Resources
Style
Planning
View All
THE blog
Written by: Lauren Chamberlain
Edited and Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
Did you know that your gut health could impact more than just digestion? From immunity to mental clarity, a healthy gut plays a pivotal role in overall well-being—and even fertility. Emerging research suggests that a balanced gut microbiome influences hormone regulation, immune function, and inflammation, all of which are crucial for reproductive health. Whether you’re looking to optimize fertility or improve general health, supporting your gut can be a game-changer for both your body and mind.
The Basic Functions of the Gut
Before diving into the more intricate details of gut health, it’s essential to understand the basic functions of the gut and why it plays such a crucial role in your overall health.
1. Digestion
The gut is responsible for breaking down the food we eat, allowing nutrients to be absorbed into the bloodstream. This process starts in the mouth and continues through the stomach and small intestine. Enzymes and acids help break down food into smaller molecules for absorption.
2. Nutrient Absorption
Once food is broken down, the small intestine absorbs essential nutrients—like vitamins, minerals, and amino acids—into the bloodstream. These nutrients are then transported throughout the body to fuel our cells and organs.
3. Immune Function
A large portion of the body’s immune system resides in the gut. It acts as a barrier to harmful pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses. A healthy gut microbiome— the community of beneficial bacteria—supports immune function and helps protect the body from infections and inflammation.
4. Detoxification
The gut plays a vital role in detoxifying the body by processing and eliminating waste. The liver, bile, and gut work together to filter out toxins, which are then excreted through the stool. This process helps maintain a clean internal environment.
5. Hormone Regulation
The gut is involved in hormone production and regulation. It helps control hormones related to digestion, hunger, and metabolism. Additionally, the gut microbiome can influence hormonal balance, which is vital for reproductive health.
6. Gut-Brain Connection
The gut and brain communicate through the gut-brain axis, a direct link between the two. This connection influences mood, mental clarity, and stress levels. Research suggests that an imbalance in the gut microbiome can impact mental health conditions like anxiety and depression.
By understanding these basic functions, we can see why maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being and fertility. Now, let’s dive deeper into how to support these functions for optimal health.
Understanding Gut Permeability and Leaky Gut
Leaky gut occurs when the intestinal barrier becomes compromised, allowing undigested food particles, toxins, and microbes to enter the bloodstream. This process can trigger systemic inflammation and is implicated in conditions like autoimmune diseases, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and even neuroinflammation. The protein zonulin regulates tight junctions in the gut lining, and its overproduction is associated with increased gut permeability.
Dietary choices, stress, and environmental toxins all influence this delicate balance.
The Role of Diet in Gut Health
Diet plays a crucial role in shaping gut microbiota and maintaining a strong intestinal barrier. Research suggests that:
- High-fiber foods (e.g., fruits, vegetables, whole grains) support beneficial bacteria and help regulate gut permeability.
- Healthy fats, such as omega-3s, promote anti-inflammatory gut conditions, whereas excessive saturated fat intake can negatively impact gut flora.
- Akkermansia muciniphila, a beneficial bacterium, is linked to improved gut barrier function, reduced inflammation, and better metabolic health.
- Bovine colostrum supplementation has been shown to decrease intestinal permeability and lower zonulin levels, particularly in athletes.
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) and Gut Dysfunction
SIBO occurs when there’s an overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine. This can lead to bloating, malabsorption, and digestive discomfort. It’s often associated with IBS, celiac disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Managing SIBO:
- Get proper testing to identify SIBO.
- Modify your diet, focusing on low FODMAP foods.
- Consider probiotics to restore balance.
- Work with a healthcare provider to determine if antibiotics are necessary.
Gut Health and Systemic Wellness
Emerging research highlights the gut-brain connection, linking gut health to cognitive function, mood regulation, and neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s. The gut microbiome also plays a role in cardiovascular health, obesity, and diabetes. Fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) have even been explored as potential treatments for age-related cognitive decline and metabolic disorders.
Gut Health and Fertility
Emerging research suggests that gut health plays a crucial role in reproductive health. The gut microbiome influences hormone regulation, immune function, and inflammation, all of which impact fertility outcomes. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance of gut bacteria, has been linked to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and unexplained infertility.
- Hormonal Balance: The gut microbiome helps regulate estrogen levels through the estrobolome, a collection of bacteria involved in estrogen metabolism. An imbalance can lead to estrogen dominance, which is associated with infertility and conditions like PCOS.
- Inflammation and Immune Function: Chronic inflammation, often driven by poor gut health, has been implicated in endometriosis and implantation failure. A healthy gut barrier helps regulate immune responses and supports a favorable reproductive environment.
- Microbiome and Pregnancy Outcomes: Research suggests that a balanced gut microbiome contributes to healthy pregnancy outcomes, reducing the risk of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and preterm birth.
Supporting Digestion
Efficient digestion breaks down food properly, allowing for optimal nutrient absorption and minimizing digestive distress.
Ways to enhance digestion include:
- Incorporating bitter foods: Foods like arugula, artichoke, bitter melon, dandelion greens, Brussels sprouts, coffee, and grapefruit stimulate stomach acid and bile production.
- Using digestive aids: Digestive enzymes, HCl supplements, apple cider vinegar, or digestive bitters may be beneficial.
- Relaxing at meals: Stress can negatively impact digestion, so mindful eating practices are essential.
- Consuming adequate minerals: Sodium (from sea salt) and zinc (from oysters and red meat) support stomach acid production.
Supporting Healthy Bile Flow
Bile is critical for fat digestion and detoxification. Signs of inadequate bile include bloating, floating stools, nausea after eating fats, and vitamin deficiencies. To support bile production:
- Consume fiber-rich foods: Legumes, beans, and avocados help bind to excess bile.
- Eat bitter foods: These naturally promote bile flow.
- Use cholagogue herbs: Globe artichoke, dandelion, burdock, and Oregon grape enhance bile movement.
- Ensure adequate taurine intake: Meat, fish, shellfish, and eggs aid in bile salt production.
Supporting Beneficial Bacteria
A balanced gut microbiome is essential for digestion, immunity, and gut barrier integrity. To nurture beneficial bacteria:
- Prioritize digestion first: Ensuring proper food breakdown is key before increasing fiber intake.
- Incorporate prebiotic foods: Apples, asparagus, garlic, onions, oats, and legumes serve as fuel for gut bacteria.
- Limit excessive alcohol intake: Alcohol can cause dysbiosis and inflammation.
Supporting Liver Detoxification
The liver plays a crucial role in gut health through bile production and detox processes. To support liver function:
- Include Phase 1 detox foods: Magnesium (leafy greens, avocado), B vitamins (liver, eggs, seafood), vitamin C (citrus, bell peppers), and zinc (oysters, beef).
- Incorporate Phase 2 detox foods: Glycine (bone broth), glutamine (beef, spinach), cysteine (broccoli, eggs), and taurine (meat, fish).
Strengthening the Gut Lining
A strong intestinal barrier prevents harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. Factors that contribute to a leaky gut include stress, poor digestion, processed foods, overuse of medications, and imbalanced gut bacteria. To support gut integrity:
- Limit inflammatory foods: Avoid heavily processed and inflammatory oils.
- Boost beneficial fibers: Prebiotic and resistant starch-rich foods enhance gut lining health.
- Consume gut-supportive nutrients: Glutamine (cabbage, fish), zinc (beef, crab), and colostrum aid in healing the gut lining.
- Use gut-healing herbs: Marshmallow root, slippery elm, aloe vera, and licorice can be beneficial.
Strengthening the Immune System
A well-functioning immune system relies on strong digestion and a balanced gut microbiome. Factors that deplete immunity include poor digestion, chronic stress, hormonal imbalances, and long-term medication use. To support immune health:
- Improve digestion and gut microbiome health
- Incorporate immune-boosting foods: Colostrum, mushrooms (reishi, shiitake), and vitamin C-rich foods (citrus, mango, papaya) support immune function.
- Use supportive herbs: Andrographis, elderberry, echinacea, and astragalus help strengthen immunity.
Prebiotics & Resistant Starch
Prebiotics are fibers that feed beneficial bacteria and help produce short-chain fatty acids, which support gut integrity and immunity.
- Prebiotic foods: Apples, asparagus, garlic, onions, oats, and legumes.
- Resistant starch sources: Cooked and cooled potatoes, green bananas, and legumes.
By focusing on these key areas, you can create a solid foundation for optimal gut health and overall well-being. Making small, sustainable changes to your diet and lifestyle can have lasting positive effects on digestion, immunity, and energy levels.
Conclusion
Maintaining gut health is essential for overall well-being, from digestion and immunity to mental clarity and chronic disease prevention. By making mindful dietary and lifestyle choices, you can support a resilient gut microbiome and improve long-term health outcomes. The science is clear: a healthy gut is a foundation for a thriving body and mind.

Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6996528/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8305009/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6313445/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38790992/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32023228/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8058106/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8674859/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25290618/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35874661/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34623232/
- https://www.imrpress.com/journal/FBL/26/5/10.52586/4921/htm
- https://www.nia.nih.gov/news/beyond-brain-gut-microbiome-and-alzheimers-disease
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34054740/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28397754/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35745242/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7971312/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28778332/

Many women with PCOS struggle to find an effective treatment plan due to its complex nature. However, recent research has begun to shine a light on the crucial role the gut microbiome plays in managing this condition. Your gut does more than just digest food; it influences hormone regulation, inflammation, and even your overall metabolic health.
This article dives into how optimizing your gut health can significantly impact PCOS management. From understanding the gut-hormone link to practical dietary changes you can make, you’ll gain valuable insights to improve your wellbeing.
Understanding PCOS: A Brief Overview
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects a significant portion of women around the world, with implications that go beyond just the reproductive system. At its core, PCOS is a hormonal disorder known for causing irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries. But, it doesn’t stop there. This complex condition often brings a host of other challenges, including insulin resistance, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular issues.
The exact cause of PCOS remains a subject of ongoing research, but genetics and lifestyle factors both appear to play substantial roles. Women with PCOS frequently exhibit elevated insulin levels, which can exacerbate symptoms and contribute to the imbalance of sex hormones. What’s more, the syndrome can profoundly impact mental health, leading to conditions like anxiety and depression.
With no known cure, managing PCOS involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, and medical treatments tailored to alleviate specific symptoms. Because PCOS affects different women in different ways, it’s crucial to approach treatment on an individualized basis. In recent years, emerging studies have started to explore the connection between gut health and PCOS, revealing that a balanced gut microbiome might be an essential key to managing this disorder.

The Gut-Health Connection: Why It Matters
Your gut health doesn’t just affect your digestion; it has a profound impact on your overall well-being. The human gut microbiome, an ecosystem of trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, plays a crucial role in many bodily functions. Notably, it helps regulate metabolism, supports the immune system, and maintains the structural integrity of the gut lining.
But the relationship between gut health and conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is particularly interesting. The gut-brain axis, a complex communication network that links your gut and brain, further illustrates this connection. When your gut microbiota is in balance, it positively influences hormonal health, which is central to managing PCOS symptoms.
Emerging research highlights how an imbalance in the gut microbiota, also known as dysbiosis, can exacerbate PCOS symptoms. Dysbiosis has been linked to increased inflammation, insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalances—all of which are critical factors in PCOS. This makes maintaining a healthy gut not just a recommendation, but a necessity for those managing PCOS.
Moreover, factors like diet, sleep, and exercise play a significant role in shaping your gut microbiome. Consuming a diet rich in diverse, fiber-rich foods, getting quality sleep, limiting alcohol intake, and engaging in regular physical activity can all foster a healthier gut. By focusing on these areas, you can support your gut health and, in turn, help manage PCOS more effectively.
How Gut Bacteria Influence Hormonal Balance
In understanding gut health’s role in PCOS, it’s essential to dive into the relationship between gut bacteria and inflammation. Gut microbiota plays a crucial role in regulating hormones and metabolism. When your gut microbiota is unbalanced, it can lead to chronic inflammation, a common issue in those with PCOS. But how exactly does this happen?
Your gut lining serves as a barrier, preventing harmful substances from entering your bloodstream. However, an imbalanced gut microbiota can weaken this barrier, allowing toxins and bacteria to escape into your system. This phenomenon, known as “leaky gut,” triggers your immune system to react, leading to chronic inflammation.
This inflammation doesn’t just stay localized in your gut. It can spread throughout your body, affecting various organs and tissues, including your ovaries. Chronic inflammation can exacerbate the symptoms of PCOS by disrupting your hormonal balance. For example, inflammation can impair insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance – a hallmark of PCOS.
Moreover, hyperandrogenism, or elevated levels of male hormones, is closely linked to gut health. Research indicates that your gut microbiota can influence sex hormone production. In those with PCOS, an imbalanced gut microbiota may contribute to increased testosterone levels, worsening symptoms like excess hair growth, acne, and menstrual irregularities.
Addressing inflammation through gut health can be a powerful strategy. By focusing on a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, you can help restore balance to your gut microbiota. Probiotics, prebiotics, and other dietary supplements may also play a vital role in reducing inflammation and supporting a healthier hormonal balance.
The Role of Inflammation in PCOS and Gut Health
Chronic inflammation is a known factor in the development of PCOS. Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of PCOS, often linked to an imbalance in gut microbiota. When your gut bacteria are out of balance, it can lead to increased intestinal permeability, commonly known as “leaky gut.” This condition allows toxins and partially digested food particles to enter the bloodstream, triggering an immune response and chronic inflammation.
This persistent inflammation can exacerbate insulin resistance, a common feature in PCOS. Insulin resistance leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which in turn can cause the body to produce more insulin. High insulin levels stimulate the ovaries to produce more androgens, contributing to symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and hirsutism.
Moreover, chronic inflammation influences ovarian function and insulin sensitivity through various biochemical pathways. For instance, certain inflammatory markers like IL-22 have been shown to affect ovarian granulosa cells, which are crucial for hormone production and ovarian health. Inflammatory cytokines can also disrupt the normal functioning of the ovaries, potentially worsening PCOS symptoms.
It’s also worth noting that Vitamin D deficiency, commonly observed in PCOS patients, can further exacerbate inflammation. Vitamin D has anti-inflammatory properties, and its lack can lead to an increase in inflammatory responses, thereby worsening both gut health and PCOS symptoms. It is also known that Women with PCOS often have altered gut microbiota compared to those without PCOS.
Given this intricate relationship, addressing inflammation by improving gut health can be a promising approach to managing PCOS. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, probiotics, and dietary changes can help maintain a balanced gut microbiota, reduce intestinal permeability, and ultimately mitigate the inflammatory processes that contribute to PCOS.
Recognizing the Signs of Poor Gut Health
Recognizing the signs of poor gut health is crucial in managing PCOS effectively. You might wonder what symptoms to look out for. Here’s a quick guide to help you identify potential gut issues:
- Digestive discomfort: Frequent bloating, gas, diarrhea, or constipation could indicate an imbalance in your gut microbiota.
- Food intolerances: If you notice increased sensitivity to certain foods, it might be linked to gut health issues.
- Fatigue: Chronic tiredness can be a sign that your gut is not absorbing nutrients properly.
- Skin conditions: Issues like eczema or acne can be linked to gut health, as inflammation in the gut often manifests on the skin.
- Mood changes: An unbalanced gut microbiota can lead to abnormal hormone changes, potentially contributing to anxiety and mood swings.
- Unintentional weight changes: Both weight gain and loss without any obvious reason can indicate a gut health problem.
It’s important to be attentive to such signs because they can be early indicators of more significant issues. If you experience any of these symptoms consistently, it might be time to take a closer look at your gut health, especially if you have PCOS.
Dietary Changes to Boost Gut Health for PCOS
Making the right dietary choices can significantly influence your gut health and, by extension, help manage symptoms of PCOS. Let’s delve into some practical and effective changes you can implement.

1. Incorporate Fiber-Rich Foods
Fiber acts as fuel for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can support these bacteria, which in turn helps regulate hormones and reduce inflammation. Aim to include at least 25-30 grams of fiber daily.
2. Add Fermented Foods
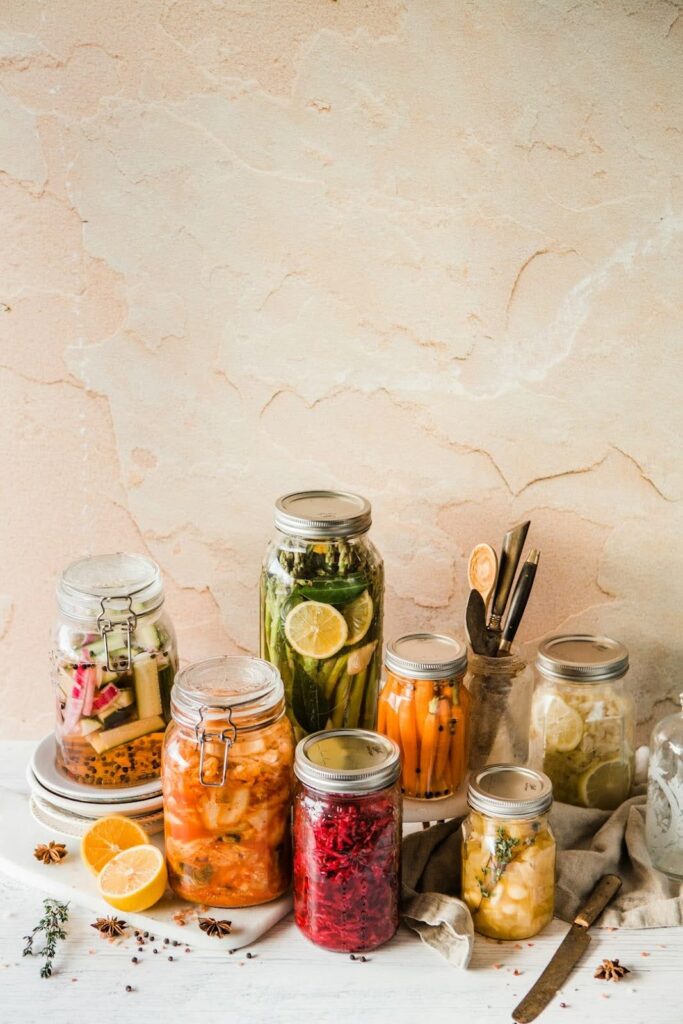

Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha are brimming with probiotics. Regularly consuming these foods can help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiota, crucial for managing PCOS symptoms. Probiotics, like bifidobacterium lactis V9, in particular, have shown promising results in improving gut health for women with PCOS.
3. Focus on Prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. Foods like garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus, and oats are excellent prebiotic sources. Integrating these into your diet can help nurture a healthy gut environment. Probiotics and prebiotics can positively influence gut microbiota.
4. Opt for Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, particularly those from omega-3 fatty acids, can reduce inflammation and support overall gut health. Include sources such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts in your meals to reap their benefits.
5. Minimize Processed Foods and Sugars
Highly processed foods and sugary snacks can promote harmful bacteria growth and contribute to gut dysbiosis. Steering clear of these foods can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which is crucial for managing PCOS effectively.
By making these dietary adjustments, you can create a supportive environment for your gut health, potentially alleviating some of the hormonal and metabolic challenges associated with PCOS. Remember, small, consistent changes can lead to significant improvements over time.
Supplements That Support Gut Health in PCOS
Supplements can play a significant role in supporting gut health, particularly for women managing PCOS. Integrating the right supplements into your routine can help rebalance your gut microbiota, leading to improved overall health.

Probiotics
One of the most well-researched supplements for gut health is probiotics. Strains like Bifidobacterium lactis V9 have shown promise in improving gut health in women with PCOS. Probiotics can help restore the natural balance of gut bacteria, which in turn may enhance metabolic and reproductive functions. One of our favorites is Megaspore biotic – which you can find inside our supplement store right here.
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are another cornerstone of gut health. These are non-digestible fibers that fuel the growth of beneficial bacteria in your gut. Incorporating prebiotic supplements can create a more favorable environment for your gut microbiota, helping to improve hormonal balance and reduce inflammation, both crucial for managing PCOS.
Synbiotics
Combining probiotics and prebiotics, synbiotics offer dual benefits. By taking these supplements, you provide your gut with beneficial bacteria while ensuring they have the nutrients they need to thrive. This synergistic approach can be particularly effective for restoring gut microbiota diversity and improving PCOS symptoms.
Vitamin D
Emerging research suggests that Vitamin D might influence the occurrence of PCOS by affecting the composition of gut microbiota. Vitamin D supplementation could improve gut health and potentially alleviate some symptoms of PCOS by enhancing the microbiota balance. *It’s important to test vitamin D levels before supplementing, as you can go *too high* with this as well.
Getting Support with Your Gut Health and PCOS
If you’re looking for more support with managing your PCOS, improving your gut health, and preparing your body for a healthy pregnancy, reach out to our team of highly trained functional fertility nutritionists.
We utilize functional lab testing such as the GI MAP, to help uncover the root cause of your fertility struggles. We’ve worked with hundreds of women in our practice, and are here to support you!

One of my favorite parts about working in functional nutrition is that I get to take a deeper dive into the root causes of health issues. Fertility is something that is so interconnected to every system in the body, that we sometimes forget that something that may seem totally unrelated, could actually be the root of everything else. That’s why I’m excited to talk about how gut health specifically impacts fertility.
he gut impacts your entire body – from modulating risk for chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer, to impacting your mood, anxiety and depression. There is A LOT of research happening these days around gut health, and there’s more coming out every day about how the gut microbiome impacts fertility.
What is the Microbiome?
So first, let’s talk about what the gut microbiome actually is. The gut microbiome is essentially all the bacteria that live inside your digestive system, specifically the large intestine. In the gut there are 100 trillion bacteria cells – more cells than our body’s own cells!
While there can certainly be bad bacteria that cause infections and disease, there’s also a whole host of beneficial bacteria that work hard to digest and absorb our food, signal neurotransmitters to our brains, fight inflammation and boost immunity.
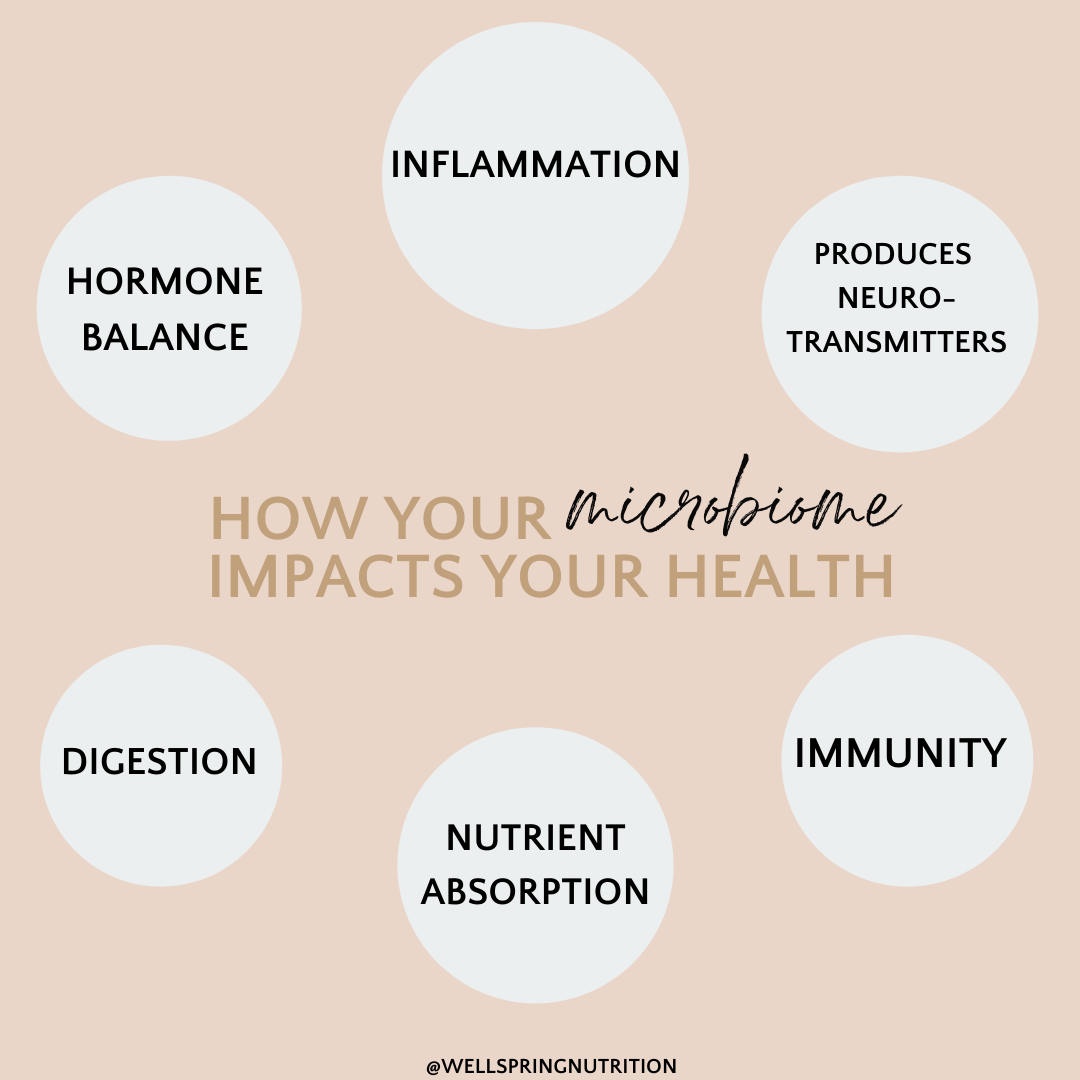
The microbiome impacts:
- Energy levels
- Mood, stress and brain health
- Digestive health
- Immune function
- Skin health
- Inflammation
- Weight
- Hormones
Keeping our microbiome happy is essential for almost everything else happening in the body! The problem is, for many of us our gut balance between good bacteria and bad bacteria is way off. Whether you’re having obvious digestive symptoms (gas, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, etc.), or something else is going on in your body – you likely need to take a closer look into the health of your microbiome.
5 Ways Gut Health Impacts Fertility
One of the most clear connections between the health of your microbiome and fertility, is through the regulation of sex hormones, namely estrogen.

Gut Health and Hormone Balance
Estrogen is a hormone that the body makes, uses and then needs to get rid of. It goes through three phases of detoxification to be able to remove it from the body. The last step in the process is controlled by the gut microbiome.
There’s an enzyme in your large intestine called Beta glucuronidase, and it’s responsible for unpacking estrogen and allowing to it be re-circulated and re-absorbed in the body.
When you have high levels of B-glucuronidase, it’s usually a sign that you likely have excess estrogen in your body (estrogen dominance) and may have even experienced some of these symptoms, like menstrual cycle problems, painful periods, heavy bleeding, etc.
Signs of Estrogen Dominance:
- Mood swings/mood instability
- Water retention
- Difficulty losing body fat
- Acne and skin issues
- Irregular periods or anovulatory cycles
- Painful cycles
- Low sex drive
- Difficulty building lean muscle mass
- Poor recovery from exercise
- Sleep issues
When our bodies can’t eliminate excess estrogen through the GI tract it actually impairs fertility because it throws off the ratio between estrogen and progesterone, and ultimately causes a higher risk for miscarriage.
Remember, any dysbiosis prior to pregnancy is also going to worsen during pregnancy, so it’s a good idea to work on your gut health prior to conceiving.
According to a recent review, without a healthy microbiome, estrogen metabolism and function becomes impaired and can lead to a number of health consequences including endometriosis, PCOS, endometrial hyperplasia, and infertility.
Authors of this review concluded that treating the gut microbiome to modulate estrogen levels should be considered as a new future treatment for estrogen-mediated diseases including infertility.
Gut Health and Weight
The gut microbiome has been associated with higher pre-pregnancy weight as well as more weight gain during pregnancy. We know that excess weight impacts fertility, and researchers have found that those who are overweight have a different microbiome, with different types of bacterial strains than their normal weight counterparts.
There’s evidence that higher calorie diets rich in sugar and processed foods actually skew the balance of microbes. In fact, a recent study showed that the diversity of these microbes can be influenced by diet within just 24 hours!
Diets based in fruits, vegetables and plenty of fiber support the microbiome, whereas the Standard American Diet (SAD) has been shown to be detrimental to the microbiome.
Gut Health and Thyroid
As mentioned earlier, when there is an imbalance in the microbiome, it impacts immunologic and metabolic functions. A study in 2015 found that hypo- and hyper-thyroidism was associated to small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), and another study in 2019 found an association between dysbiosis and thyroid cancer and thyroid nodules.
Since your thyroid health is so important for not only all metabolic function, but also fertility, it’s important to take this into consideration.
An under-active thyroid can impact fertility in a few different ways:
- Decreased cellular energy – meaning less mitochondria (your cell’s powerhouse) on ovarian cells, causing irregular or absent cycles.
- Increased prolactin – which suppresses ovulation by blocking the release of FSH
- Decreased insulin sensitivity – more insulin in the blood increases androgens, which can disrupt ovulation and is especially detrimental for women with PCOS
Gut Health and Inflammation
You don’t need to have inflammatory bowel disease to have inflammation in the gut, or your gut causing inflammation in other parts of the body. For example, if you have intestinal permeability (aka “leaky gut”), there could be bacterial products entering the blood stream, causing your immune system to attack them and cause chronic inflammation.
Since inflammation is linked to so many chronic diseases and infertility, this is an important link to consider.
Gut Health and Pregnancy Complications
Research has shown the poor gut health was associated with higher risk of preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and preterm birth. The microbiome has also been looked at for infant health and studies have shown a connection between imbalances in the microbiome with increased risk of eczema, asthma, and allergies. A healthy microbiome will also contribute to your baby’s immune function, inflammation, and healthy weight throughout their life.
How Do I know if I need Help with my Gut Health and Fertility?
So by now I’m sure you’re convinced that gut health plays a major role in fertility. But how do you know if taking a daily probiotic is enough? Ask yourself:
- Have I been suffering with digestive issues for years (this is just my new “normal”)
- Do I often fluctuate between feeling constipated or having loose stools?
- Are there foods that I avoid because I can’t tolerate them?
- Do I have frequent acid reflux?
- Do I have signs of estrogen dominance? (heavy period, PMS, excess weight and weight loss resistance, etc.)
If you answered yes to any of these questions or you just feel that it’s time to take a closer look into your gut health, then set up a free discovery call with me to see how functional nutrition can help you on your fertility journey.
And let me know in the comments below what was surprising for you about this blog post!
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28778332
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25564410
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4216449/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4137456/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4845518/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2701523/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28388917
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30584647
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs12020-014-0509-2
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32070720
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32064643
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32063084
What is the GI-MAP test?
If you’ve ever heard that the gut is like the second brain, then you probably know that our gut health impacts our overall health, especially for fertility. Research has found that the gut microbiome impacts our digestion, immunity, metabolic and neuroendocrine functions, sleep, stress and so much more.
The GI MAP is a functional lab test that does a comprehensive analysis of your gut health. It looks at parasites, bacteria, fungi, inflammation markers, digestive enzymes and much more, and does so by targeting specific DNA of the organisms it tests.
The test looks at the DNA of pathogenic organisms like bacteria and viruses, but also the beneficial organisms (ie good bacteria) and the opportunistic bacteria as well.
The test looks at the specific genomes of these organisms that reside in the intestinal ecology. It’s a “Quantitate DNA test” – or real time test – which differentiates this test from other tests on the market.
The GI-MAP will actually measure how much of each strain exists in the gut, rather than just looking at a percentage.

Some Functional Markers in the GI MAP Test:
- Calprotectin– a measure of inflammation in the gut. Can be a sign of Crohn’s disease or IBD.
- Pancreatic elastase– the level of enzyme activity- how good are your levels of enzymes that digest protein, fat, carbs and fiber.
- Secretory IgA– a marker of the ‘reactivity’ of your gut immune layer. It represents the first line of immune defense of the gut. This is important when evaluating food intolerances
- Zonulin– a marker of leaky gut (intestinal permeability)
- B-glucoronidase- a measure of re-circulating toxins between the gut and the liver. You’ll see this marker elevated with excess estrogen and in people with poor liver detoxification.
- Steatocrit- amount of fat in the stool- measures fat absorption
- Gliadin IgA– an excellent measure of gluten intolerance

Why Not Order a Cheaper Gut Health Test?
Many of the consumer facing microbiome tests don’t actually give you a full picture of what’s happening in the gut – they don’t count bacteria or parasites present.
In fact, I’ve taken one of those tests in the past and just felt like I didn’t have any more answers to my questions.
The GI MAP is used by clinicians and provides the most comprehensive analysis of the gut microbiome compared to any other gut health test on the market. If you’re looking for real answers – test, don’t guess.
Why You Might Need a GI-MAP Stool Test for Gut Health and Fertility
Some conditions that could benefit from taking a GI Map stool test would be someone with:
- Autoimmune disease
- IBS/IBD
- Digestive complaints like diarrhea or constipation
- Brain fog, fatigue
- Joint pain
- Skin problems, like acne, rashes, hives or psoarisis
- Mood disorders, depression, anxiety
- Diabetes and weight loss issues
- Food intolerances
Why is Gut Health Important for Fertility?
I’ll be spending the next few weeks talking about how gut health impacts fertility, but there are a few high level concepts when it comes to the connection between fertility and gut health:
1. Hormone Balance- your gut directly plays a role in balancing the levels of estrogen in your body. If you suspect you have estrogen dominance, taking a comprehensive stool test would be a good place to start investigating.
2. Inflammation- your gut can cause some serious inflammation in the rest of your body. I love that the GI MAP can test for Zonulin, which is a marker of intestinal permeability or “leaky gut.” When toxins from the GI tract can leak into the bloodstream, this causes an immune response by the body, and triggers inflammation. When we work on fertility issues, the broad goal is to reduce overall inflammation so the body can prioritize reproductive health.
3. Insulin Resistance – A 2012 study found that dysbiosis and intestinal permeability impacted insulin levels, which then affected egg and sperm development.
The researchers also found that leaky gut and inflammation was a common cause of PCOS, and that insulin disruption was the most common cause for menstrual disruption and problems with ovulation.
How to Order the GI MAP Test
The test needs to be ordered by a qualified practitioner, such as myself. Interpreting the results requires understanding of gut bacteria, functional gastrointestinal health and experience dealing with dysbiosis or microbiome imbalances.
Interested to learn more? Book a free discovery call with me here to learn how we can use functional lab testing to address fertility.
If you suspect leaky gut or experiencing some of the symptoms listed above, we can discuss some options for you and work on your nutrition and lifestyle together to improve your microbiome.
Want more support?
1:1 Coaching: Let’s hop on a call to discuss what working together could look like & determine if we are a good fit
Grab my free Fertility Nutrient Guide and get added to our mailing list to get information like this sent to your inbox directly!
References
- Tremellen, K and Pearce, K (2012). Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota (DOGMA) – A novel theory for the development of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Med Hyspotheses’ 79, 1, 104-12.
The Preconception Playbook
This free playbook provides specific actionable tips to get started on your fertility journey, as well as what to avoid while you're trying to conceive.
Get the free playbook

