Resources
Style
Planning
View All
THE blog
For individuals and couples struggling to conceive, the road to parenthood can be filled with emotional and physical challenges. One lesser known yet significant factor in infertility is progesterone deficiency, a hormonal imbalance that plays a crucial role in the reproductive process. Understanding this condition and addressing it can make a profound difference in achieving conception and maintaining a healthy pregnancy.
What is Progesterone and Why Is It Important?
Progesterone is a steroid hormone primarily produced by the ovaries after ovulation, during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
It is essential for:
- Preparing the Uterine Lining: Progesterone thickens the endometrium, creating an optimal environment for a fertilized egg to implant.
- Maintaining Pregnancy: Once implantation occurs, progesterone supports the early stages of pregnancy by preventing the uterine lining from shedding.
- Regulating Menstrual Cycles: It balances estrogen levels, ensuring a regular and healthy cycle.
- Supporting Embryonic Development: Adequate progesterone levels contribute to the development of the placenta and the overall health of the embryo.
- Brain Health: Progesterone acts as a neurosteroid, promoting brain health, reducing anxiety, and supporting restful sleep. Progesterone’s calming effects can help mitigate stress and its negative impact on reproductive hormones.
Causes of Progesterone Deficiency

Progesterone deficiency, also known as luteal phase defect (LPD), can result from several underlying conditions or lifestyle factors, including:
- Ovulatory Disorders: Irregular or absent ovulation leads to inadequate progesterone production.
- Chronic Stress: Elevated cortisol levels can suppress progesterone synthesis. Chronic stress diverts resources from progesterone production to cortisol creation, exacerbating hormonal imbalances.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can disrupt progesterone production.
- Thyroid Dysfunction: Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can interfere with progesterone levels.
- Hypothalamic Amenorrhea: A condition often caused by excessive exercise, low body weight, or chronic stress. It disrupts the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis, preventing ovulation and leading to low progesterone levels.
- Insulin Resistance: High insulin levels can alter ovarian function, reducing progesterone production and contributing to irregular cycles.
- Brain Injury: Trauma or injuries affecting the brain can disrupt the signaling between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovaries, leading to hormonal imbalances and inadequate progesterone production.
- High Prolactin Levels: Elevated prolactin, often due to pituitary gland issues or breastfeeding, can suppress ovulation and reduce progesterone output.
- Hormonal Birth Control: Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives can suppress natural ovulation and progesterone production, sometimes leading to imbalances even after discontinuation.
- Steroid or Opioid Medications: Chronic use of these medications can interfere with the HPO axis and suppress ovarian function, impacting progesterone levels.
- Age: Natural declines in progesterone occur as women approach menopause, but they can also affect younger individuals.
- Poor Nutrition: A lack of key nutrients, such as vitamin B6, magnesium, and zinc, may impair hormone production.
Symptoms of Progesterone Deficiency
Recognizing the symptoms of progesterone deficiency is essential for early intervention. Progesterone plays a key role in regulating several aspects of health, particularly related to the menstrual cycle, mood, and cognitive function. When progesterone levels are insufficient, a wide array of symptoms may manifest, signaling the need for further evaluation.
Common Signs and Symptoms Include:
- Shortened Menstrual Cycles or Spotting Between Periods:
Progesterone plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy menstrual cycle. A deficiency can lead to shorter cycles, often less than 21 days, or cause spotting or bleeding between periods. This happens because insufficient progesterone may prevent the endometrial lining from fully developing, resulting in early shedding. - Difficulty Conceiving or Recurrent Miscarriages:
Progesterone is crucial for preparing the uterus for implantation and sustaining pregnancy. A deficiency can impair implantation, increase the risk of miscarriage, or lead to early pregnancy loss, particularly in the first trimester. Couples who have difficulty conceiving or who experience multiple miscarriages may find progesterone testing and support beneficial in addressing this issue. - Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) Symptoms, Such as Mood Swings and Irritability:
Low progesterone can disrupt the delicate balance between estrogen and progesterone during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, exacerbating PMS symptoms. Common mood-related symptoms include increased irritability, mood swings, anxiety, and emotional sensitivity. These hormonal fluctuations can also make it harder to manage stress or negative emotions during the premenstrual phase. - Breast Tenderness or Swelling:
Progesterone affects the mammary glands and contributes to breast tissue changes throughout the menstrual cycle. A deficiency can lead to discomfort, tenderness, or swelling of the breasts, especially in the days leading up to menstruation. - Fatigue and Low Energy Levels:
Progesterone is involved in regulating energy metabolism and promoting restorative sleep. Low levels can lead to chronic fatigue, feelings of sluggishness, or low energy levels. This can impact daily activities and create challenges in maintaining productivity and an active lifestyle. - Insomnia or Disrupted Sleep:
Progesterone has a calming effect on the nervous system, and low levels can interfere with sleep quality. Individuals with progesterone deficiency may struggle with insomnia or experience broken sleep, often waking up in the middle of the night. The disruption of sleep patterns can exacerbate other symptoms, such as fatigue and irritability. - Anxiety or Depression:
Progesterone has neuroprotective properties that support brain health and mood regulation. A deficiency may contribute to heightened feelings of anxiety, depression, or general emotional instability. Progesterone’s calming influence is essential for regulating the body’s stress response, and without it, individuals may feel more vulnerable to stressors. - Brain Fog and Difficulty Concentrating: Since progesterone plays a role in cognitive function, low levels can lead to brain fog, memory lapses, and difficulty concentrating. This is particularly noticeable during the luteal phase when progesterone naturally rises and falls. Women may find it harder to focus or process information, leading to decreased productivity and mental fatigue.

Additional Symptoms of Progesterone Deficiency May Include:
- Hot Flashes or Night Sweats:
Though more commonly associated with menopause, hot flashes and night sweats can also occur in individuals with low progesterone levels. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and disrupt daily routines or sleep. - Changes in Libido:
Progesterone contributes to a balanced hormonal environment, which includes regulating sexual desire. A deficiency may lead to a decreased libido or difficulty achieving sexual satisfaction. - Dry Skin or Hair Loss:
Low progesterone can disrupt the balance of other hormones, like estrogen, that support healthy skin and hair. As a result, individuals may experience dry or thinning skin, hair loss, or brittle nails. - Headaches or Migraines:
Progesterone deficiency can contribute to hormonal headaches or migraines, especially in the days leading up to menstruation. These headaches may be triggered or worsened by fluctuating hormone levels. - Digestive Issues:
Some individuals with progesterone deficiency may experience gastrointestinal symptoms like bloating, constipation, or changes in appetite. This is often linked to hormonal fluctuations that affect digestion and gut health.
Why Early Intervention Matters
Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking treatment is crucial to prevent long-term hormonal imbalances that can affect fertility and overall well-being. If multiple symptoms are present, especially if they interfere with daily life or reproductive health, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and to explore potential treatments.
How Progesterone Deficiency Impacts Fertility
A deficiency in progesterone can significantly affect fertility in the following ways:
- Implantation Failure: Without adequate progesterone, the uterine lining cannot sustain an implanted embryo.
- Early Pregnancy Loss: Low progesterone levels increase the risk of miscarriage, particularly in the first trimester.
- Irregular Ovulation: Insufficient progesterone disrupts the hormonal feedback loop necessary for regular ovulation.
- Impaired Stress Resilience: Low progesterone can amplify the body’s stress response, further hindering reproduction.
Diagnosing Progesterone Deficiency
Diagnosing progesterone deficiency requires a multifaceted approach:
- Symptom Assessment: A detailed medical history and symptom evaluation provide initial clues.
- Blood Tests: Measuring serum progesterone levels during the luteal phase can confirm deficiency.
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Charting: Tracking BBT helps identify ovulation and luteal phase length.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Evaluates ovulation and the thickness of the uterine lining.
Treatment Options for Progesterone Deficiency
The good news is that progesterone deficiency is often treatable. Here are some commonly recommended approaches:
Treating PCOS, thyroid disorders, or other contributing factors is critical for restoring hormonal balance.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Stress Management: Incorporate yoga, meditation, or other relaxation techniques to lower cortisol levels. Managing stress is a cornerstone of restoring hormonal balance.
Nutrition: Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, including leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins. Consuming foods that support progesterone production, such as vitamin B6-rich bananas and magnesium-rich spinach, is crucial.
Exercise: Moderate physical activity can improve hormonal balance without overtaxing the body.
Nutritional Supplements:
Vitamin B6: Supports progesterone production and helps regulate hormonal balance.
Magnesium: Aids in reducing stress and supporting endocrine health.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Promotes overall reproductive health.
Chasteberry (Vitex): An herbal remedy that can stimulate progesterone production by improving luteal phase function.
Hormonal Therapies:
Progesterone Supplements: Available as oral capsules, vaginal suppositories, or injections.
Clomiphene Citrate: Stimulates ovulation in cases of anovulatory cycles.
HCG Injections: Triggers ovulation and supports the corpus luteum.
Addressing Underlying Conditions:
Consider Acupuncture and Traditional Medicine
Acupuncture, a cornerstone of traditional Chinese medicine, has shown promise in improving reproductive health. By stimulating specific points in the body, acupuncture can enhance blood flow to the ovaries and uterus, regulate the menstrual cycle, and promote the release of hormones like progesterone. Consult a licensed acupuncturist with experience in fertility support for the best results.
Address Environmental Factors

Environmental toxins, known as endocrine disruptors, can interfere with hormone production. These chemicals, often found in plastics, cosmetics, and household products, mimic or block hormones, contributing to imbalances.
- Reduce Plastic Use: Opt for glass or stainless steel containers instead of plastic for food storage.
- Choose Clean Beauty Products: Look for skincare and makeup brands free from parabens, phthalates, and other hormone-disrupting chemicals.
- Filter Your Water: Install a water filtration system to reduce exposure to contaminants like pesticides or heavy metals that can interfere with reproductive health.
Build a Strong Support System
Hormonal imbalances, including progesterone deficiency, can feel isolating. Surrounding yourself with a support network can alleviate stress and provide encouragement. This might include:
- Joining fertility support groups to share experiences and gain emotional support.
- Seeking guidance from a holistic health practitioner, such as a naturopath, who specializes in hormone balance.
- Leaning on family and friends for reassurance and positivity throughout the journey.
When to Seek Help
If you suspect progesterone deficiency or have been trying to conceive without success for over a year (or six months if over 35), it’s time to seek professional guidance. Recurrent miscarriages or irregular menstrual cycles are also red flags that warrant medical evaluation.
Empowering Yourself Through Education and Advocacy
Understanding the impact of progesterone deficiency empowers individuals to advocate for their reproductive health. By recognizing symptoms, seeking appropriate medical care, and adopting a proactive approach to wellness, overcoming this hidden barrier to conception is possible.
Final Thoughts
Progesterone deficiency, though often overlooked, can profoundly impact fertility and overall well-being. With the right interventions and support, many individuals can overcome this challenge and achieve their dream of starting a family. Whether through lifestyle changes, nutritional support, or medical treatments, addressing progesterone deficiency is a key step toward reproductive success.
For anyone navigating infertility, remember you are not alone, and solutions exist. With persistence, knowledge, and the right healthcare team, the journey to conception becomes a shared effort with a hopeful destination.
Sources
https://drbrighten.com/boost-low-progesterone
https://drbrighten.com/hormones-affect-brain-health
https://integrative-medicine.ca/progesterone-in-functional-medicine/ https://whnacademy.com/courses/dutch/

Estrogen is a crucial hormone that significantly impacts health across all genders, but it plays an especially vital role in women. It’s essential for reproductive health, bone density, cardiovascular function, and mood regulation. However, imbalanced estrogen levels—particularly when excessive compared to other hormones—can lead to a range of issues, from weight gain to more severe conditions like breast cancer. This is where estrogen detoxification becomes essential.
Understanding how estrogen is metabolized, why detoxification matters, and how to support your body in maintaining hormonal balance is key. Below, we’ll explore the science of estrogen detox, the factors that can disrupt this process, and actionable steps to promote optimal hormone clearance.
What Is Estrogen Dominance?
Estrogen dominance occurs when there is too much estrogen in the body relative to progesterone. This imbalance can disrupt normal hormonal functions and lead to symptoms such as:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- PMS (premenstrual syndrome)
- Weight gain, especially around the hips and thighs
- Breast tenderness
- Mood swings, anxiety, or depression
- Low libido
- Fatigue
If left unmanaged, estrogen dominance may contribute to more severe conditions, including:
- Breast, ovarian, and uterine cancers
- Endometriosis
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Fibroids
- Insulin resistance
Factors contributing to estrogen dominance include chronic stress, poor liver function, gut dysbiosis, exposure to environmental toxins (xenoestrogens), and diet. These disruptors impair the body’s ability to properly metabolize and clear estrogen, leading to its accumulation in tissues.
How the Body Metabolizes Estrogen
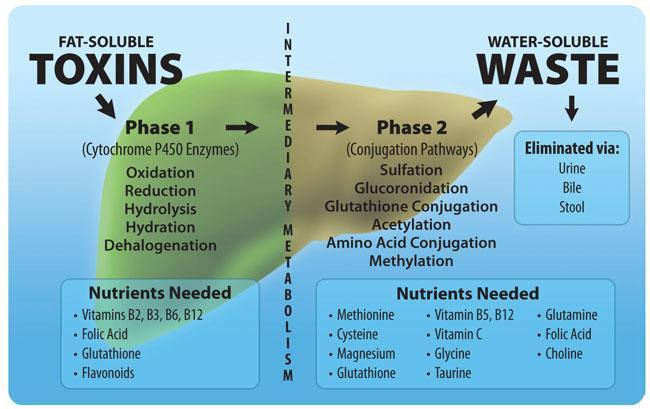
Estrogen detoxification primarily occurs in the liver through three interconnected phases:
Phase 1 Detoxification
In this phase, liver enzymes convert estrogen into three main metabolites:
- 2-hydroxyestrone (2-OH-E1): Protective and beneficial for the body.
- 4-hydroxyestrone (4-OH-E1): Potentially harmful if not detoxified further, as it can damage DNA and promote cancer cell growth.
- 16α-hydroxyestrone (16α-OH-E1): Harmful in excess and linked to increased estrogenic activity.
Phase 2 Detoxification
Here, estrogen metabolites are made water-soluble through conjugation. This step ensures they can be safely excreted via bile or urine. Methylation, a key part of this process, relies on nutrients like B vitamins and magnesium.
Phase 3 DetoxificationIn this final phase, conjugated estrogen is excreted through the gut or kidneys. A healthy gut microbiome is crucial because an enzyme called beta-glucuronidase, produced by gut bacteria, can reactivate conjugated estrogen, allowing it to re-enter circulation.

Why Estrogen Detox Matters
Efficient estrogen detoxification is essential to prevent the harmful effects of estrogen dominance. Improper clearance of estrogen metabolites can:
- Bind to estrogen receptors in tissues, promoting conditions like endometriosis and fibroids.
- Increase cancer risk, particularly estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. The metabolite 4-OH-E1 can damage DNA and stimulate cancer cell growth if not detoxified properly.
When estrogen metabolites are not effectively processed and eliminated, they can circulate in the body, amplifying hormonal imbalances. This can exacerbate symptoms of PMS, disrupt menstrual cycles, and lead to inflammation. Additionally, high levels of harmful estrogen metabolites can interfere with other hormonal pathways, contributing to issues like insulin resistance and thyroid dysfunction.
Supporting your body’s ability to produce protective estrogen metabolites (like 2-OH-E1) and ensuring efficient elimination reduces these risks and improves overall hormonal balance. This not only lowers the likelihood of developing hormone-related cancers but also enhances quality of life by alleviating symptoms such as mood swings, bloating, and fatigue.
Factors That Impair Estrogen Detox
Estrogen detoxification is a delicate process that can be easily disrupted by various factors. When any of these factors are present, your body’s ability to clear excess estrogen effectively is compromised, leading to an accumulation of harmful metabolites. This, in turn, can contribute to hormone imbalances and related health issues. Here are the key factors that can hinder estrogen detoxification:
1. Poor Liver Health
The liver is your body’s powerhouse for processing and detoxifying estrogen. It converts estrogen into metabolites that can be safely excreted from the body. However, if your liver is overburdened or not functioning optimally, estrogen metabolism can be slowed down, leading to a buildup of harmful estrogen metabolites.
- Diet Impact: Diets high in alcohol, processed foods, and trans fats can overwhelm the liver, making it less efficient at detoxifying estrogen. These foods create a toxic environment in the body, leading to inflammation and oxidative stress, which interfere with the liver’s detoxification pathways.
- Support for the Liver: To support liver function, focus on a nutrient-dense diet rich in antioxidants, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and kale, which promote healthy liver detox processes.
2. Gut Dysbiosis: The Role of Your Microbiome
Did you know that your gut plays a crucial role in estrogen detoxification? An imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can significantly impact estrogen metabolism. When the gut is not balanced, harmful bacteria can thrive, leading to an increase in an enzyme called beta-glucuronidase. This enzyme has the ability to reactivate estrogen metabolites that have already been processed by the liver, causing them to re-enter circulation and elevate estrogen levels.
- Gut Health and Estrogen: Conditions like small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) can exacerbate gut dysbiosis, further contributing to this reactivation process. A compromised gut microbiome not only disrupts estrogen clearance but can also lead to symptoms like bloating, digestive discomfort, and inflammation.
- Supporting Gut Health: To support your gut health and estrogen detox, incorporate fiber-rich foods into your diet. Fiber helps bind to estrogen in the digestive tract and ensures its safe excretion. Probiotics and prebiotics, found in foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables, can also help balance your gut bacteria and reduce beta-glucuronidase activity.

3. Exposure to Xenoestrogens: The Hidden Estrogen Mimics
Xenoestrogens are synthetic compounds that mimic the structure and effects of estrogen in the body. These chemicals are found in many common products, from plastics and pesticides to personal care items like lotions, shampoos, and deodorants. Over time, repeated exposure to xenoestrogens adds to your overall estrogen burden, making it harder for your body to maintain balance and clear excess estrogen effectively.
- Environmental Toxins: These synthetic estrogen mimics can disrupt the body’s natural hormone balance, causing estrogen dominance and increasing the risk of estrogen-related conditions like fibroids, endometriosis, and certain types of breast cancer.
- Reducing Exposure: To minimize exposure to xenoestrogens, choose natural personal care products that are free of parabens and phthalates. Opt for BPA-free plastics or glass containers for food storage, and choose organic produce to reduce pesticide exposure. Small changes like these can help reduce your body’s overall toxic load and support better estrogen detox.
4. Chronic Stress: The Hormonal Balancer Under Siege
Chronic stress is a modern-day epidemic that impacts nearly every aspect of our health, including hormonal balance. When you’re stressed, your body releases cortisol, a hormone that is crucial for managing stress responses. However, prolonged high levels of cortisol can have a negative impact on estrogen detox.
- Cortisol and Estrogen: Elevated cortisol suppresses the production of progesterone, the hormone that works in balance with estrogen. When progesterone levels drop, estrogen dominance is more likely to occur. Additionally, chronic stress can interfere with liver function, impairing the detoxification process even further.
- Stress Management: To manage stress and support hormonal balance, prioritize self-care practices like mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and yoga. Regular physical activity can also help lower cortisol levels and improve overall hormonal health. Ensuring you get enough sleep is another key factor in managing stress and supporting your body’s detox pathways.
By understanding how these factors impair estrogen detoxification, you can take steps to minimize their impact and support your body’s ability to metabolize and eliminate estrogen effectively. A balanced diet, healthy gut, stress management, and minimizing exposure to environmental toxins are all important actions that can help optimize estrogen clearance and promote overall hormonal health.
How to Support Estrogen Detox
The good news is that you can take proactive steps to enhance your body’s estrogen detoxification process. Here are key strategies:
1. Prioritize Liver Health
The liver plays a central role in estrogen metabolism. To support liver function:
- Eat cruciferous vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, kale, and Brussels sprouts are rich in indole-3-carbinol (I3C) and sulforaphane, which promote protective estrogen metabolism.
- Increase antioxidants: Foods like berries, green tea, and turmeric combat oxidative stress and support liver enzymes.
- Support methylation: Consume foods high in B vitamins (leafy greens, eggs, and legumes) and magnesium to aid conjugation in phase 2 detox.
- Limit alcohol intake: Alcohol burdens the liver and disrupts estrogen detox.
- Use liver-supportive herbs: Milk thistle and dandelion root enhance liver function.
2. Optimize Gut Health
A healthy gut is essential for proper estrogen clearance:
- Consume fiber-rich foods: Fiber binds to estrogen in the gut, promoting excretion. Aim for 25-30 grams daily from vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains.
- Take probiotics: Strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium reduce beta-glucuronidase activity and improve gut health.
- Avoid inflammatory foods: Limit processed foods, sugar, and artificial additives.
- Stay hydrated: Adequate water intake supports bowel regularity and estrogen elimination.
3. Manage Stress
Chronic stress disrupts hormonal balance. To manage stress:
- Practice mindfulness techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Prioritize sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality rest.
- Engage in regular exercise: Physical activity reduces cortisol and supports estrogen metabolism.
4. Limit Exposure to Xenoestrogens
Minimize environmental toxin exposure by:
- Using natural personal care products free of parabens and phthalates.
- Avoiding plastic containers: Opt for glass or stainless steel for food storage.
- Choosing organic produce: Reduce pesticide exposure.
5. Consider Supplements
Certain supplements can enhance estrogen detox, but consult a healthcare provider before starting any new regimen. Common options include:
- DIM (diindolylmethane): Supports protective estrogen metabolism.
- Calcium-D-Glucarate: Reduces beta-glucuronidase activity, preventing estrogen reabsorption.
- Milk Thistle: Promotes liver function and detoxification.
- Probiotics: Help balance gut bacteria for efficient estrogen clearance.
The Bigger Picture: Estrogen and Breast Cancer
The link between estrogen and breast cancer highlights the importance of efficient hormone clearance. As experts note, it’s not estrogen itself but the balance of its metabolites that determines risk. Shifting your body’s metabolism toward protective pathways while ensuring effective elimination can lower the risk of hormone-related cancers.
Moreover, addressing estrogen dominance isn’t just about reducing disease risk. It’s also about improving quality of life by alleviating symptoms like mood swings, fatigue, and PMS, allowing you to feel more balanced and energized.
Final Thoughts
Estrogen detox is a vital aspect of hormonal health. By supporting your liver, optimizing gut health, managing stress, and reducing exposure to environmental toxins, you can promote efficient estrogen metabolism and lower the risk of hormone-related conditions.
Remember, achieving estrogen balance takes time and consistent effort. If you suspect estrogen dominance or experience related symptoms, consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance. Taking proactive steps now can pave the way for a healthier, more balanced future.
Sources
https://drbrighten.com/what-is-estrogen-dominance-what-to-do-about-it/#h-what-is-estrogen-dominance
https://drbrighten.com/estrogen-and-breast-cancer/#h-how-exactly-is-estrogen-linked-to-breast-cancer
https://future-woman.com/the-basics-of-oestrogen-detox/ https://drruscio.com/flush-out-excess-estrogen/

Secondary infertility—the challenge of conceiving or carrying a pregnancy to term after previously giving birth—can be an emotional and frustrating experience for many families. But just remember: you’re not alone. This condition affects about 10% of couples. The good news is that functional nutrition offers an empowering way to address some of the root causes of secondary infertility, supporting your body and boosting your chances of growing your family. In this post, we’ll explore evidence-based nutritional strategies to help you on your journey.

Secondary infertility is complex, with causes ranging from hormonal imbalances and structural issues to lifestyle factors like stress and diet. Age-related fertility changes, ovulation disorders, diminished ovarian reserve, and male infertility are common culprits. Functional nutrition focuses on addressing these root causes through personalized dietary and lifestyle changes, helping to create the best possible conditions for conception and a healthy pregnancy.
How Functional Nutrition Supports Fertility
Functional nutrition takes a whole-person approach, targeting underlying factors that might be affecting your fertility. From reducing inflammation to balancing hormones, these strategies are here to support your health and your baby dreams. Let’s dive into the key areas:
1. Taming Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress—an imbalance between damaging free radicals and protective antioxidants—can harm both egg and sperm quality. Research reveals that oxidative stress disrupts hormone production and even affects embryo implantation.
Oxidative stress is particularly problematic because it can reduce ovarian reserve and negatively impact sperm motility and morphology. Studies emphasize the importance of addressing oxidative damage to improve reproductive outcomes. Furthermore, chronic oxidative stress can exacerbate conditions like endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), compounding fertility challenges.

Here’s how to tackle oxidative stress:
- Eat Your Antioxidants: Fill your plate with colorful fruits and veggies like berries, oranges, spinach, and bell peppers. Antioxidant-rich foods combat oxidative damage and protect reproductive cells.
- Boost Omega-3s: Fatty fish like salmon and plant-based options like flaxseeds and walnuts help lower inflammation and protect against oxidative stress.
- Consider CoQ10: This powerful antioxidant, found in organ meats and supplements, improves mitochondrial function in eggs and sperm, enhancing their quality and viability.
- Include Vitamin E and C: These vitamins work synergistically to neutralize free radicals and improve reproductive outcomes. Nuts, seeds, citrus fruits, and strawberries are excellent sources.
- Explore Selenium and Glutathione: Selenium, found in Brazil nuts, and glutathione, synthesized within the body, are essential antioxidants that play key roles in reducing oxidative stress in reproductive tissues
2. Balancing Hormones Naturally
Hormonal imbalances are a common barrier to conception. Functional nutrition can help stabilize blood sugar, enhance liver detoxification, and supply key nutrients to support hormone health:
- Balance Blood Sugar: Swap refined carbs for whole grains, legumes, and veggies to avoid insulin spikes, which can throw hormones out of sync. Studies have shown that stable blood sugar levels support ovulation and reduce symptoms of PCOS.
- Support Your Liver: Include cruciferous veggies like broccoli, kale, and Brussels sprouts to help your body metabolize hormones effectively. Your liver plays a crucial role in detoxifying excess estrogen, maintaining hormonal harmony.
- Power Up with Micronutrients: Zinc (in pumpkin seeds and oysters), magnesium (in spinach and almonds), and vitamin B6 (in bananas and chickpeas) are all hormone heroes. Research highlights the importance of these nutrients in regulating the menstrual cycle and promoting fertility.
- Manage Stress Hormones: Chronic stress can disrupt the delicate balance of reproductive hormones. Incorporate stress-relief practices like yoga, meditation, or even gentle walks in nature alongside stress-adaptable foods like leafy greens and whole grains.
- Include Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, walnuts, and chia seeds help build the building blocks of reproductive hormones while reducing inflammation.
3. Prioritizing Gut Health
Your gut health impacts everything from inflammation to hormone regulation. An imbalance in gut bacteria, called dysbiosis, can disrupt reproductive health. Emerging research shows the connection between gut microbiota and fertility, with gut health influencing hormone metabolism, immune function, and nutrient absorption
Studies show that:
- Gut Dysbiosis Affects Hormonal Balance: An imbalanced microbiome can interfere with estrogen metabolism, potentially leading to conditions like PCOS and endometriosis that hinder fertility.
- A Healthy Gut Reduces Inflammation: A diverse and balanced microbiome helps lower systemic inflammation, creating a more favorable environment for conception.
- Probiotic Support Can Boost Fertility: Specific probiotic strains have been shown to improve reproductive health by modulating the immune system and supporting a balanced microbiota.
Here’s how to nurture your gut:
- Load Up on Fiber: Whole grains, fruits, and veggies provide prebiotic fiber that feeds beneficial gut bacteria. Fiber-rich foods also help eliminate excess hormones, maintaining hormonal balance.
- Try Fermented Foods: Yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut are rich in probiotics that support a healthy gut microbiome.
- Add Probiotic Supplements: Consider strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which have been shown to improve gut and reproductive health. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
- Skip Processed Foods: Refined sugars and additives can harm your gut microbiome and increase inflammation. Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods to support gut health and fertility.
- Hydrate Well: Drinking plenty of water aids digestion and supports the gut lining, promoting overall gut health.

4. Filling Nutrient Gaps
Certain nutrient deficiencies can hinder fertility. Functional nutrition ensures you’re getting enough of the essentials:
- Folate: Found in leafy greens, lentils, and fortified cereals, folate supports egg quality and early fetal development. Studies show folate also plays a critical role in reducing neural tube defects and supporting sperm health.
- Vitamin D: This sunshine vitamin is linked to better fertility and pregnancy outcomes. Enjoy fatty fish, fortified milk, or a walk in the sun to keep levels up. Research highlights its role in improving ovarian function and endometrial health.
- Iron: Essential for ovulation and pregnancy, iron is abundant in lean meats, beans, and dark leafy greens. Low iron levels can disrupt ovulatory cycles and impact embryo implantation.
- Vitamin B12: Found in eggs, dairy, and fortified foods, this nutrient supports red blood cell production and neurological health, both of which are critical for a healthy pregnancy.
- Choline: Often overlooked, choline, found in eggs and fish, is vital for fetal brain development and placental function.
5. Stress Less for Better Fertility
Stress has a profound impact on fertility by disrupting the hormonal balance necessary for ovulation and implantation. Chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol and other stress hormones, which can suppress the production of reproductive hormones like luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This hormonal imbalance may lead to irregular menstrual cycles and impaired ovulation, making conception more challenging.
Evidence-Backed Strategies to Reduce Stress:
- Mind-Body Interventions: Practices like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) have been shown to decrease cortisol levels and improve fertility outcomes. MBSR can enhance emotional resilience, which is crucial for couples navigating the challenges of secondary infertility.
- Regular Physical Activity: Moderate-intensity exercise like walking, swimming, or cycling helps lower stress hormone levels and improve mood. However, it’s essential to avoid overtraining, as excessive physical stress can negatively impact ovulation.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT has been effective in reducing stress-related infertility. It helps individuals reframe negative thoughts and develop coping mechanisms, ultimately improving reproductive outcomes.
- Dietary Support: Foods rich in magnesium (dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds) and adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha may help regulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, reducing cortisol levels and improving hormonal harmony.
- Social Support and Counseling: Emotional support from partners, friends, or support groups can significantly reduce stress and improve mental health during the journey of secondary infertility.

6. Don’t Forget Male Fertility
Male fertility plays an equally critical role in conception, with sperm quality being a significant factor in secondary infertility. Up to 50% of infertility cases involve male factors, such as low sperm count, poor motility, or abnormal morphology.
- Antioxidant Supplementation: Oxidative stress is a major contributor to sperm dysfunction. Antioxidants like CoQ10, vitamin C, and selenium have been shown to improve sperm motility, count, and overall quality (PubMed 33750412, PMC6102891). A daily intake of CoQ10, for instance, enhances mitochondrial function in sperm, leading to improved motility and fertilization capacity.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Reducing alcohol and tobacco use is essential, as both have been linked to sperm DNA damage and reduced motility (PubMed 15327187). Limiting exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metals, can further protect sperm health (PMC10956697).
Nutritional Support:
- Zinc and Selenium: Found in oysters, Brazil nuts, and seeds, these trace minerals are critical for sperm production and protection against oxidative stress.
- Folate and B12: These vitamins support DNA synthesis and repair in sperm, reducing the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
Healthy Weight Management: Obesity negatively affects testosterone levels and sperm quality. Adopting a balanced diet and regular exercise routine can improve hormonal balance and reproductive outcomes.
Regular Medical Check-Ups: Conditions like varicocele, hormonal imbalances, or infections can impair sperm quality. Early diagnosis and treatment of underlying issues significantly enhance fertility potential.
Your Action Plan for Functional Nutrition
Ready to take charge? Here are some steps to get started:
- Identify and Address Deficiencies: Partner with a healthcare provider to test for and correct nutrient gaps.
- Adopt a Whole-Foods Approach: Stick to nutrient-dense, minimally processed foods for maximum health benefits.
- Avoid Toxins: Limit exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals in plastics, pesticides, and cosmetics.
- Track Your Cycle: Monitoring your menstrual cycle can reveal patterns and help time conception.
- Prioritize Rest and Movement: Moderate exercise and quality sleep are vital for hormonal balance and stress management.
The Bottom Line
Secondary infertility can be a challenging journey, but it’s one you don’t have to face alone. Functional nutrition offers a hopeful path forward by addressing the root causes of infertility and optimizing your body for conception. By nourishing yourself with the right foods, reducing stress, and supporting your overall health, you’re giving your body the best chance to thrive.
If you’re struggling with secondary infertility, consider reaching out to a functional nutrition expert for a personalized plan. With the right tools and support, your family dreams are within reach. Here’s to hope, health, and new beginnings!
Sources
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21139-secondary-infertility
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15327187
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28677273
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33750412
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10956697
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10766669
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10608597
https://rep.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/rep/164/6/REP-22-0152.xml
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6102891
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9800796
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8582214
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34918486/ https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10349861/

The postpartum period is a transformative and challenging time for new mothers. As you care for your newborn, your own health often takes a backseat. However, prioritizing nutrition is essential for recovery, energy, and overall well-being. Here, we’ll explore the key nutritional considerations for postpartum moms, supported by expert insights and practical tips.

1. Supporting Hormonal Balance
After childbirth, your hormone levels experience significant fluctuations. Estrogen and progesterone drop rapidly, while prolactin rises to support breastfeeding. This hormonal upheaval can contribute to mood swings, fatigue, and even postpartum depression.
Key Nutrients to Focus On:
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA and EPA, found in salmon, sardines, walnuts, and flaxseeds, support brain health and may help stabilize mood. Research highlights that omega-3s can also play a role in reducing inflammation and supporting cognitive function during the postpartum period. Additionally, these fats are essential for the development of the baby’s brain and nervous system, especially during breastfeeding.
- B Vitamins: These are crucial for neurotransmitter production, which helps combat “mommy brain” and postpartum depression. Vitamin B6, found in salmon, poultry, and bananas, aids serotonin production, while B12, abundant in eggs and lean meats, supports energy metabolism and neurological health. Studies link B vitamin deficiencies to mood disorders, emphasizing their importance during postpartum recovery.
- Magnesium: This essential mineral helps regulate stress, improve sleep quality, and support muscle recovery. Found in dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, magnesium’s calming effects are particularly beneficial for new moms facing sleep deprivation and stress.
Lifestyle Tip: Adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha and Rhodiola can help balance cortisol levels and support adrenal health, which are often compromised during the postpartum period. These herbs may aid in reducing fatigue and enhancing resilience to stress, but they should be used under professional guidance
2. Boosting Energy Levels
Fatigue is a common postpartum challenge, often exacerbated by interrupted sleep and physical recovery from childbirth. Nutritional strategies can play a pivotal role in boosting your energy reserves.

Key Foods for Sustained Energy:
- Complex Carbohydrates: Foods like sweet potatoes, quinoa, and oats are rich in fiber and slow-digesting carbohydrates that provide steady energy throughout the day. These complex carbs help prevent energy crashes by stabilizing blood sugar levels.
- Protein-Rich Foods: Protein is essential for muscle repair, recovery, and sustained energy. Incorporate eggs, lean meats, tofu, and legumes into your meals. Protein also supports satiety, helping you stay energized and focused for longer periods of time.
- Iron-Rich Foods: Postpartum moms are at an increased risk of iron deficiency, especially after blood loss during delivery. Include iron-rich foods like spinach, red meat, and lentils in your diet. Pair these with vitamin C-rich foods (bell peppers, citrus fruits) to enhance absorption and combat fatigue associated with anemia
- Healthy Fats: Don’t overlook the importance of healthy fats like avocados, olive oil, and nuts, which provide a slow-burning source of energy and support overall cellular health.
Hydration: Dehydration can exacerbate feelings of fatigue and hinder milk production for breastfeeding mothers. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, and consider incorporating herbal teas or electrolyte-rich drinks for added hydration. Keep a water bottle handy to remind yourself to sip throughout the day.Snack Smart: Opt for nutrient-dense snacks that combine protein, healthy fats, and complex carbs to maintain steady energy levels. Examples include Greek yogurt with granola, apple slices with almond butter, or hummus with whole-grain crackers.
3. Enhancing Breastfeeding Nutrition

For breastfeeding moms, the nutritional demands increase significantly. Breast milk production requires an additional 450-500 calories per day, along with a higher intake of certain nutrients.
Breastfeeding-Friendly Nutrients:
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Essential for maintaining bone health, these nutrients are crucial for both mom and baby. Calcium can be found in dairy products, fortified plant-based milks, almonds, and dark leafy greens, while vitamin D can be obtained from fortified foods and sunlight exposure. Adequate vitamin D is particularly vital for preventing bone demineralization in breastfeeding moms.
- Zinc: This mineral is critical for immune function and cellular repair. Zinc is abundant in foods like shellfish, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Its role in wound healing is especially important for moms recovering from childbirth or C-sections.
- Choline: Found in eggs, liver, and fish, choline is vital for infant brain development and maternal cognitive function. Research emphasizes the importance of choline for neurodevelopment, particularly during lactation.
Foods to Avoid or Limit:
- Caffeine: While small amounts are generally safe, excessive caffeine can pass into breast milk and disrupt your baby’s sleep patterns. Limit intake to one to two cups of coffee per day.
- Alcohol: Alcohol can also pass into breast milk and affect your baby’s development. If you choose to drink, wait at least two hours per drink before breastfeeding to allow your body to metabolize the alcohol.
Snack Ideas for Breastfeeding Moms:
- Greek yogurt with berries and granola: Provides calcium, probiotics, and antioxidants.
- Hummus with carrot and cucumber sticks: Packed with fiber and plant-based protein.
Almond butter on whole-grain toast: A nutrient-dense snack rich in healthy fats, protein, and complex carbs.
4. Promoting Postpartum Recovery
Healing after childbirth requires specific nutrients to support tissue repair and combat inflammation. This is particularly important for moms recovering from C-sections or Healing after childbirth requires specific nutrients to support tissue repair and combat inflammation. This is particularly important for moms recovering from C-sections or perineal tears.

Recovery-Boosting Foods:
- Collagen-Rich Foods: Foods like bone broth, chicken skin, and gelatin provide collagen, a structural protein that aids in tissue repair and skin elasticity. Collagen is especially beneficial for healing wounds and repairing connective tissues stressed during childbirth.
- Vitamin C: This powerful antioxidant is vital for collagen production and wound healing. Include vitamin C-rich foods such as oranges, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli in your diet to support tissue regeneration and enhance your immune system.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Turmeric, ginger, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel are rich in anti-inflammatory compounds. These foods help reduce inflammation, promote faster recovery, and alleviate postpartum discomfort.
5. Addressing Postpartum Hair Loss
Many moms experience postpartum hair loss due to hormonal changes. While this is usually temporary, certain nutrients can support hair regrowth.
Key Nutrients for Hair Health:
- Biotin: Found in eggs, nuts, seeds, and sweet potatoes, biotin strengthens hair and nails by supporting keratin production. Studies suggest that biotin supplementation can help reduce hair shedding and improve hair thickness.
- Iron and Zinc: Both minerals are crucial for healthy hair follicles and preventing excessive shedding. Iron-rich foods include lean meats, spinach, and lentils, while zinc can be obtained from shellfish, legumes, and some seeds like pumpkin, hemp, and chia. Iron deficiency anemia is a common postpartum issue that can exacerbate hair loss.
- Protein: Since hair is made of keratin, a structural protein, consuming adequate protein is essential for hair health. Incorporate lean meats, fish, eggs, and plant-based proteins like quinoa and tofu into your diet.
Lifestyle Tip: Avoid tight hairstyles and harsh treatments, such as excessive heat styling or chemical processes, which can weaken fragile postpartum hair. Opt for gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners enriched with nourishing ingredients like argan oil or keratin.
6. Preventing Postpartum Depression
Nutrition plays a significant role in mental health, and deficiencies in key nutrients can contribute to postpartum depression.

Mood-Boosting Nutrients:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These essential fats, found in fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and algae-based supplements, are crucial for brain function and mood regulation. Research shows that omega-3s can help reduce the risk of postpartum depression (PPD) by supporting the brain’s ability to produce mood-regulating neurotransmitters like serotonin. For those who don’t consume fish, algae-based supplements offer a plant-based option that can help meet your omega-3 needs.
- Vitamin D: A deficiency in vitamin D has been strongly linked to depression. Adequate levels of vitamin D help regulate mood and may reduce the risk of PPD. Vitamin D is produced in the skin through sunlight exposure, but it can also be obtained through fortified foods and supplements.
- Probiotics: Gut health and mental health are deeply interconnected, with studies showing that a balanced gut microbiome can positively impact mood and reduce stress. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut, rich in beneficial bacteria, can support gut health and, in turn, emotional well-being.
Mindfulness Tip: Combine good nutrition with self-care practices like meditation, gentle exercise, and connecting with loved ones. These practices can help to reduce stress, support emotional resilience, and promote overall well-being during the postpartum period.
7. Practical Tips for Postpartum Nutrition
Balancing your own nutrition with the demands of a newborn can be overwhelming. Here are some practical strategies to make it easier:

Meal Prepping: Prepare and freeze nutrient-dense meals before delivery. This ensures you have access to nourishing food during the busy postpartum weeks. Consider meals with healthy fats, protein, and complex carbs to sustain your energy.
Nutrient-Dense Snacks: Keep easy, nutrient-packed snacks like trail mix, hard-boiled eggs, protein bars, and even pre-portioned fruit or veggie packs. These can help keep your blood sugar stable and give you the energy needed for breastfeeding and taking care of your baby.
Accept Help: Allow friends and family to assist with meal preparation, groceries, or even just getting a little extra sleep. It’s important to remember that self-care involves accepting support when needed.
Supplements: Consider a high-quality postpartum multivitamin and specific supplements like omega-3s and probiotics. These can help fill any nutritional gaps, especially if you’re feeling depleted during the early stages of motherhood. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
8. Long-Term Nutrition for Postpartum Health
The postpartum period extends beyond the initial weeks after birth. Continued attention to your diet can support long-term health and energy levels.

Key Focus Areas:
- Balance of Macronutrients:Maintaining a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is key for sustained energy. Whole foods, such as lean meats, legumes, and whole grains, provide necessary nutrients and help balance blood sugar, which is essential for both mood stability and physical recovery.
- Prioritize Whole, Unprocessed Foods: A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods is beneficial for reducing inflammation, supporting hormonal balance, and providing the necessary nutrients for recovery. This includes incorporating fresh fruits and vegetables, healthy fats (like those from avocado, nuts, and olive oil), and quality protein sources (such as eggs, lean meat, and legumes). Anti-inflammatory foods like berries, leafy greens, and turmeric can also help reduce any postpartum swelling and improve recovery time.
- Stay Active: Gentle exercises, such as walking, yoga, or pilates, can be beneficial for postpartum recovery. These activities can help improve mood, reduce stress, and support physical recovery. Hormonal fluctuations can also contribute to fatigue and emotional highs and lows, but light movement can help regulate these changes over time. Avoid overexertion, especially if you’re still adjusting to your new physical condition.
- Adrenal Fatigue and Postpartum Care: Postpartum mothers often experience adrenal fatigue, which can exacerbate feelings of exhaustion and mood instability. This occurs due to the stress of labor, childbirth, and the transition to motherhood. To support your adrenal health, make sure you’re getting enough sleep, managing stress, and eating nutrient-dense foods rich in vitamin C (such as citrus fruits, bell peppers, and leafy greens) and B vitamins (found in whole grains and lean meats).
Conclusion
Postpartum nutrition is about more than just eating; it’s about nourishing your body, mind, and spirit as you navigate motherhood. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods, staying hydrated, and listening to your body’s needs, you can promote recovery, boost energy, and enhance overall well-being. Remember, taking care of yourself is not selfish—it’s essential for being the best mom you can be.
Your journey to postpartum health is unique, so tailor these recommendations to your personal needs and consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Sources:
https://drbrighten.com/adrenal-fatigue-mom
https://drbrighten.com/balance-hormones-while-breastfeeding
https://drbrighten.com/5-ways-to-improve-your-early-postpartum-care
https://drbrighten.com/8-ways-to-eliminate-postpartum-depression-and-be-free-of-mommy-brain
https://drbrighten.com/can-you-prevent-postpartum-hair-loss
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6380979
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25573272
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32357982/ https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0235806

Written by: Lauren Chamberlain
Edited and Reviewed By: Anabelle Clebaner MS, RDN
Endometriosis—what a mouthful, right? This chronic condition affects an estimated 10% of women of reproductive age worldwide. But despite how common it is, endometriosis often feels like a lonely battle. Essentially, it involves endometrial-like tissue growing outside the uterus, leading to pain, infertility, and a host of other pesky symptoms. While traditional treatments like hormonal therapy and surgery can help, functional nutrition offers a fresh, empowering perspective.
Let’s dig into how the right foods can help you take charge of your health and tackle endometriosis head-on.
Let’s Break It Down: What Causes Endometriosis?
Spoiler alert: scientists are still piecing together the puzzle of endometriosis. While the exact cause remains unclear, research points to several contributing factors:
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation plays a central role, fueling lesion growth and pain.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Estrogen dominance often exacerbates symptoms.
- Immune Dysregulation: The immune system may fail to recognize and clear out misplaced endometrial-like tissue.
- Oxidative Stress: Elevated oxidative stress can worsen symptoms by damaging tissues and promoting inflammation.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) like BPA and phthalates may increase your risk.
Good news? Many of these factors can be influenced by your diet and lifestyle choices. Let’s unpack the connection between what’s on your plate and how your body feels.
Inflammation and Food: The Connection
Inflammation is like the annoying party guest that just won’t leave—especially for those dealing with endometriosis. Here’s how your food choices can either fan the flames or help cool things down:
The Culprits
- Processed Foods: Packaged snacks, fast food, and sugary treats are loaded with additives that promote inflammation.
- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread, pasta, and other refined carbs cause blood sugar spikes, triggering inflammatory pathways.
- Seed Oils: Vegetable oils like soybean, corn, and sunflower oils are loaded with omega-6 fatty acids, which can exacerbate inflammation if not balanced by omega-3s or when consumed in excess.
The Heroes
- Fruits and Vegetables: Packed with antioxidants and phytochemicals, these help neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation. Focus on leafy greens, berries, and cruciferous veggies like broccoli and cauliflower.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in salmon, chia seeds, and walnuts, omega-3s reduce prostaglandins, compounds that worsen pain and inflammation.
- Herbs and Spices: Turmeric, ginger, and cinnamon have anti-inflammatory properties that can calm flare-ups.
Pro Tip
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet doesn’t mean a complete overhaul overnight. Start small—swap out your usual snack for a handful of nuts, or add a side of roasted veggies to your dinner. Every bite counts!
Eat This, Not That: Functional Nutrition for Endometriosis
Functional nutrition isn’t about deprivation—it’s about giving your body the tools it needs to thrive. Let’s dive into some strategies:
1. Fight Fire with Food: Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Inflammation is the not-so-secret villain in the endometriosis saga. Luckily, you can put out the flames with foods rich in omega-3s, like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds. These goodies help reduce prostaglandin production, which means less pain.
Load up on: Leafy greens, berries, turmeric, and ginger—nature’s anti-inflammatory superstars.
Steer clear of: Processed foods, seed oils and sugary treats. Sorry, donut lovers.
2. Hormonal Harmony: Balancing Estrogen
Estrogen dominance is a common villain in the endometriosis story. When estrogen levels are out of whack, it can exacerbate symptoms like pain and bloating. Here’s how to bring balance back:
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, kale, and Brussels sprouts contain indole-3-carbinol, a compound that supports estrogen detoxification in the liver.
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Whole grains, legumes, and flaxseeds help your gut efficiently excrete excess estrogen. Bonus: They also feed your friendly gut bacteria!
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: These can interfere with your liver’s ability to metabolize hormones, so moderation is key.
3. Gut Check: Heal from the Inside Out
Did you know your gut is like the command center for inflammation and hormones? A happy gut equals a healthier you. Here’s how to give it some love:
- Fermented Foods: Kimchi, sauerkraut, and yogurt are packed with probiotics that support a healthy microbiome.
- Prebiotics: Garlic, onions, and asparagus provide food for your gut’s good bacteria.
- Reduce Gut Irritants: Cut back on processed foods, artificial sweeteners, and excessive dairy if they’re causing distress.
A well-nourished gut can reduce systemic inflammation, support hormone balance, and even improve your mood—talk about multitasking!
4. Oxidative Stress, Be Gone
Endometriosis often goes hand-in-hand with oxidative stress. Antioxidants to the rescue! Vitamin C from oranges and polyphenols from green tea are your secret weapons against free radicals. Studies show that antioxidants may help reduce the oxidative stress associated with endometriosis, alleviating pain and inflammation.
5. Magnesium and Zinc: The Dynamic Duo
Crampy? Magnesium-rich foods like spinach and dark chocolate (yay!) can help. Magnesium plays a key role in muscle relaxation and can soothe the cramps that are so common with endometriosis. Zinc, found in pumpkin seeds and lean meats, supports your immune system and calms inflammation, making it an excellent mineral for those dealing with this condition.
Supplements: Small Pills, Big Impact
Supplements can complement your diet and fill in gaps that food alone may not cover. While not a cure-all, they can be powerful allies when used correctly. Here’s the lowdown:
• Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These healthy fats are like the bodyguards of your body, especially when it comes to inflammation. Omega-3s, found in fish oil or algae-based supplements, are potent inflammation fighters. They work by reducing the production of prostaglandins—those pesky compounds that increase pain and inflammation in the body. Consuming omega-3s regularly has been linked to a reduction in endometriosis-related pain, making them an essential part of any functional nutrition plan.
• Vitamin D: Vitamin D isn’t just for strong bones; it also plays a critical role in immune function and hormone regulation. Studies have found that low levels of vitamin D are often associated with more severe symptoms of endometriosis. This sunshine vitamin can help regulate your immune system and may even shrink those troublesome lesions over time. Just a heads up—vitamin D is fat-soluble, so it’s best absorbed when taken with a fat-containing meal, like avocado or olive oil.
• Curcumin: Derived from the golden root of turmeric, curcumin is a superstar in the world of anti-inflammatory supplements. It’s known for its ability to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, which is especially important for managing endometriosis flare-ups. But wait—there’s more! Studies suggest that curcumin can also inhibit the growth of endometrial tissue, potentially slowing the progression of the condition. Plus, curcumin is a multitasker; it supports joint and gut health, making it an all-around wellness booster.
• N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC): This powerful antioxidant is a detox champion. NAC helps to reduce oxidative stress in the body—something that’s important for minimizing inflammation and supporting overall health. What’s more, research indicates that NAC may improve fertility outcomes for women with endometriosis, a major win if fertility is a concern. It’s like giving your body a reset button to help it function more efficiently and reduce the impact of oxidative damage.
• Magnesium Glycinate: Endometriosis can bring on cramping and muscle tension, but magnesium glycinate is here to help! Magnesium is known for its muscle-relaxing properties, making it perfect for relieving cramps and soothing discomfort. It’s also a sleep promoter, helping you unwind and get better rest—a key component of healing. Plus, magnesium can calm the nervous system, so you’re less likely to be overwhelmed by stress, which can make symptoms worse.
• Probiotics: Your gut is the epicenter of your health, and a healthy gut microbiome is essential for managing both hormone balance and inflammation. Probiotics can help by replenishing your beneficial gut bacteria, improving digestion, and even supporting your immune system. For those with endometriosis, a healthy gut may contribute to reduced systemic inflammation and better hormone regulation. To get the most out of probiotics, choose a multi-strain formula to ensure you’re covering all the bases.
While these supplements can be incredibly effective, remember that they’re not magic bullets—they’re just one part of the puzzle. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, so you can personalize your approach based on your unique needs. With the right guidance and the help of functional nutrition, you can take meaningful steps toward managing your endometriosis and improving your overall health.
It’s Not Just About Food: Lifestyle Matters
Managing endometriosis goes beyond meal plans and supplements; it’s about embracing the bigger picture, where everyday habits and choices play a crucial role. Stress, for example, is like a hidden villain—it ramps up inflammation and can make your symptoms even worse. So, let’s talk about ways to manage it!
Mindfulness practices and yoga are not just buzzwords; they’re powerful tools that can help reduce your stress levels, calm your nervous system, and lower overall inflammation. It’s amazing what a little breathing exercise or a gentle yoga flow can do for both your mind and body.
Don’t forget the power of rest! Skipping sleep is like ignoring your body’s recharge button. Getting enough high-quality sleep is essential for hormone regulation, tissue repair, and keeping your immune system in check. So, while you’re working on nourishing your body with food, make sure you’re nourishing your mind and taking time to recharge with some peaceful rest.
Real Talk: Why Personalization Is Key
When it comes to managing endometriosis, one size does NOT fit all. No two people experience the condition the same way, and that’s why a personalized approach is absolutely essential. Everyone has different triggers, so working with a dietitian or a functional medicine professional is key. They can help you pinpoint your unique triggers and craft a tailored plan that fits your lifestyle and needs. You might need to experiment with different foods, supplements, or lifestyle strategies to see what makes the biggest difference for you. The beauty of working with a pro is that they can provide you with the expertise and support to navigate this process and fine-tune your plan as you go along. It’s all about what works for YOU—not a generic, one-size-fits-all solution.
Wrapping It Up
Endometriosis doesn’t have to dictate your life. By embracing the principles of functional nutrition, you’re giving your body the tools it needs to fight back and thrive. Focus on anti-inflammatory foods, hormone balance, gut health, and tackling oxidative stress, and you’re already on the right path. But don’t forget that mindfulness, stress management, and quality sleep are just as important. Add in a dash of self-care and personalization, and you’ve got the perfect recipe for living your best life with endometriosis.
Sources:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9983692
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8224039
https://www.rbmojournal.com/article/S1472-6483(13)00007-2/fulltext
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8065992
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7226034
https://drbrighten.com/causes-endometriosis-5-natural-treatment-strategies
https://drbrighten.com/endometriosis-relief-naturally
https://drbrighten.com/endometriosis-flare-up/#h-endometriosis-pain-control-nbsp
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9528818
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10058497/#sec5-life-13-00654

While much of the conversation around fertility and pregnancy complications is often centered around women, emerging research is revealing the significant role that male fertility and reproductive health play in pregnancy outcomes. For couples struggling to conceive or facing pregnancy-related complications such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, or severe nausea/vomiting, the health of the male partner should not be overlooked. Recent studies indicate that men, too, have a substantial role in preventing complications during pregnancy by optimizing their reproductive health. So, what can men do to maintain optimal sperm health and manage their fertility status?
Let’s dive into how male fertility influences pregnancy and how men can play an active role in optimizing pregnancy outcomes.
Understanding the Link Between Male Fertility and Pregnancy Complications
Male fertility isn’t just about the ability to conceive; it has a direct influence on the overall health of the pregnancy and the well-being of both the mother and baby. Emerging studies indicate that poor sperm health, genetic factors, and underlying metabolic conditions in men are associated with an increased risk of certain pregnancy complications. These include preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and severe nausea/vomiting (morning sickness).
While women’s health is understandably critical, men’s health is equally vital for pregnancy success and should be considered when preparing for conception or managing pregnancy complications.
Preeclampsia and Male Fertility
Preeclampsia is a potentially life-threatening pregnancy complication marked by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Traditionally, preeclampsia has been associated with maternal health, but emerging research is suggesting that male fertility factors, such as sperm DNA fragmentation, may play a significant role in the development of this condition.
How male fertility influences preeclampsia:
Poor sperm quality, particularly sperm with damaged DNA, is linked to an increased risk of preeclampsia. The body’s immune response to abnormal fetal development—potentially triggered by sperm DNA damage—can lead to conditions like preeclampsia. Additionally, paternal age, obesity, and certain metabolic conditions (such as diabetes) can exacerbate this risk. Men who aim to conceive should take steps to improve sperm health and minimize risk factors associated with preeclampsia.
Research indicates that sperm DNA fragmentation can disrupt early fetal development, which may cause an immune response from the mother that leads to complications such as preeclampsia. It also has been found that men who have poor sperm quality or higher paternal age are more likely to have partners who experience preeclampsia during pregnancy:
- Men should focus on maintaining optimal sperm health, as sperm quality directly impacts pregnancy outcomes. Nutrient-rich diets, antioxidants, and supplements that support sperm health can help mitigate these risks.
- Regular check-ups to assess sperm health (e.g., semen analysis) and health conditions such as obesity and diabetes can also help reduce the chance of complications.
Gestational Diabetes and Male Fertility
Gestational diabetes is a common pregnancy condition characterized by high blood sugar, which can lead to complications such as preterm birth, high birth weight, and increased risk of type 2 diabetes for both mother and baby. While gestational diabetes is often attributed to maternal health, emerging evidence points to the fact that paternal health and fertility also play a role in the development of this condition.
The male factor in gestational diabetes:
Studies show that men with metabolic disorders—such as obesity, hypertension, or insulin resistance—are more likely to have partners who develop gestational diabetes. The father’s health may affect placental function and insulin sensitivity in the mother, contributing to the risk of gestational diabetes. Therefore, men who are overweight or have metabolic conditions can increase the likelihood of their partner developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
How men can work to avoid this: Men should aim for overall metabolic health. This includes achieving a healthy weight through diet and exercise. This will help to manage conditions such as hypertension, hypocholesteremia, hyperglycemia or insulin resistance. By reducing inflammation and optimizing metabolic health, men can help reduce the likelihood of gestational diabetes in their partners.
- A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins can support sperm quality and metabolic health. This is essential for maintaining healthy pregnancy outcomes for both partners.
Severe Nausea and Vomiting (Morning Sickness)
Morning sickness, or severe nausea and vomiting during pregnancy, is one of the most common early signs of pregnancy. While it is usually attributed to hormonal changes in the mother’s body, recent evidence suggests that male factors, such as sperm health, can influence the severity of morning sickness.
Male fertility and nausea/vomiting:
Studies suggest that sperm quality and paternal age may contribute to the likelihood of morning sickness. Sperm DNA damage, oxidative stress, and even certain paternal health conditions, such as hormonal imbalances and metabolic stress, could affect the early stages of pregnancy, leading to more severe nausea and vomiting. Additionally, oxidative stress in the father may indirectly affect the mother’s pregnancy experience, potentially exacerbating morning sickness symptoms.
How men can reduce the risk
By improving diet and lifestyle choices, men can support sperm health and reduce the risk of severe nausea in their partner. Nutrients such as zinc, folate, and antioxidants are crucial for maintaining sperm health and reducing oxidative stress in both men and women.
- A healthy lifestyle that includes stress management, proper sleep, and regular physical activity can reduce hormonal imbalances in men, which may reduce the likelihood of complications such as severe nausea and vomiting.
How Men Can Improve Their Fertility to Prevent Pregnancy Complications
Now that we understand the role of male fertility in these complications, let’s explore actionable steps men can take to support their fertility and reduce the risks of pregnancy complications for their partners.
1. Optimize Sperm Health
To optimize sperm health, men should focus on:
- Antioxidant-rich foods: These protect sperm from oxidative damage, which can affect sperm DNA and motility. Selenium, vitamins A, C, E, CoQ10, and N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine (NAC) are particularly effective antioxidants. This can be found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and meats
- Zinc: This essential mineral is crucial for healthy sperm production and hormone regulation. Zinc-rich foods like pumpkin seeds, shellfish, and lean meats should be included in the diet.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fatty fish like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, omega-3s support healthy sperm membranes and motility.
2. Support Healthy Weight Management
Obesity in men is linked to lower sperm quality and increased risk of metabolic conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can improve sperm quality and reduce the likelihood of passing on metabolic diseases that contribute to complications such as gestational diabetes and preeclampsia.
3. Reduce Exposure to Environmental Toxins
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals such as BPA, phthalates, and pesticides can impair sperm quality. Men can reduce their exposure to these toxins by choosing organic foods, avoiding plastics, and using natural personal care products with no fragrance.
4. Manage Chronic Health Conditions
Men who have chronic health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or thyroid disorders should prioritize managing these conditions through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular check-ups. Well-managed chronic conditions reduce the risk of pregnancy complications.
5. Prioritize Stress Management and Sleep Optimization
Chronic stress and poor sleep can disrupt hormonal balance and impair sperm health. Men should aim to manage stress through activities such as meditation, yoga, and regular physical activity, while also ensuring they get 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
6. Preconception Counseling
Just as women benefit from preconception counseling, men can benefit from fertility evaluations to assess sperm health and identify any underlying conditions that may affect their fertility. Semen analysis and hormone level testing can provide valuable insights into male reproductive health.
Conclusion: A Team Effort for a Healthy Pregnancy
While much of the focus during pregnancy often falls on the health of the mother, it’s clear that male fertility plays an equally crucial role in pregnancy outcomes. By improving sperm health, managing weight, reducing exposure to toxins, and supporting overall health, men can contribute to a healthier pregnancy and help prevent complications like preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and severe nausea.
Pregnancy is a team effort, and both partners need to be proactive about their health and fertility. With the right lifestyle choices, nutritional support, and medical care, men can optimize their reproductive health and contribute to a healthier, smoother pregnancy journey for their partners.
Looking For More Support on Your Fertility Journey?
Our team of expert fertility dietitians can help you and your partner with nutrition, lab testing, and lifestyle changes to naturally improve your fertility – regardless of how you conceive.
Apply to work with our team right here – we can’t wait to speak with you!
References
- Hyman, M. (2021, November 17). Decline in men’s fertility: What you need to know. Dr. Mark Hyman. https://drhyman.com/blogs/content/decline-in-mens-fertility?_pos=3&_sid=2a7f588e5&_ss=r
- Ashraf, U. M., Hall, D. L., Rawls, A. Z., & Alexander, B. T. (2021). Epigenetic processes during preeclampsia and effects on fetal development and chronic health. Clinical science (London, England : 1979), 135(19), 2307–2327. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8948502/
- Fox, R., Kitt, J., Leeson, P., Aye, C. Y. L., & Lewandowski, A. J. (2019). Preeclampsia: Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Management, and the Cardiovascular Impact on the Offspring. Journal of clinical medicine, 8(10), 1625. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31590294/
- Galaviz-Hernandez, C., Sosa-Macias, M., Teran, E., Garcia-Ortiz, J. E., & Lazalde-Ramos, B. P. (2019). Paternal Determinants in Preeclampsia. Frontiers in physiology, 9, 1870. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6330890/#:~:text=Different%20lines%20of%20evidence%20have,a%20well%2Dknown%20risk%20factor.
- Khoshkerdar, A., Eryasar, E., Morgan, H. L., & Watkins, A. J. (2021). REPRODUCTIVE TOXICOLOGY: Impacts of paternal environment and lifestyle on maternal health during pregnancy. Reproduction (Cambridge, England), 162(5), F101–F109. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33544695/
- Montagnoli, C., Ruggeri, S., Cinelli, G., Tozzi, A. E., Bovo, C., Bortolus, R., & Zanconato, G. (2021). Anything New about Paternal Contribution to Reproductive Outcomes? A Review of the Evidence. The world journal of men’s health, 39(4), 626–644. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4453485/#:~:text=Main%20findings,than%20male%20involvement%20during%20delivery
- Mora-Esteves, C., & Shin, D. (2013). Nutrient supplementation: improving male fertility fourfold. Seminars in reproductive medicine, 31(4), 293–300. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23775385/
- University of Tennessee, Animal Science Department. (2022). Paternal impacts on gestational diabetes and preeclampsia. Retrieved from https://animalscience.tennessee.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2022/06/Relevant-Repro-Blog-8_-Paternal-Impacts-on-GEM-and-Pre-eclampsia.pdf
- Rehman, S., Usman, Z., Rehman, S., AlDraihem, M., Rehman, N., Rehman, I., & Ahmad, G. (2018). Endocrine disrupting chemicals and impact on male reproductive health. Translational andrology and urology, 7(3), 490–503. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6043754/
- Yargawa, J., & Leonardi-Bee, J. (2015). Male involvement and maternal health outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of epidemiology and community health, 69(6), 604–612. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33474842/

The Preconception Playbook
This free playbook provides specific actionable tips to get started on your fertility journey, as well as what to avoid while you're trying to conceive.
Get the free playbook