can help mitigate oxidative stress and improve egg quality.
3. Decreased Ovarian Reserve and Endometriomas
Many individuals with endometriosis develop ovarian cysts known as endometriomas. These cysts, filled with old blood, can impact ovarian function in several ways:
- Damage to ovarian tissue: As endometriomas grow, they can infiltrate and compromise healthy ovarian tissue, reducing the number of viable eggs.
- Lower response to fertility treatments: Studies indicate that individuals with endometriomas often have a lower ovarian response to stimulation during assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like in vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Surgical risks: While surgical removal of endometriomas may relieve symptoms, it can also reduce ovarian reserve if healthy ovarian tissue is inadvertently removed during the procedure. Those considering surgery should discuss fertility preservation strategies, such as egg freezing, beforehand.
4. Blocked Fallopian Tubes and Pelvic Adhesions
Endometriosis can cause adhesions—bands of fibrous scar tissue that develop between organs. These adhesions may:
- Block or distort the fallopian tubes, preventing eggs from traveling to meet sperm.
- Interfere with ovulation, making it more difficult for the ovaries to release eggs effectively.
- Cause fluid buildup in the fallopian tubes (hydrosalpinx), which can create an inhospitable environment for embryos and decrease implantation success.
For those with significant tubal damage, natural conception may be challenging, and assisted reproductive technologies like IVF may be necessary.
5. Implantation Challenges and Uterine Dysfunction
Successful pregnancy depends on a fertilized egg implanting into a healthy uterine lining. Endometriosis can interfere with this process due to:
- Abnormal endometrial receptivity: The endometrium (uterine lining) may not develop properly due to chronic inflammation, hormonal imbalances, or scarring.
- Increased uterine contractility: The uterus may contract excessively, making it harder for an embryo to implant and remain stable.
- Altered immune response: Inflammatory and immune factors in the uterine environment may mistakenly attack the embryo, leading to implantation failure or early miscarriage.
Pregnancy with Endometriosis: Risks & Considerations
While many individuals with endometriosis achieve healthy pregnancies, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and considerations:
1. Increased Risk of Obstetrical Complications
Studies have identified a higher incidence of certain complications in pregnant individuals with endometriosis:
- Preterm Birth: There is an elevated risk of delivering before 37 weeks of gestation.
- Placenta Previa: The placenta may implant low in the uterus, covering the cervix, which can lead to bleeding and necessitate a cesarean section.
- Hypertensive Disorders: Conditions like preeclampsia, characterized by high blood pressure and potential damage to other organ systems, are more common.
- Gestational Diabetes: An increased likelihood of developing diabetes during pregnancy has been observed.
- Cesarean Delivery: The necessity for cesarean sections is higher among those with endometriosis.
These findings underscore the importance of vigilant prenatal care for individuals with endometriosis to monitor and manage potential complications effectively.
2. Impact of Surgical Treatment on Pregnancy Outcomes
Surgical interventions for endometriosis, such as laparoscopic excision, aim to alleviate symptoms and improve fertility. However, the effects of surgery on pregnancy outcomes are complex:
- Adhesion Formation: Post-surgical adhesions can lead to chronic pelvic pain and may impact fertility.
- Ovarian Reserve: Surgical removal of endometriomas (ovarian cysts associated with endometriosis) can reduce ovarian reserve, potentially affecting fertility.
Therefore, surgical decisions should be individualized, weighing the benefits against potential risks, and discussed thoroughly with a healthcare provider.
3. Importance of Preconception Counseling
Given the potential challenges associated with endometriosis and pregnancy, preconception counseling is highly recommended. This process involves:
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Assessing the extent of endometriosis and its impact on reproductive organs.
- Fertility Assessment: Evaluating ovarian reserve and tubal patency to determine the best conception strategies.
- Risk Discussion: Understanding the potential obstetrical risks and planning appropriate monitoring and interventions.
Engaging in preconception counseling allows for informed decision-making and the development of a tailored care plan to optimize pregnancy outcomes.
4. Nutritional and Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting specific dietary and lifestyle changes can positively influence fertility and pregnancy outcomes in individuals with endometriosis:
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Consuming foods rich in antioxidants can reduce oxidative stress and improve egg quality.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in moderate exercise can enhance overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Stress Management: Incorporating stress-reduction techniques like yoga or meditation may improve hormonal balance.
Implementing these modifications can support reproductive health and may increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy.
5. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
For those experiencing difficulty conceiving naturally, ART options such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be considered. While endometriosis can impact the success rates of ART, individualized treatment protocols and close monitoring can enhance outcomes. Consulting with a fertility specialist can provide personalized guidance on the most appropriate interventions.
Ultimately, while endometriosis can pose challenges to conception and pregnancy, understanding the potential risks and proactively managing them with a healthcare team can lead to successful outcomes.
What Can You Do?
If you have endometriosis and are concerned about your fertility, there are steps you can take to optimize your chances of conception:
- Adopt an anti-inflammatory diet: Eat foods rich in antioxidants, such as leafy greens, berries, turmeric, and omega-3 fatty acids, to combat oxidative stress and support egg quality.
- Consider medical treatment: Hormonal therapies like GnRH agonists, birth control pills, or progestin therapy may help manage symptoms and improve fertility outcomes.
- Support gut health: A balanced gut microbiome helps regulate inflammation. Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut, or consider a high-quality probiotic supplement.
- Optimize lifestyle factors: Engage in regular, low-impact exercise like yoga or walking to reduce inflammation and support reproductive health. Prioritize stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, and ensure you’re getting enough quality sleep.
- Work with a fertility specialist: A reproductive endocrinologist or fertility dietitian can assess your specific needs and create a personalized plan, whether you’re trying to conceive naturally or exploring medical interventions.
- Discuss fertility preservation: If you’re not trying to conceive yet but may want to in the future, options like egg freezing can help safeguard your reproductive potential.
Final Thoughts
Endometriosis may make conception more challenging, but it doesn’t mean it’s out of reach. Every fertility journey is different, and while endometriosis can present obstacles, there are many ways to take control of your reproductive health. Whether through lifestyle changes, medical treatments, or working with a specialist, you have options. If you’re struggling, reach out to a healthcare provider to explore the best path for you. Knowledge is power, and by understanding the impact of this condition, you can approach your fertility journey with confidence and clarity.

Sources
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9983692
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8224039
https://www.rbmojournal.com/article/S1472-6483(13)00007-2/fulltext
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8065992
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7226034
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9528818
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10058497/#sec5-life-13-00654
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10820275

The Preconception Playbook
This free playbook provides specific actionable tips to get started on your fertility journey, as well as what to avoid while you're trying to conceive.
Get the free playbook