Resources
Style
Planning
View All
THE blog
Hormonal fluctuations impact your energy levels, mood, and overall well-being throughout your menstrual cycle. By aligning your diet with these hormonal changes—a practice known as cycle syncing—you can optimize your energy, reduce PMS, and improve overall cycle health. This guide will help you understand the phases of the menstrual cycle and how nutrition can play a vital role in supporting hormonal balance.
Let’s begin by breaking down the menstrual cycle and understanding how your hormones fluctuate during each phase!
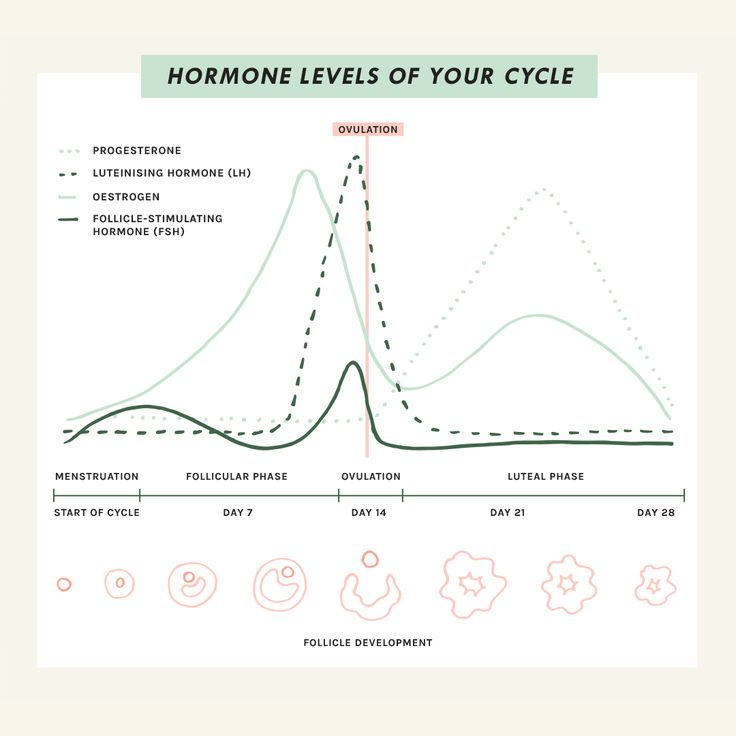
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle has four distinct phases: the menstrual phase, follicular phase, ovulatory phase, and luteal phase. Each phase brings unique hormonal shifts that influence your body’s nutritional needs and energy requirements.
1. Menstrual Phase
(Day 1-6)
- This phase begins with menstruation. Hormone levels of estrogen and progesterone are at their lowest.
- Symptoms may include fatigue, cramping, and low energy levels.
2. Follicular Phase
(Day 7-13)
- Estrogen levels begin to rise, stimulating the growth of follicles in the ovaries and increasing energy.
- This is often when women feel their best, with improved mood and vitality.
3. Ovulatory Phase
(Day 14-16)
- Estrogen peaks, and luteinizing hormone (LH) surges to trigger ovulation.
- Energy levels and libido are typically at their highest.
4. Luteal Phase
(Day 17-28)
- Progesterone rises to prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy, while estrogen levels dip. If fertilization does not occur, both hormones decrease, leading to PMS symptoms.
- Symptoms may include bloating, fatigue, and cravings.
Understanding these phases allows you to tailor your diet and lifestyle to support your body’s natural rhythms.
How Nutrition Supports Each Phase
Menstrual Phase: Focus on Iron and Hydration
During the menstrual phase, many individuals experience common symptoms such as cramping, fatigue, and irritability. While it may be tempting to indulge in comfort foods like sweets, pizza, and chips, these choices can disrupt hormonal balance and deplete important nutrients needed to support your body during this phase. Instead, focusing on nutrient-dense foods that support iron levels, reduce inflammation, and promote hydration. These all can help alleviate symptoms and maintain overall well-being.
- Foods to prioritize: One of the most important considerations during the menstrual phase is replenishing iron lost through bleeding. Incorporating iron-rich foods like lean red meat, spinach, lentils, beans, and beets can help restore iron levels. To optimize iron absorption, pair these foods with sources of vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, berries, broccoli, and bell peppers. Vitamin C enhances the bioavailability of iron, ensuring that your body can make the most of the iron you consume. Vitamin K is another key nutrient that can help reduce heavy bleeding. Leafy greens, blueberries, cheese, and eggs are excellent sources of vitamin K, which supports blood clotting and helps regulate menstrual flow. Omega-3 fatty acids are also beneficial during this phase, as they have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce cramping. Incorporate omega-3-rich foods like salmon, flaxseed, and tree nuts to support your body’s natural processes and ease discomfort.
- Hydration: This is particularly important during the menstrual phase, as it can help reduce bloating and prevent dehydration, which can exacerbate fatigue. Herbal teas such as ginger or chamomile are soothing options that can help alleviate cramps, reduce bloating, and promote relaxation.
- Avoid: Avoid high-sodium foods during your period, as they can exacerbate bloating and lead to water retention. Instead, focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins and minerals, as well as plenty of hydration, to help you feel your best during this time.
Follicular Phase: Build Energy with Nutrient-Dense Foods
As estrogen rises, focus on foods that provide sustained energy and promote gut health. Maintaining gut health is deeply connected to hormonal balance, playing a crucial role in maintaining a healthy menstrual cycle. A well-functioning gut microbiome, particularly the estrobolome, aids in estrogen metabolism, preventing hormonal imbalances that could lead to PMS or heavy periods. Incorporating fiber-rich foods, probiotics, and fermented options can support gut health. These choices not only benefit your cycle but also improve digestion, energy, and mood, contributing to overall well-being!
- Foods to prioritize: Incorporate fiber-rich foods such as quinoa, oats, fresh vegetables, and seeds, which aid in digestion and promote stable blood sugar levels. Fermented foods like kimchi, sauerkraut, and yogurt are excellent choices as they provide beneficial probiotics that support gut health. Omega-3-rich foods like walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are also important as they have anti-inflammatory properties that can help balance hormones during this phase.
- Key nutrients: Prioritize B vitamins which support energy production and help combat fatigue, and omega-3 fatty acids, which promote overall hormonal balance and reduce inflammation.
- Avoid: It’s crucial to avoid refined sugars, as they can cause blood sugar spikes that disrupt energy levels and hormone regulation.
Ovulatory Phase: Support Detoxification
During the ovulatory phase, estrogen levels peak, and the body enters a high-energy phase, making it important to support both hormonal balance and overall vitality. Since the liver plays a key role in breaking down and detoxifying excess estrogen, it’s crucial to include foods that promote liver function and aid in estrogen metabolism.
- Foods to prioritize: Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale, Brussels sprouts) are excellent choices, as they contain compounds such as sulforaphane that help the liver process estrogen more efficiently. Berries help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which can support overall hormonal health. Flaxseeds are also beneficial as they contain lignans that can bind to excess estrogen, helping to regulate levels in the body.
- Key nutrients: Zinc is a key nutrient for supporting ovulation, making it important to include zinc-rich foods like pumpkin seeds, shellfish, and legumes.
- Avoid: It’s important to avoid alcohol and excessive caffeine during this phase. Both substances can burden the liver, slowing down its detoxification processes and potentially causing hormonal imbalances. Drinking plenty of water and consuming foods rich in fiber will further support liver health and overall detoxification.
Luteal Phase: Balance Blood Sugar and Reduce Inflammation
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly increased progesterone, can contribute to common symptoms such as cravings, mood swings, fatigue, and bloating during this phase of your cycle. The key to managing these symptoms is balancing blood sugar levels, reducing inflammation, and nourishing your body with foods that support hormonal balance.
- Foods to prioritize: One effective strategy is to focus on complex carbohydrates, which provide steady energy and help stabilize blood sugar. Foods such as sweet potatoes, whole grains, and high-fiber vegetables, including cruciferous vegetables, can help curb hunger and keep blood sugar levels steady.
- Magnesium-rich foods are also important during this phase, as magnesium has been shown to alleviate PMS symptoms, including mood swings, irritability, and cramps. Magnesium-rich options like dark chocolate, almonds, and pumpkin seeds are excellent choices.
- Anti-inflammatory spices like turmeric and ginger can also be beneficial, as they help reduce inflammation, soothe cramps, and support overall well-being. These spices have natural properties that may help ease discomfort associated with PMS, including bloating and muscle tension.
- Key nutrients: Vitamin B6 is another important nutrient during the luteal phase, as it helps regulate mood and reduce irritability, which can be exacerbated by hormonal changes. Foods such as bananas, poultry, and potatoes are rich in vitamin B6 and can be incorporated into your meals to support emotional well-being during this time.
Avoid: If you’re craving something sweet or salty, opt for healthier alternatives such as dark chocolate, fruit, nuts, and seeds. These foods can satisfy cravings without causing the blood sugar spikes and crashes that processed snacks can induce. Additionally, staying hydrated is crucial during the luteal phase, as water helps reduce bloating, brain fog, and PMS-related discomfort.

Seed Cycling for Hormonal Balance
Seed cycling is a holistic dietary practice that involves eating specific seeds at different phases of the menstrual cycle to support hormone balance. The idea behind seed cycling is that different phases of the menstrual cycle require different hormone support, and specific seeds contain the nutrients necessary for this. This method is particularly beneficial for regulating irregular cycles and managing PMS symptoms.
Follicular Phase (Day 1-14)
During the follicular phase, estrogen is the dominant hormone. The goal is to support estrogen production and metabolism. The recommended seeds for this phase are raw, freshly ground flaxseeds and pumpkin seeds. Flaxseeds are rich in lignans, which have weak estrogenic properties and support elimination. Pumpkin seeds, on the other hand, provide zinc, an essential mineral for testosterone production and healthy hormone levels.
- Seeds: Flaxseeds and pumpkin seeds
- Benefits: Flaxseeds contain lignans that help balance estrogen levels. Pumpkin seeds provide zinc to support progesterone production later in the cycle.
Luteal Phase (Day 15-28)
After ovulation, progesterone becomes the dominant hormone. To support this, the recommended seeds are raw, freshly ground sunflower seeds and sesame seeds. Sunflower seeds are rich in vitamin E, which helps reduce PMS symptoms and supports estrogen detoxification. Sesame seeds are high in lignans and fatty acids, which help balance progesterone and reduce inflammation.
- Seeds: Sesame seeds and sunflower seeds
- Benefits: Sesame seeds contain lignans to modulate estrogen, and sunflower seeds provide selenium to support liver detoxification.
Can Seed Cycling Be Used Mid-Cycle? Yes, seed cycling can be started at any point in the cycle, depending on where you are in your menstrual phase. If you’re tracking your cycle closely, you can adjust your seed rotation accordingly to match your ovulation timing.
Seed Cycling’s Nutritional Basis The seeds used in seed cycling are rich in essential nutrients that support hormone production, including omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, magnesium, and antioxidants. These nutrients help optimize hormone balance by supporting estrogen and progesterone levels, promoting healthy testosterone levels, and reducing inflammation, which can lead to hormonal imbalances.
Seed Cycling Science Although the term “seed cycling” itself is not widely researched in scientific literature, the individual nutrients in the seeds have been extensively studied for their health benefits. For example, lignans in flaxseeds have been linked to improved estrogen and progesterone balance, and the zinc in pumpkin seeds supports testosterone production. Research has also shown that these seeds can benefit cardiovascular health, gut health, and even cancer prevention.
Does Seed Cycling Really Work? While more research is needed to fully validate seed cycling as a hormone-balancing practice, many women have reported positive changes in their menstrual health, including improved hormone balance, reduced PMS symptoms, and better skin health. The key is consistency and combining seed cycling with other healthy lifestyle practices, such as a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management.
Additional Benefits of Seed Cycling
- For Menopause: Seed cycling can be continued post-menopause by aligning the seed rotation with the moon cycle. This can help manage symptoms like hot flashes and mood swings.
- For PCOS: Seed cycling can help balance testosterone and estrogen levels in women with PCOS, potentially alleviating symptoms like acne and hirsutism.
- For Acne: Seed cycling may help improve acne by balancing hormones, particularly when coming off hormonal birth control, which can trigger an androgen rebound and worsen acne.
- For Painful Periods: Seed cycling may help reduce period pain by balancing estrogen and progesterone levels and supporting inflammation reduction.
How to Start Seed Cycling To begin seed cycling, it’s recommended to consume 1-2 tablespoons of freshly ground, raw seeds daily. You can add them to smoothies, salads, oatmeal, or even make homemade seed-based snacks! Consistency is key, and it’s best to give the practice at least one full cycle (about a month) to assess its effectiveness.
Exercise and Cycle Syncing
Adjusting your exercise routine to match your cycle phases can optimize performance and reduce hormonal stress.
- Menstrual Phase: Prioritize rest and gentle movements like yoga or walking.
- During your period, light activities like walking, stretching, or gentle movement can help ease discomfort and match your energy levels, especially if you’re dealing with cramps.
- While it’s natural to feel less active on the first day of your period, exercise can actually relieve cramps, boost energy, and improve your mood! Surprisingly, even in the early follicular phase, you might find you can lift heavier weights or handle more intense workouts. The key is to listen to your body and adjust your activity based on how you feel rather than sticking to rigid rules or expectations.
- Follicular Phase: Increase intensity with strength training and cardio as energy levels rise.
- During this phase of your cycle, rising estrogen and testosterone levels can enhance muscle-building potential, making cardio and strength training feel more effective. By as early as day three of your period, you might notice a boost in energy and exercise stamina as estrogen levels continue to climb!
- Ovulatory Phase: Engage in high-intensity workouts like HIIT or running.
- This typically occurs between the end of week two and the start of week three in your cycle and can leave you feeling more energized. During this time, many women notice they can handle higher levels of physical exertion compared to other phases.
- Luteal Phase: Shift to moderate-intensity exercises like Pilates or swimming to accommodate fatigue.
- After ovulation, some women notice a quick drop in exercise tolerance, while others experience this closer to their period. The week before your period can bring challenges like reduced tolerance, trouble cooling down, and water retention, which may affect workouts. Staying hydrated, focusing on electrolytes, wearing breathable clothing, and exercising in a cool space can help. This is a great time to prioritize recovery with activities like yoga or Pilates.
- Increased hunger is normal due to higher calorie needs, especially carbohydrates, as your body becomes less insulin sensitive. You can honor your cravings or increase your intake by 5–10%, choosing what works best for you!
This cyclical approach helps prevent overtraining and supports hormonal balance.
Lifestyle Tips for Cycle Health
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance. Incorporate mindfulness practices like meditation or journaling.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours per night to support hormone production and recovery.
- Track Your Cycle: Use apps or journals to monitor your symptoms and identify patterns.
Conclusion
Cycle syncing empowers you to take control of your health by aligning nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle with your menstrual cycle! By nourishing your body with the right foods at the right time, you can alleviate symptoms, enhance energy levels, and promote overall well-being. Implementing practices like seed cycling and phase-specific exercise further supports hormonal harmony.
Start small and make gradual changes to experience the benefits of cycle syncing. Your body will thank you for it!
Sources
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10251302
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/search/research-news/17857
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/nutrition-and-exercise-throughout-your-menstrual-cycle
https://drbrighten.com/how-to-exercise-with-your-cycle
https://drbrighten.com/seed-cycling-for-hormone-balance
https://drbrighten.com/seed-cycling-menopausal-hormones
https://drbrighten.com/gut-hormone-connection
Images
Female Cycle https://www.pinterest.com/pin/962222276632847842/


My work as a fertility nutritionist has shown me how dietary changes can improve egg quality. Many women believe age alone determines egg health. But I can tell you that your food choices and lifestyle can substantially affect your fertility in just 30 days.
Better egg quality doesn’t need complicated recipes or strict diets. My experience creating customized fertility meal plans has taught me something important. Simple, science-backed nutrition strategies make a real difference. The fertility diet I suggest centers on nutrient-rich foods. It includes practical lifestyle changes that boost reproductive health.
This detailed guide shows you my tested approach to enhance egg quality in 30 days. You’ll learn about fertility superfoods, when to take supplements, and ways to manage stress that optimize your fertility potential. This plan gives you practical steps to succeed, whether you’re new to fertility improvement or want to enhance your current routine.
Understanding Your Egg Quality Journey
Let me explain what egg quality really means. My experience as a fertility nutritionist has taught me that knowing the science behind your eggs is vital to making meaningful improvements, especially over the age of 35.
What determines egg quality
Egg quality basically tells us if an egg is genetically normal (euploid) or abnormal (aneuploid) [1]. Several key elements affect egg quality:
- Age-related factors (chromosomal health)
- Nutritional status and BMI
- Environmental exposures
- Stress levels
- Genetic predisposition
By age 35, about 50% of a woman’s eggs remain chromosomally normal [2]. Your starting point matters, which is why proper testing is essential. FSH testing helps identify fertility issues [1], and AMH testing serves as an early indicator of ovarian aging [3].
The 30-day transformation window
The complete egg maturation takes about 90 days [4], but targeted interventions can improve egg quality substantially within 30 days. Research shows positive changes in egg quality after just two weeks of specific supplementation [4]. This brings hope to women preparing for fertility treatments or natural conception.
The sort of thing I love comes from studies that show women using melatonin supplementation during IVF cycles had better fertilization rates and higher quality embryos in just two weeks [4]. This proves we can influence egg quality in a shorter timeframe, even though the complete egg development cycle takes longer.
(And if you’re looking for high quality professional grade supplements, you can head to my Fullscript store right here and use my practitioner discount for all your fertility supplements – you’re welcome ;)) —
Setting realistic expectations
You should know exactly what’s achievable. The timeline for egg quality improvements varies based on your health, age, and specific treatment protocols [5]. We can’t reverse aging, but we can optimize your egg quality within your current reproductive window.
Research shows that a Mediterranean diet six months before IVF can boost success rates to 65-68% [1]. My fertility diet meal plans can create positive changes in less time. Your genetic makeup won’t change, but we can influence how your eggs develop through targeted nutrition and lifestyle modifications.
Note that egg quality isn’t just about age – it’s about creating the best environment for your eggs to thrive. My work with hundreds of women shows how the right fertility superfoods and lifestyle changes can make a remarkable difference, even within a 30-day window (though I do encourage you to make these changes for 90 days for the best results!).
The Fertility Nutrition Blueprint
My experience as a fertility nutritionist has led me to develop a complete nutrition blueprint that helps women optimize their egg quality. The framework I use in my practice stems from recent research and clinical success.
Power foods for egg health
My fertility diet meal plan builds on foods rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients. Research demonstrates that a Mediterranean-style diet can substantially increase IVF success rates to 65-68% [6]. These power foods should be part of your diet:
- Omega-3 rich seafood: Salmon and sardines for essential fatty acids
- Antioxidant-packed berries: Blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries
- Leafy greens: Broccoli and spinach for folate
- Selenium-rich nuts: Just 2 Brazil nuts daily meets your selenium needs [7]
- Whole grains: For stable blood sugar and hormone balance
Meal timing strategies
Your meal timing matters as much as your food choices. Blood sugar regulation plays a vital role in creating a fertility diet meal plan. Women with PCOS benefit from consuming most calories during breakfast to regulate testosterone and insulin levels [8].
Steady blood sugar throughout the day remains the goal. Here’s what you should do:
- Eat every 3-4 hours
- Include protein with each meal
- Focus on complex carbohydrates
- Avoid refined sugars and processed foods [9]
Hydration and fertility connection
Proper hydration stands among the overlooked aspects of fertility nutrition. Women should drink 2.2 liters (9 cups) of water daily [10]. This amount matters because dehydration can lead to:
- Poor egg health
- Decreased cervical mucus production
- Reduced blood flow to reproductive organs [10]
My clients’ fertility improves substantially once they prioritize hydration with proper nutrition. Water helps transport hormones throughout your body and supports the thick environment needed in your endometrium for successful implantation [10].
Note that while following these fertility superfood recommendations, you must avoid items that can harm egg quality. Research shows trans fats, refined carbohydrates, and added sugars can substantially affect fertility [9]. Your daily meals should include more plant-based proteins, healthy fats, and fiber-rich foods instead.
Strategic Supplementation for Egg Health
My fertility practice has taught me a lot about helping hundreds of women. I found that the right supplements can boost egg quality by a lot when paired with good nutrition. Here’s the supplement protocol I’ve refined through years of clinical experience.
Everything in supplements explained
My research-backed recommendations for egg health include these core supplements:
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): Studies show 600mg daily can improve egg quality and embryo quality [11]
- Methylated folate: Take 400 micrograms daily before pregnancy to reduce neural tube defects [12]
- Vitamin D: Research indicates 10 micrograms daily between September and March [13]
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: 500-1000mg daily to support embryo implantation and reduce premature labor [11]
- Myo-inositol: Studies suggest 4g daily can improve egg quality and maturation [14]
Timing your supplements
My fertility practice uses this precise timing schedule to get the best absorption:
| Supplement | Best Time to Take | Duration |
| CoQ10 | With breakfast and dinner | Until positive pregnancy test [11] |
| Methylated Folate | Daily before pregnancy | Through 12 weeks of pregnancy [12] |
| Vitamin D | Morning with food | Ongoing as needed [13] |
| Omega-3 | With meals | Ongoing |
| Myo-inositol | Split dose morning/evening | As directed [14] |
Supplement combinations to avoid
My experience as a fertility nutritionist has helped me identify several important precautions:
Never combine:
- Folic acid with certain epilepsy medications or antidepressants [15]
- CoQ10 with blood thinners [15]
- Vitex (chasteberry) with fertility drugs or hormone therapy [15]
Starting supplements 2-3 months before trying to conceive gives optimal results [16]. Note that you should consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, especially if you:
- Take prescription medications
- Undergo fertility treatments
- Have underlying health conditions
Supplements complement a nutrient-rich diet rather than replace it. My clients get the best results when they combine strategic supplementation with the fertility superfoods we discussed earlier.
Lifestyle Modifications That Matter
The fertility superfoods and supplements we discussed are important, but lifestyle changes can greatly affect egg quality. Small adjustments in three vital areas can improve your fertility chances.
Sleep optimization techniques
Quality sleep plays a key role in hormone regulation. Research shows that 7-8 hours of sleep helps conception [17]. Your body produces essential reproductive hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and luteinizing hormone during sleep [18].
My proven sleep optimization protocol includes:
- Set a consistent sleep schedule between 10 PM and 7 AM [19]
- Avoid caffeine in the late afternoon
- Turn off electronics one hour before bed
- Create a cool, dark sleeping environment
- Practice gentle stretching before bed
- Utilize red light in the evenings to promote deeper sleep
Stress management practices
Stress can really affect your fertility. It produces hormones like cortisol that interfere with ovulation [20]. My clients have shown remarkable improvements with these evidence-based stress reduction techniques.
Studies reveal that women in mind-body programs achieved a 55% pregnancy rate compared to 20% in those who didn’t [21]. Here’s what I suggest:
Daily Stress-Relief Practices:
- Meditation or deep breathing exercises
- Regular yoga sessions (especially fertility-focused poses)
- Mindfulness techniques
- Gentle massage therapy
- Identifying Emotions
- Tapping
- Joining Fertility Support Groups – like ours
Exercise guidelines for fertility
Exercise and fertility need balance. The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week [22]. Many women either exercise too much or avoid it completely.
My evidence-based exercise framework suggests:
Recommended Activities:
- Brisk walking
- Swimming
- Light cycling
- Gentle yoga or pilates
- Dancing
- Strength training
Exercise Guidelines:
- Limit vigorous exercise to less than 5 hours weekly [23]
- Keep intense workouts under 60 minutes per day
- Avoid exhausting yourself
- Focus on moderate-intensity activities where you can still talk
My clients with PCOS have shown that 30 minutes of vigorous exercise three times weekly can boost conception chances [24]. If you’re having IVF treatments, stick to your regular activities but don’t start any new intense exercise routines [25].
Note that these lifestyle changes work best with the fertility diet meal plan and supplement protocol we covered earlier. Many women have improved their egg quality by combining these changes with their nutrition strategy.
Creating Your 30-Day Action Plan
Let’s create your customized 30-day action plan to improve egg quality. My clinical experience as a fertility nutritionist shows that breaking down this trip into weekly goals guides you to the best results.
Week-by-week breakdown
Here’s the plan I use with my clients:
| Week | Focus Areas | Action Items |
| Week 1 | Foundation | Start Mediterranean diet, begin supplements, establish sleep routine |
| Week 2 | Optimization | Incorporate fertility superfoods, adjust meal timing, start exercise |
| Week 3 | Integration | Fine-tune supplement timing, add stress management, increase hydration |
| Week 4 | Maintenance | Balance all elements, prepare for long-term sustainability |
Research shows that positive dietary changes can influence outcomes at any point in your fertility trip [26]. My clients see remarkable improvements with this well-laid-out approach, since nutritional status directly influences ovarian reserve [26].
Progress tracking methods
These tracking methods will help you stay on course:
- Physical Markers:
- Basal body temperature
- Cervical mucus changes
- Sleep quality (aim for 7-8 hours) [4]
- Energy levels throughout the day
- Dietary Compliance:
- Daily food journal
- Water intake (minimum 2.2 liters)
- Supplement schedule adherence
- Meal timing consistency
Studies show that women who track their cycles using fertility awareness methods have higher chances of conceiving [5]. Modern tracking apps work great alongside a complete fertility diet meal plan journal.
Adjusting your approach
The 90-day egg maturation cycle is prominent in research, yet positive changes can appear within 30 days [27]. My flexible approach adapts to individual responses:
Week 1-2 Assessment: Your digestive system might need time to adjust to fertility superfoods or supplements. We’ll modify portions and timing instead of removing them completely. Research confirms that small dietary improvements can boost fertility outcomes [26].
Week 3-4 Fine-tuning: Your energy levels and sleep quality will guide adjustments to exercise intensity or timing. Studies confirm that knowing how to get pregnant in your 30s and 40s involves small improvements to your existing routine [4].
Consistency matters more than perfection with the fertility diet meal plan. Missing a supplement dose or enjoying non-fertility-friendly foods occasionally isn’t a problem. Just return to the plan at your next meal.
Note that this 30-day plan builds on our earlier nutritional foundation. Small changes work best while you monitor your body’s response. My practice shows that women who stay flexible with modifications see the most consistent improvements in their fertility trip.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
My experience counseling women about fertility nutrition has shown several recurring mistakes that affect egg quality improvement. These critical pitfalls can impact your path to fertility.
Supplement pitfalls
My practice reveals that many women take the “more is better” approach to supplementation. Studies show that 55% of women going through IVF take various dietary supplements without proper guidance [5]. The most concerning aspects are:
Dangerous Combinations: Multiple supplements taken without understanding their interactions can be counterproductive. To name just one example, your body will excrete excess water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C or B vitamins [28]. Fat-soluble supplements like vitamins A, D, and E can build up to toxic levels and potentially cause:
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Blood clotting issues
- Irregular heartbeat
Clinical evidence supports this interaction guide:
| Supplement | Avoid Combining With | Reason |
| Folic Acid | Epilepsy medications | Reduced effectiveness |
| CoQ10 | Blood thinners | Interaction risk |
| Vitex | Hormone therapy | Hormonal interference |
Diet misconceptions
Fertility diets often lead to misunderstandings. Research indicates that individual micronutrients and macronutrients may help, but specific dietary variations show limited evidence of improving fertility in women without ovulatory dysfunction [5].
My clients often have these misconceptions:
- They believe all dairy should be eliminated (full-fat dairy actually benefits fertility) [29]
- They assume gluten-free diets automatically boost fertility [29]
- They think caffeine must be completely avoided (1-2 cups daily is generally safe) [5]
Research shows that caffeine intake above 500mg (>5 cups of coffee per day) decreases fertility [5]. Moderate caffeine consumption (1-2 cups of coffee daily) shows no apparent negative effects on fertility outcomes [5].
Lifestyle habits to eliminate
Research proves that certain lifestyle habits can affect your fertility potential by a lot. My clients receive this essential advice:
Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking speeds up follicular depletion and raises miscarriage risk [5]. Moderate alcohol consumption’s effects remain unclear, but more than two drinks daily can reduce fertility and extend conception time [5].
Environmental Exposures: Evidence suggests that endocrine-disrupting chemicals in food, water, air, and consumer products may reduce fertility [5]. My recommendations include:
- Choose organic produce when possible
- Use non-toxic cleaning products
- Avoid plastic food containers
- Select clean beauty products
Stress Management: High stress levels interfere with ovulation hormones [30]. A fertility diet meal plan should include stress-reduction techniques. Poor sleep affects reproductive hormone production, so you need 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night [30].
The implementation of fertility superfoods must avoid these common pitfalls. Research demonstrates that couples without adverse lifestyle factors achieved an 83% pregnancy rate over 12 months, compared to 38% for those with four adverse factors [31].
Conclusion
Nutrition strategies backed by science, targeted supplements, and lifestyle changes can improve your egg quality by a lot within 30 days. Women who follow this complete approach see remarkable improvements in their fertility trip, based on my experience as a fertility nutritionist.
The right fertility superfoods, precise supplement timing, and consistent lifestyle habits lead to success. Your egg health improves with strategic changes in your daily routine – from better sleep patterns to stress management.
Your fertility trip is unique. This piece provides a strong framework to improve egg quality, though some women need individual-specific support. Our high-touch functional fertility program – Whole Health Fertility – offers 1:1 support if you need it.
My proven method focuses on practical, eco-friendly changes instead of restrictive protocols. These evidence-based strategies will amaze you with what your body achieves in just 30 days. Your dedication to these changes, plus patience and consistency, will boost your chances of conception success.
FAQs
Q1. Is it possible to enhance egg quality within 30 days? While the complete egg maturation process takes about 90 days, significant improvements in egg quality can be seen within 30 days through targeted nutrition, supplementation, and lifestyle changes. However, for optimal results, it’s best to maintain these changes for at least 2-3 months before trying to conceive.
Q2. What dietary changes can improve egg quality? A Mediterranean-style diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients can significantly boost egg quality. Focus on consuming omega-3 rich seafood, antioxidant-packed berries, leafy greens, selenium-rich nuts, and whole grains. It’s also important to maintain stable blood sugar levels and stay properly hydrated.
Q3. Which supplements are most effective for enhancing egg health? Key supplements for egg health include Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), folic acid, vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and myo-inositol. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, especially if you’re taking medications or undergoing fertility treatments.
Q4. How does lifestyle impact egg quality? Lifestyle factors significantly affect egg quality. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep, practice stress management techniques like meditation or yoga, and engage in moderate exercise for about 150 minutes per week. Avoid smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and minimize exposure to environmental toxins.
Q5. What are common mistakes to avoid when trying to improve egg quality? Common pitfalls include over-supplementation without proper guidance, misunderstanding fertility diets (like unnecessarily eliminating all dairy), and neglecting the impact of lifestyle factors. It’s important to follow a balanced approach, avoid dangerous supplement combinations, and address harmful habits like smoking or excessive alcohol consumption.
References
[1] – https://www.eurocareivf.com/fertility-blog/how-to-improve-your-egg-quality-for-ivf-success/
[2] – https://coolspringsobgyn.com/egg-quality-and-fertility/
[3] – https://www.yalemedicine.org/news/fertility-test
[4] – https://fertileweb.com/now-may-be-the-perfect-time-to-improve-your-egg-quality/
[5] – https://www.asrm.org/practice-guidance/practice-committee-documents/optimizing-natural-fertility-a-committee-opinion-2021/
[6] – https://fertility.womenandinfants.org/blog/fertility-diet
[7] – https://birdandbe.com/blogs/the-nest/fertility-diet-to-improve-egg-quality?srsltid=AfmBOoqlAWFTEgDq-nyOfnz9eaIksv6czp0Is2AaU6dFbf4iQKcde78K
[8] – https://fertiltree.com/blogs/top-foods-to-improve-female-egg-quality/
[9] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8634384/
[10] – https://www.repromedfertility.com/blog/how-hydration-affects-fertility-4153/
[11] – https://www.fertilityclinicsandiego.com/resources/supplements-to-aid-fertility/
[12] – https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/trying-for-a-baby/planning-your-pregnancy/
[13] – https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/keeping-well/vitamins-supplements-and-nutrition/
[14] – https://www.rbmojournal.com/article/S1472-6483(23)00869-6/fulltext
[15] – https://rescripted.com/posts/fertility-supplements-that-should-not-be-mixed-what-to-avoid-when-ttc
[16] – https://www.nashvillefertility.com/do-fertility-supplements-work/
[17] – https://www.fertstert.org/article/S0015-0282(13)01207-7/fulltext
[18] – https://axiawh.com/resources/relationship-between-sleep-and-fertility/
[19] – https://carolinasfertilityinstitute.com/can-lack-sleep-affect-fertility/
[20] – https://www.fcionline.com/article/improve-egg-quality-tips/
[21] – https://www.mayoclinichealthsystem.org/hometown-health/speaking-of-health/infertility-and-stress
[22] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7614776/
[23] – https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/female-fertility/art-20045887
[24] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10310950/
[25] – https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/planning-a-pregnancy/are-you-ready-to-conceive/being-active-when-trying-conceive
[26] – https://fertilitydietitian.co.uk/how-to-improve-egg-quality-meal-plan-and-guide/
[27] – https://fertilitydietitian.co.uk/2022/09/30/how-to-improve-egg-quality/
[28] – https://www.thebump.com/a/what-to-avoid-when-trying-to-conceive
[29] – https://thedietologist.com.au/fertility-nutrition-the-5-biggest-myths-debunked/
[30] – https://www.rockymountainfertility.com/blog/10-things-to-avoid-while-trying-to-conceive
[31] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8812443/

Understanding Male Fertility: An Overview
Male fertility is more than just the ability to conceive. It encompasses a complex interplay of various biological processes, lifestyle factors, and environmental influences, all working in tandem to produce viable sperm capable of fertilizing an egg. Approximately 50% of infertility cases have a male factor component, emphasizing the importance of understanding this aspect of reproductive health. Additionally, Sperm count has declined significantly in the last few decades.
To truly grasp the intricacies of male fertility, one must first acknowledge the role of sperm production and health. Healthy sperm are crucial to conception, and any disruptions in their production or function can lead to infertility challenges. The journey from sperm production to ejaculation involves a series of tightly regulated steps, each sensitive to different internal and external influences.
Whether you’re just starting to explore your reproductive health or seeking solutions to an ongoing fertility issue, a deeper dive into the factors affecting male fertility can provide clarity and guidance on potential areas for improvement. Identifying these factors is key to exploring treatment options, understanding possible interventions, and making informed decisions regarding family planning.
Understanding the Sperm Production Process
Sperm production, also known as spermatogenesis, is a complex and intricate process that occurs within the male reproductive system. It primarily takes place in the testicles, where specialized cells transform into sperm through several stages. This process is not instantaneous; in fact, it takes approximately 64 days for a single sperm cell to develop fully. Understanding this timeline is crucial, especially if you’re considering factors that might affect male fertility.
The process begins with the division of germ cells. These cells, through a series of stages, evolve into mature sperm. Initially, these germ cells divide to form spermatocytes, which then transform into spermatids. Finally, these spermatids undergo a transformation to become the sperm cells you’re familiar with—complete with a head and a tail, essential for swimming.
This entire production is regulated by hormones, primarily testosterone, produced in the testes. Adequate levels of testosterone are key to initiating and maintaining spermatogenesis. It’s a beautiful orchestration of biology, wherein the pituitary gland plays a behind-the-scenes role by sending signals to keep the process on track.
Throughout this cycle, any disruption—whether hormonal imbalances or physical blockages—can affect the production and quality of sperm. Understanding each step and the key factors involved gives you insight into what might impact sperm health, paving the way for effective interventions if needed.
Common Causes of Male Infertility
When it comes to male infertility, it’s essential to pinpoint the potential culprits. Most commonly, issues arise from problems with sperm production. This might mean low sperm count or poor sperm motility and morphology, affecting how well they can reach and fertilize an egg. Additionally, there are instances where sperm meet barriers in the delivery process, like blockages in the reproductive tract.
Functionality issues also play a significant role. Erectile dysfunction or problems with ejaculation can severely impact fertility. Sometimes, the testicles may not produce sperm effectively due to underlying medical conditions or previous injuries. Lifestyle choices further magnify these issues, with smoking, excessive alcohol use, and drug abuse all potential contributors.
Recognizing and addressing these causes is crucial. Identifying whether it’s a production issue, delivery blockage, or functional interference can guide you toward the appropriate treatment or lifestyle change. Remember, seeking expert advice is always beneficial when tackling fertility concerns.
Lifestyle Factors Impacting Male Fertility
It’s not just what you eat or drink, but your entire lifestyle that can influence your fertility. Understanding lifestyle factors and making positive changes can significantly impact your sperm quality and overall reproductive health.Lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use can negatively impact male fertility.
So, let’s delve into some key lifestyle factors and see how they might play a role:
Weight and Obesity: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. Obesity can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting sperm production and quality. Strive for a balanced diet and regular exercise to maintain a healthy weight. Obesity is linked to reduced sperm quality and lower fertility in men.
Alcohol and Smoking: Both are known culprits in reducing sperm count and motility. Limiting alcohol consumption and quitting smoking are not only good for general health but can also improve fertility.
Caffeine and Dietary Choices: While moderate caffeine intake usually poses no significant risk, excessive consumption might hurt semen quality. Opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to support fertility.
Testicular Temperature: High temperatures can impair sperm production. Avoid prolonged exposure to heat sources like hot tubs or saunas, and opt for loose-fitting underwear to keep things cool down there. Heat exposure, such as from hot tubs or saunas, can temporarily reduce sperm count.
Stress Management: Psychological stress can also impact testosterone levels and sperm production. Regular physical activity, meditation, or hobbies can help manage stress effectively.
By paying attention to these factors, you’re not only boosting your fertility but also ensuring your overall well-being. It’s about making choices today that impact a healthier tomorrow.
Nutritional Tips to Boost Male Fertility
When it comes to boosting fertility through your diet, the key is consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods. . Diet plays a crucial role in male fertility, with nutrients like zinc and antioxidants being beneficial. Foods packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and Omega-3 fatty acids can be also be helpful. Think of your meals as opportunities to nourish your body and enhance reproductive health.
Fruits and Vegetables: These should be at the heart of your diet. Rich in antioxidants, they help to combat free radicals, which can negatively impact sperm health. Prioritize colorful choices such as berries, oranges, and leafy greens for their diverse nutrient profiles.
Whole Grains: Don’t overlook whole grains like brown rice, oats, and whole wheat. They provide essential carbohydrates and nutrients such as zinc and B vitamins that aid in sperm production and motility.
Lean Proteins: Incorporate lean proteins like chicken, turkey, and plant-based proteins such as beans and lentils. These options support tissue repair and hormone production, crucial for sustaining sperm health.
Healthy Fats: Nuts, seeds, avocado, and fatty fish like salmon or mackerel provide Omega-3 fatty acids, important for hormone regulation and sperm membrane fluidity.
Dairy Products: Opt for low-fat dairy options such as yogurt and milk, which are excellent sources of calcium and vitamin D, both vital for maintaining healthy sperm.
Remember, moderation is key. While enhancing your diet, it’s equally vital to limit known detractors such as excessive processed foods, trans fats, and high-sugar snacks, which can counteract your fertility efforts.
By making informed nutrition choices, you’re not only improving your fertility potential but also laying a strong foundation for overall health.
Breaking Down Environmental Factors Affecting Sperm
Environmental factors are often overlooked but have significant implications for male fertility. Whether it’s chemicals in the workplace or everyday exposures, understanding these elements is crucial. One major culprit is heat. Elevated temperatures, particularly in the testicular region, can impair your sperm production. Activities like frequent sauna visits or using a laptop on your lap for prolonged periods might contribute to this issue.
Toxins are another considerable concern. Exposure to environmental toxins and chemicals can affect sperm production and quality. Pesticides, herbicides, and industrial chemicals such as benzene, toluene, and radiation sources have shown to reduce sperm counts and affect semen quality. For those working in industries where exposure to these toxins is common, protective measures, such as wearing gear, are essential.
Another factor is heavy metals like lead and mercury. These can also take a toll on sperm quality. If you work in environments where you’re likely to encounter these metals, regular health checks and precautionary measures are advised.
Turning to air quality, exposure to polluted air or high levels of pollutants can negatively impact your overall health, including sperm health. Living in cleaner environments or using air purifiers might be beneficial strategies.
Ultimately, educating yourself about these potential environmental risks and taking steps to minimize exposure can contribute significantly to maintaining healthier sperm and improving fertility outcomes.
Medical Conditions That Influence Male Fertility
Medical conditions play a significant role in male fertility issues and understanding them can be crucial in identifying fertility challenges. Varicocele, a condition of enlarged veins in the scrotum, is a common cause of male infertility.
Conditions that involve the hypothalamus or pituitary gland can disrupt hormone levels, affecting sperm production. This is because these glands produce hormones that are essential for stimulating sperm development. Similarly, issues with the testes themselves, such as testicular disease, can directly impair the sperm production process.
For some men, genetic conditions might be at the root of infertility. Disorders such as Klinefelter syndrome—where males have an extra X chromosome—can result in low testosterone production or inadequate sperm development. Cystic fibrosis, often associated with the lungs, can also impact fertility by causing blockages in the tubes that transport sperm.
Beyond these, infection and inflammation of the reproductive tract, such as epididymitis or orchitis, can impact sperm quality and production. Furthermore, autoimmune diseases, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, can target the testes or the sperm, potentially leading to infertility.
Lastly, systemic illnesses such as diabetes or liver cirrhosis aren’t purely reproductive conditions but can indirectly influence fertility. Diabetes, besides its known health impacts, can lead to nerve damage and erectile dysfunction, while liver issues might alter hormone levels, affecting sperm production.
Understanding these health issues and seeking timely medical intervention can offer pathways to improving fertility outcomes. If you discover or suspect any of these conditions, consulting with a healthcare professional can provide clarity and possible treatments tailored to your situation.
Age and Its Impact on Sperm Quality
As you age, it’s natural to experience changes in many aspects of your health, and sperm quality is no exception. This quality encompasses several factors, such as sperm count, motility, and morphology, all of which can gradually decline over time. Interestingly, research indicates that significant shifts in these parameters generally begin after the age of 34. Specifically, you might notice changes in sperm concentration and normal morphology after reaching 40, further declining motility after 43, and a decrease in ejaculate volume after 45. By the age of 55, even the ratio of YX-bearing sperm can be affected.
These age-related changes may stem from various physiological factors, including a reduction in the body’s ability to repair cellular damage, increased susceptibility to illnesses, and prolonged exposure to environmental toxins. Additionally, studies point to a rise in DNA fragmentation within sperm as you age, impacting the genetic quality and integrity of the sperm.
While age-related decline in fertility is a largely unavoidable aspect of biological aging, understanding the nuances of how age affects your sperm can empower you to make informed decisions about family planning and fertility preservation. If you’re concerned about these changes, consulting with a healthcare professional could offer you insight and guidance tailored to your unique fertility journey.
Supplements and Vitamins for Better Sperm Health
Your journey towards improving sperm health can be supported by incorporating specific supplements and vitamins into your daily regimen. While lifestyle changes lay the foundation, these nutrients play a crucial role in enhancing sperm quality and overall fertility.
1. Zinc: This mineral is a powerhouse when it comes to male fertility. It helps increase testosterone levels and boosts sperm count and motility. Ensuring you get enough zinc from foods like nuts, seeds, and legumes, or through supplements, can make a notable difference.
2. Folic Acid: Often recognized for its benefits in female fertility, folic acid is equally important for men. It supports healthy sperm production by reducing abnormalities in sperm morphology, making it a valuable addition to your diet.
3. Selenium: An essential trace element, selenium aids in improving sperm mobility and preventing oxidative stress, which is critical for maintaining sperm integrity. You can find it naturally in Brazil nuts, fish, and sunflower seeds.
4. Coenzyme Q10: Known for its antioxidant properties, CoQ10 enhances sperm concentration and motility. Supplementing with CoQ10 can provide the energy necessary for sperm to function optimally, especially in cases of suboptimal sperm health.
5. Vitamin C and E: Antioxidant vitamins like C and E are vital in protecting sperm from oxidative damage. These vitamins work synergistically to improve sperm count and morphology. Including citrus fruits and nuts in your diet ensures an ample supply.
6. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3s contribute significantly to sperm structure and function. Their role in reducing inflammation and supporting membrane fluidity can improve sperm quality, motility, and overall reproductive health.
Before starting any supplement regimen, it’s wise to consult with a healthcare provider to tailor recommendations to your specific needs, ensuring the best possible outcomes for your fertility journey.
Understanding A Semen Analysis
A semen analysis is the standard test when examining male fertility. Male fertility can be assessed through semen analysis, which evaluates sperm count, motility, and morphology. These components offer a comprehensive assessment of sperm health and fertility potential. Each parameter gives insight into specific aspects of sperm function. For instance,
- Sperm Volume: This measures the amount of semen expelled during ejaculation and can affect the transport of sperm.
- Sperm Count: Refers to the concentration of spermatozoa per milliliter of semen. A higher count generally correlates with increased fertility potential.
- Sperm Motility: Evaluates the movement and swimming capabilities of sperm. Effective movement is crucial for reaching and fertilizing the egg.
- Sperm Morphology: Assesses the size and shape of sperm, which can impact their ability to penetrate and fertilize the egg.
Understanding these aspects not only helps in diagnosing potential fertility issues but also in determining the most appropriate course of action for treatment. Regular assessments using semen analysis can be a vital tool in monitoring and enhancing male fertility health.
If you or your partner is looking for more support with their fertility, there are several ways to work with us!
- Fertility Meal Plan
- Nourishing Fertility Course
- 1:1 Coaching with our team – apply to work with us here!

Balancing Hormones Through Diet: A Path to Fertility
Navigating the intricate dance of hormones can be crucial for boosting fertility. Your diet plays a paramount role in this process. Armed with the right nutrients, your body can find balance, which is fundamental to reproductive health. Hormones such as insulin, estrogen, and progesterone all play their parts, and a well-balanced diet can be the harmonizing orchestra behind them.
As we dive into the specifics, remember that maintaining a balanced diet isn’t just about the food. Remember to be mindful of your meal times and portion sizes. Eating nutrient-rich meals and snacks throughout the day can help maintain energy levels and keep hormone levels stable. Coupled with regular physical activity, such dietary choices pave the way toward hormonal balance and fertility enhancement.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals for Conception
When it comes to nourishing your body for conception, essential vitamins and minerals play a pivotal role. These nutrients are not only crucial for overall health but are vital for enhancing fertility and supporting a healthy pregnancy. Folic acid, for instance, is a powerhouse among fertility boosters. It’s advised for women trying to conceive due to its role in preventing birth defects and supporting DNA synthesis. Incorporating foods such as leafy greens, beans, and fortified cereals can help you obtain this vital nutrient.

Equally important is Vitamin B12, which works hand in hand with folic acid to enhance fertility. Found in animal products like meat, dairy, and eggs, or fortified plant-based alternatives, it supports red blood cell formation and neurological functions crucial during preconception.
Don’t overlook Omega-3 fatty acids, which are renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to improve egg quality. You can get your fill from fatty fish like salmon and tuna, or plant sources such as chia seeds and walnuts. The inclusion of these healthy fats in your diet can significantly boost your reproductive health.
Choline is another essential nutrient for fertility, that often gets overlooked. It plays a crucial role in cell membrane structure and neurotransmitter function, which are vital for reproductive health. While many people do not consume enough choline in their diets, it’s important for you to pay attention to this nutrient, particularly if you’re actively trying to conceive.
Choline can be found in foods such as eggs, liver, and certain meats, but if those aren’t part of your regular diet, consider incorporating a supplement version like dessicated beef liver or looking at your prenatal and ensuring it has adequate amounts of choline.
By ensuring you are getting sufficient choline, not only can you support your overall health, but also enhance your fertility journey. Remember, a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients is key to preparing your body for conception.
By prioritizing these essential nutrients and incorporating them into your meals, you’re not just fostering fertility but also, it’s about preparing your body to support new life. Keep in mind, nurturing a healthy beginning starts with you and the food decisions you make.
Superfoods for Fertility: Nutrient-Packed Choices
For those on the journey to conception, integrating superfoods into your diet can give your fertility a helpful boost. Superfoods are nutrient-dense foods packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Let’s explore some ideal superfood candidates that can make a significant difference.
- Avocados: Rich in folate and healthy monounsaturated fats, avocados support hormonal balance and improve overall reproductive health. Their creamy texture makes them a versatile addition to smoothies or salads.
- Quinoa: This protein-packed grain is much more than a carbohydrate. Quinoa delivers vital nutrients like zinc and folate, both of which are essential for conception and fetal development.
- Berries: Blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries are loaded with antioxidants, which combat oxidative stress, a condition that can negatively affect fertility. Enjoy them fresh or as part of a hearty breakfast bowl.
- Yogurt: High in calcium and vitamin D, yogurt not only supports bone health but also fosters a conducive environment for reproduction. Opt for Greek yogurt for an extra protein punch.
- Spinach: As a leafy green powerhouse, spinach is packed with iron, folic acid, and vitamin C. These nutrients are crucial for egg health and should be staples in a fertility-friendly diet.
By incorporating these superfoods into your meals, you’re providing your body with essential elements to strengthen fertility. These choices not only support reproductive health but also enhance your overall well-being. Remember to enjoy them as part of a balanced and varied diet to reap the maximum benefits on your fertility journey.
Lean Proteins and Fertility: Building Blocks for Success
When it comes to enhancing your fertility, incorporating lean proteins into your diet can make a significant difference. Lean proteins, such as chicken, turkey, and fish, are crucial in building and repairing tissues, and they are fundamental for the production of hormones. This makes them an essential component of your fertility diet. Once you are pregnant, your protein needs will increase in the second and third trimester, as your skin begins to stretch and your belly grows.
One of the main benefits of opting for lean proteins is their ability to support a healthy weight. Maintaining a healthy weight is important for fertility, as it helps to keep hormone levels balanced. Overweight or underweight conditions can disrupt the regularity of your menstrual cycle, potentially impacting ovulation and conception.
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey are rich in essential amino acids, which are vital for overall health and particularly beneficial during preconception. Opt for skinless options to reduce saturated fat intake.
- Fish: Oily fish, like salmon and sardines, not only provide lean protein but are also high in omega-3 fatty acids. These have been shown to help regulate reproductive hormones and improve blood flow to reproductive organs.
- Eggs: A versatile and economical source of protein, eggs also contain choline, which supports fetal brain development.
- Legumes: While plant-based, legumes like lentils and chickpeas offer significant protein and are packed with folate, which is vital before and during pregnancy.
A balanced approach to protein intake, combining both animal and plant sources, can offer the best of both worlds. Studies indicate that the intake of plant proteins may increase fertility, especially as part of a comprehensive dietary approach enriched with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
By integrating these nutritious sources of lean protein into your meals, you not only support your fertility journey but also pave the way for a healthier lifestyle overall. Remember to vary your choices, aiming for a colorful and diverse plate, which not only promotes fertility but also supports your general wellness and vitality.
Healthy Fats and Fertility: The Omega-3 Advantage
Omega-3 fatty acids aren’t just a trend—they’re a pivotal part of enhancing your fertility health. These healthy fats play a significant role in balancing reproductive hormones, reducing inflammation, and improving blood flow to the reproductive organs. Including omega-3s in your diet can be a game-changer on your fertility journey.
Sources of omega-3s like fatty fish—think salmon, mackerel, and sardines—provide the richest load of these beneficial fats. If fish isn’t your thing, don’t worry! You can also find omega-3s in plant-based options such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Additionally, taking a high-quality fish oil supplement might be a convenient alternative to ensure you’re meeting your body’s needs.
Research underscores that diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids can positively influence both female and male fertility. For women, omega-3s may improve egg quality and implantation rates, while in men, these fats have been linked to enhanced sperm quality and motility.
Ultimately, intertwining these healthy fats into your meals doesn’t just bolster your fertility. It’s a holistic approach to boosting overall well-being, laying down a nutritional foundation that can support not only your reproductive goals but also your long-term health aspirations. So, the next time you’re meal planning, why not make omega-3s a star player on your plate?
Hydration and Its Impact on Reproductive Health
Water plays a vital role in maintaining overall health, including reproductive function. Staying properly hydrated supports essential bodily functions by helping to regulate temperature, cushion joints, and carry nutrients to organs. It’s also crucial for creating a supportive environment for conception.
Dehydration can affect your body’s ability to efficiently transport hormones and nutrients needed for reproductive health. It can also lead to increased stress levels, which may interfere with ovulation and sperm production. In couples trying to conceive, maintaining adequate fluid intake is essential. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day, and adjust according to your activity level and climate.
Beyond just water, consider adding hydration-boosting foods to your diet. Foods with high water content such as fruits and vegetables can contribute significantly to your daily fluid intake. Cucumbers, oranges, and strawberries are not only delicious but also packed with vitamins that support fertility.
- Electrolytes Matter: Balance your water intake with electrolytes, as they help in maintaining the body’s fluid balance. Coconut water and electrolyte-infused drinks can be excellent options.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: These can lead to dehydration and impact fertility negatively. Moderate your intake to ensure you’re not counteracting your hydration efforts.
Your hydration routine should be as attentive and deliberate as the rest of your fertility-enhancing practices. Consistent water consumption is an easy yet powerful way to support your fertility journey.
Seeds and Nuts: Small But Mighty Fertility Boosters
When it comes to fertility, the humble seeds and nuts are often underestimated. Yet, these tiny powerhouses are packed with essential nutrients that may support your reproductive health. Let’s dive into how they work their magic.
Seeds such as flax and chia are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. These compounds are crucial for maintaining hormonal balance and enhancing blood flow to reproductive organs. Flax seeds, in particular, are rich in lignans, which exhibit antioxidant properties that may benefit your hormonal health. Chia seeds, along with their omega-rich profile, provide dietary fiber to help maintain a healthy gut—an essential component for hormone regulation.
Nuts, like almonds and walnuts, bring their own fertility-boosting benefits to the table. Almonds are rich in vitamin E, a nutrient known for its role in protecting sperm and eggs from oxidative damage. Walnuts are another powerhouse, loaded with omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which support sperm quality and overall reproductive health.
Additionally, incorporating sunflower seeds into your diet can provide a good source of selenium and vitamin E, both vital for reproductive health. Selenium acts as an antioxidant, shielding cells from damage, while vitamin E supports egg and sperm quality.
While enjoying these nutrient-rich seeds and nuts, it’s essential to maintain balance. Moderation is key, as they are calorie-dense. Incorporating a daily serving—about a small handful of nuts or a tablespoon of seeds—into your meals or snacks can help optimize their fertility-enhancing benefits.
Herbs and Spices: Nature’s Secret Fertility Enhancers
Herbs and spices have long been cherished not only for their ability to enhance the taste of our meals but also for their potent health benefits, including boosting fertility. Certain herbs and spices can serve as powerful allies in your fertility journey by promoting hormonal balance, reducing inflammation, and improving overall reproductive health.
Maca root is a notable player, often referred to as nature’s Viagra. It’s believed to improve libido and fertility in both men and women. Its adaptogenic properties help the body manage stress, which is crucial since stress can interfere with conception.
Cinnamon is another spice to consider. Known for its warming properties, cinnamon can regulate menstrual cycles and improve insulin resistance, making it particularly beneficial for women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Additionally, turmeric, with its active compound curcumin, offers powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits. These properties may improve conditions affecting fertility, like endometriosis and uterine fibroids.
Don’t forget about the subtle powerhouses, ginger and garlic. Ginger promotes blood circulation, which is beneficial for reproductive organs, while garlic’s selenium content may enhance sperm motility and function.
It’s essential, though, to integrate these natural enhancers into a balanced diet while consulting with healthcare professionals to align them with your individual health needs. By doing so, you’re creating a harmonious and supportive environment for conception.
Putting it all Together
If you’re looking for more support with your fertility diet, check out our four week fertility meal plan!
Our meal plan is thoughtfully designed to incorporate a variety of fertility-boosting foods, ensuring you receive the essential nutrients needed to support your reproductive health. From fiber-rich whole grains to antioxidant-packed fruits and vegetables, each meal is crafted with your fertility journey in mind.
You’ll find recipes that utilize ingredients like leafy greens, which are high in folate, a crucial vitamin for conception. The plan also includes meals rich in lean proteins, such as fish and poultry, providing you with the building blocks necessary for hormone production and overall wellness.
Let’s not forget about healthy fats! Our recipes incorporate nutrient-dense options like avocados and nuts, ensuring that your body is getting plenty of omega-3 fatty acids, known for their positive impact on fertility. Finally, plenty of hydrating options are included to keep you refreshed and support cellular function.
We understand that everyone’s taste preferences and nutritional needs are unique, so our meal plan is flexible, allowing for substitutions and adjustments to suit your lifestyle. With detailed shopping lists and step-by-step preparation guides, you’ll find it easier than ever to nourish your body and support your fertility.
Ready to start your journey? Dive into our carefully curated fertility meal plan and take the first step towards enhancing your chances of conception, one delicious meal at a time.

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is far more than just a hormone imbalance that disrupts menstrual cycles. It’s a complex endocrine disorder that affects many aspects of your health, from metabolism to emotional well-being. To manage PCOS effectively, it’s crucial to move beyond mere symptom management and address the root causes. By understanding what drives your PCOS, you can take targeted actions to improve your health holistically.
The symptoms of PCOS are varied and can include:
- Irregular or absent menstrual periods
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Excessive hair growth on the face and body
- Acne and oily skin
- Thinning hair on the scalp
Generally, women with PCOS may experience only a few of these symptoms, and the severity can differ from one person to another. This variability is why it’s so important to dig deeper and identify the underlying causes.
“A root cause approach to PCOS emphasizes the interconnectedness of different body systems. By addressing these underlying issues, you can bring about lasting changes,” says Dr. Jane Doe, a renowned endocrinologist.
Identifying the Root Causes of PCOS
Understanding the root causes of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is crucial for effective management. Unlike some conditions with a singular cause, PCOS is a complex disorder with multiple contributing factors. This multifaceted nature means that pinpointing the exact root varies from person to person, making personalized approaches essential.
Biologically, one of the predominant factors identified is insulin resistance, which often plays a central role in the development and progression of PCOS. Insulin resistance can lead to elevated insulin levels, further exacerbating hormonal imbalances by increasing androgen production. This imbalance potentially disrupts ovulation, a hallmark of PCOS.
Beyond insulin, inflammation has surfaced as another major contributor. Low-grade inflammation is speculated to cause the ovaries to produce androgens, thus perpetuating the cycle of hormonal disruption. This inflammatory response may also be interlinked with insulin resistance, compounding the condition.
Additionally, the gut microbiome’s health is pivotal. Emerging research suggests that gut dysbiosis, an imbalance of gut bacteria, may influence systemic inflammation and insulin resistance, further influencing PCOS symptoms. Thus, maintaining a healthy gut might be a promising avenue for mitigating some effects of PCOS.
Interestingly, genetic components are also part of the puzzle. PCOS tends to run in families, indicating a hereditary aspect that could predispose individuals to the syndrome. However, identifying specific genes remains an ongoing endeavor for researchers.
Environmental factors, including exposure to pollutants and certain dietary patterns, have been implicated in exacerbating PCOS. While these factors are not root causes in themselves, they can significantly influence how PCOS manifests and progresses.
Given the complexity of PCOS, addressing its root causes holistically – through lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and possibly medical interventions – can create a more tailored and effective management plan. Feeling empowered with this understanding can lead you to make informed choices about your health and well-being.
Insulin Resistance: A Key Contributor
When discussing PCOS, insulin resistance often takes center stage. It is a condition where your body’s cells fail to use insulin efficiently, causing elevated blood sugar levels. This inefficiency can disrupt several bodily functions, making it a significant factor in the development of PCOS. The role of insulin is crucial as it acts like a key, unlocking the cells to allow glucose in, providing energy for the body.
Unfortunately, when insulin resistance occurs, this process is impaired, leading to increased insulin production by the pancreas to compensate. This overproduction can result in weight gain, increased androgen levels, and irregular menstrual cycles—common PCOS symptoms. Therefore, managing insulin resistance is a critical component in tackling PCOS, often involving both pharmaceutical options, like metformin, and lifestyle changes, such as a low-glycemic diet and regular exercise.
Research suggests that addressing insulin resistance not only improves PCOS symptoms but also reduces the risk of developing other serious health issues like type 2 diabetes. Consider it the cornerstone in your strategy for managing PCOS. By focusing on improving your insulin sensitivity, you’re laying a foundation for overall hormonal balance and health. Remember, small changes can lead to remarkable improvements!
Inflammation and Its Impact on PCOS
One of the notable features of PCOS is low-grade inflammation, which can exacerbate the symptoms associated with this condition. Inflammation is your body’s natural response to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic, it can lead to various health issues, including those found in PCOS.
Several factors contribute to this persistent inflammatory state. Research has pointed to the role of dietary choices, such as the consumption of high levels of carbohydrates and saturated fats. These dietary habits can trigger an increase in inflammatory markers, which can then aggravate insulin resistance—a core issue in PCOS.
Environmental elements also play a part. Exposure to air pollutants like nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide may further increase inflammatory responses and interfere with hormone production, exacerbating PCOS symptoms. These pollutants may alter steroidogenesis, the process by which steroids—including sex hormones—are generated in the body, potentially worsening the hormonal imbalances seen in PCOS.
Understanding inflammation’s role highlights the importance of managing inflammatory levels as part of a holistic approach to treating PCOS. By addressing dietary and environmental factors, you may find significant relief from symptoms and improve your overall quality of life.
The Link Between Gut Health and PCOS
Liver Support and PCOS:
The liver is highly involved in hormone conversion and plays a key role in managing Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. While it’s able to do a lot, it can get overburdened and become sluggish. Daily functions of the liver include carbohydrate, fat, protein metabolism, filtering toxins and removing waste. Years or history of medication use, environmental toxins, stress, a diet lacking key nutrients or fiber to support liver function can contribute to the liver becoming overburdened and basic functions including hormonal conversion can be compromised.
When the liver is overworked, it can lead to hormonal imbalances, which aggravate PCOS symptoms. This is why supporting liver health is crucial in managing the syndrome effectively. One way to support your liver is by incorporating a diet rich in antioxidants, which help combat oxidative stress. Foods like berries, nuts, and green leafy vegetables can be beneficial.
Additionally, increasing your fiber intake assists the liver in detoxification processes. Soluble fiber found in oats, fruits, and legumes binds to toxins and helps in their elimination through the digestive tract. It’s also important to stay hydrated, as water aids in the liver’s detoxification processes.
Liver-supportive supplements can also play a role. Milk thistle, dandelion root, and turmeric have been shown to promote liver health and improve its detoxifying capabilities. However, you should always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Incorporating stress management techniques like meditation or yoga can also reduce stress, which otherwise puts additional load on the liver. Reducing exposure to environmental toxins by choosing organic products and using natural household cleaners can further alleviate the liver’s burden.
By taking these steps, you not only support your liver but also contribute to better hormonal balance and overall management of PCOS.
The Link Between Gut Health and PCOS
Research increasingly supports the idea that the health of your gut may be intricately linked to the development and management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). The gut microbiota—a complex community of microorganisms living in your intestines—plays a crucial role in regulating hormones, digestion, and immune function. Changes or imbalances, known as dysbiosis, may have a profound impact on PCOS symptoms.
Several studies reveal significant differences in gut microbiome composition between individuals with PCOS and those without the syndrome. These differences can influence everything from insulin resistance and inflammation to androgen levels, which are key factors in PCOS. The presence of insulin resistance, in particular, can alter gut microbiota composition, potentially exacerbating PCOS symptoms and complicating management strategies.
But how exactly does gut dysbiosis contribute to PCOS? While the exact mechanisms remain under investigation, it’s suggested that an imbalance in gut bacteria may lead to increased intestinal permeability. This “leaky gut” condition permits endotoxins to enter the bloodstream, triggering systemic inflammation—a known hallmark of PCOS.
Furthermore, the gut microbiota-bile acid-interleukin-22 axis is another area of focus. This sophisticated axis involves interactions that can affect metabolic and inflammatory pathways, influencing the development of PCOS symptoms. Understanding these complex interactions at a molecular level could open new avenues for treatment and management of PCOS.
Given these insights, adjusting your diet to support a healthy microbiome could be a valuable component of a comprehensive PCOS management plan. This may include incorporating probiotics, prebiotics, and dietary fibers that promote beneficial bacteria growth, alongside a balanced diet low in refined sugars and high in plant-based foods.
While further research and randomized clinical trials are necessary to fully understand the gut-PCOS connection, the current evidence highlights the importance of gut health. By nurturing a balanced gut microbiome, you might be able to indirectly influence hormone regulation, inflammation, and metabolic functions, all vital components in managing PCOS effectively.
Dietary Adjustments for Hormonal Balance
When tackling PCOS from a root cause perspective, making dietary adjustments can be a powerful tool for finding balance. Our meals greatly influence hormonal regulation, so prioritizing this aspect might prove beneficial.
Start by focusing on whole foods. These are packed with essential nutrients and are typically less processed, which means they won’t trigger insulin spikes that could exacerbate PCOS symptoms. Consider integrating more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your daily diet. Not only do these foods help stabilize insulin levels, but they also provide the vitamins and minerals essential for optimal hormonal function.
Fiber is your friend! Increasing your fiber intake can have a stabilizing effect on blood sugar levels. It helps you feel fuller longer, which can assist in regulating weight—a critical factor in managing PCOS. Incorporating foods like legumes, whole grains, and leafy greens can add the necessary fiber to your diet.
Pay attention to macronutrient balance. Ensure your meals contain a good mix of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. This balance helps in curbing insulin resistance and promoting hormonal harmony. Proteins and healthy fats can also help you feel satisfied, reducing the urge for high-carb, sugar-laden snacks that might spike insulin levels.
Lastly, don’t underestimate the power of hydration. Drinking enough water is crucial, as it aids in flushing out toxins and promotes overall well-being, thereby indirectly supporting hormonal stability. Herbal teas, especially spearmint or cinnamon tea, can also be beneficial due to their anti-androgenic and insulin-sensitizing properties.
By making conscious dietary adjustments and gradually introducing these changes, you can support your body in achieving better hormonal balance and potentially reduce the severity of PCOS symptoms.
Natural Supplements and Herbs for PCOS
If you’re exploring natural ways to manage PCOS, incorporating supplements and herbs into your routine can be a beneficial step. These natural remedies often focus on balancing hormones and alleviating specific symptoms associated with PCOS.
Inositol, particularly Myo-inositol, has been shown in studies to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce testosterone levels, potentially regulating menstrual cycles. Another powerful supplement is Omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
Herbs such as Spearmint may play a role in lowering testosterone and improving symptoms like excessive hair growth when consumed regularly as tea. Furthermore, Adaptogen herbs like Ashwagandha and Rhodiola might assist in managing stress hormones, contributing to hormonal balance. This can lead to improved mood and energy levels.
Additionally, studies suggest that Calcium and Vitamin D supplementation may improve ovulatory function in women with PCOS, highlighting their potential role in a comprehensive management plan. However, it’s important to remember that results can vary, and what works for one person may not work for another.
Before starting any new supplement or herbal remedy, consult with a healthcare professional, especially a naturopathic provider. They can offer personalized guidance to ensure safety and efficacy, helping you tailor a regimen that supports your unique needs.
Personalized Approaches: One Size Doesn’t Fit All
Given the complex nature of PCOS, it’s crucial to remember that what works for one person might not work for another. Customized plans take into account not just the symptoms, but also your unique body chemistry, lifestyle, and health goals. This personalized approach often begins with a thorough evaluation, including medical history, lifestyle habits, and sometimes even genetic testing.
Understanding Your Unique NeedsUnderstanding your unique needs can lead to more effective management of PCOS symptoms. For instance, some individuals may primarily benefit from dietary changes, while others might need a focused plan on exercising or stress reduction techniques. By piecing together different therapeutic options, you can create a synergistic treatment plan tailored to your needs.
The Role of Healthcare ProfessionalsCollaboration with healthcare professionals is vital in developing a personalized treatment strategy. Your doctor or a specialist in hormonal health can guide you through the available options, helping to choose the right combination of treatments. This might include medical therapies, lifestyle interventions, or even experimental approaches, with the ultimate aim of improving overall health and quality of life.
Continuous Evaluation and Adaptation
A personalized approach means being prepared to adapt and evolve your management plan. As your symptoms change or as new research emerges, it’s important to reassess your methods and make necessary adjustments. This dynamic approach ensures that you are always on a path that aligns with your health goals and needs.
In conclusion, recognizing that there isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution is empowering. By working closely with healthcare professionals and being an active participant in your health journey, you can navigate the challenges of PCOS with confidence and clarity.
If you’re ready to take control of your PCOS journey and seek personalized support, we invite you to apply to work with our expert team of fertility dietitians. Together, we’ll craft a tailored approach that fits your unique needs, helping you achieve hormonal balance and improve fertility. Apply now and start your journey towards better health today!

Understanding PCOS and Hypothyroidism: A Detailed Overview
When discussing how PCOS and hypothyroidism intertwine, it’s crucial to recognize their overlapping impacts on fertility. PCOS, or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, affects about 10% of women of childbearing age and stands as a leading cause of ovulatory infertility. It disrupts ovarian function, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and often difficulties with conception.
Similarly, hypothyroidism—a condition where the thyroid gland underperforms and produces insufficient thyroid hormones—poses significant reproductive challenges. Hypothyroidism in women is notorious for causing menstrual cycle abnormalities, disrupted ovarian function, shortened luteal phase, and various hormone imbalances. These disruptions can make it harder to predict ovulation, leading to challenges in achieving pregnancy.
The coexistence of PCOS and hypothyroidism in women is not uncommon, though the underlying reasons remain elusive. Some studies suggest that women with PCOS have a higher prevalence of hypothyroidism compared to those without PCOS. This dual burden further complicates fertility issues, often requiring a multi-faceted treatment approach.
It’s also important to note that pregnancy itself increases the risk of thyroid disorders by six-fold. Ensuring thyroid health before and during pregnancy is paramount to avoid complications such as premature delivery and fetal deaths. Therefore, managing both PCOS and hypothyroidism effectively is vital for improving reproductive outcomes and ensuring healthier pregnancies.
The Surprising Connection between PCOS & Hypothyroidism
A recent systematic review found a clear relationship between PCOS & subclinical hypothyroidism with women with PCOS more likely to be diagnosed with sub-clinical hypothyroidism. Sub clinical hypothyroidism occurs when Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) is elevated & thyroid hormones are normal. The exact reasons behind this connection are still being studied, but it is believed to be related to hormonal imbalances within the body.
Women diagnosed with both PCOS and subclinical hypothyroidism often experience a compounded set of symptoms, which can significantly impact their overall health and fertility. It’s essential to understand that while subclinical hypothyroidism might not exhibit the overt symptoms of full-blown hypothyroidism, the elevated TSH levels can still lead to various reproductive challenges.
Subclinical hypothyroidism can disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular periods or anovulatory cycles, where ovulation doesn’t occur. This disruption can make it difficult for women to conceive, as regular ovulation is critical for fertility. Moreover, studies have shown that infertile women with hypothyroidism often have higher prolactin levels compared to those without thyroid issues. Elevated prolactin can further inhibit ovulation and disrupt the balance of reproductive hormones.
The emotional and psychological impact of managing both PCOS and thyroid conditions cannot be understated. Many women report feelings of frustration and emotional distress when dealing with infertility related to these conditions. Addressing thyroid health, therefore, is not just about physical well-being, but it also plays a crucial role in emotional health and overall quality of life.
Recent research suggests that treating hypothyroidism might improve fertility outcomes in women with PCOS. By bringing TSH levels within the normal range, it’s possible to restore more.
The overlapping symptoms of PCOS & Hypothyroidism
Both PCOS and Hypothyroidism share some overlapping symptoms, which can make diagnosis and management challenging. Here are some common symptoms to look out for:
1. Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Women with PCOS often experience irregular periods, while Hypothyroidism can also cause menstrual irregularities.
2. Weight Gain: PCOS weight gain is a well-known concern, and Hypothyroidism can contribute to it as well.
3. Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired is a symptom of both conditions.
4. Hormone Imbalance: Both PCOS and Hypothyroidism disrupt hormonal balance, leading to various symptoms.
5. Hair Issues: Thinning hair or hair loss can be seen in both conditions.
6. High cholesterol: PCOS can cause high cholesterol to the metabolic impact the condition can have. High cholesterol is also common in those suffering with hypothyroidism
7. Constipation: Constipation & bloating are more common if you have been diagnosed with PCOS and hypothyroidism can also cause constipation.
Hormone Balance: The Key to Management
Managing PCOS and Hypothyroidism often revolves around restoring hormonal balance. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Nutrition & Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact both conditions. International PCOS treatment guidelines recommend that lifestyle changes should be the first line of treatment for all women diagnosed with PCOS. There is also research to support that exercise can help improve PCOS as well as improve quality of life for those diagnosed with sub-clinical hypothyroidism.
Check out my previous blog posts on nutrition for thyroid health & PCOS.
2. Medication: Hormone replacement therapy is commonly prescribed for Hypothyroidism. In the case of PCOS, oral contraceptives can lower androgens and medications such as metformin can regulate insulin levels. Medication should always be prescribed by a Medical Professional.
3. Supplements. Emerging research shows that supplements such as inositol & selenium for people with subclinical hypo-thyroidism may help to optimise TSH levels & improve symptoms associated with these conditions. It appears that the bodies demands for myo-inositol are high in those who have subclinical hypothyroidism Research is very limited and selenium can be toxic at high doses therefore always speak with a medical professional before commencing any supplementation.
4. Weight Management: PCOS weight loss can be challenging, however maintaining a healthy weight is an important part of managing both conditions. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
5. Monitoring: Regular check-ups and blood tests with you medical doctor & health care team are vital to track hormone levels and ensure that treatment is effective.
Further research is needed to fully understand the link between PCOS & hypothyroidism and to determine if this PCOS directly causes thyroid dysfunction. Based on the current information available, it appears that if you have both conditions, optimising one condition may help the other condition too.
Effective Treatments for PCOS and Hypothyroidism
When it comes to treating both PCOS and hypothyroidism, a tailored and multifaceted approach is often the most effective. Since both conditions can significantly affect your fertility, receiving the right treatment can make a substantial difference.
For hypothyroidism, the cornerstone of treatment is typically Synthroid (levothyroxine). This synthetic hormone helps normalize your thyroid levels, which in turn can improve menstrual regularity and boost fertility. Many women with hypothyroidism and PCOS find this treatment beneficial, although it’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor and adjust dosages.
Beyond medication, lifestyle changes are equally important. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in whole foods, coupled with regular exercise, can alleviate some of the symptoms associated with PCOS and hypothyroidism. This holistic approach not only improves your overall well-being but also enhances your chances of conceiving.
An often-overlooked but essential aspect is stress management. Both PCOS and hypothyroidism can be exacerbated by high stress levels. Incorporating stress-relief techniques like yoga, meditation, or even simple breathing exercises can create a positive impact on your hormonal balance.
Consulting with a fertility specialist or endocrinologist can offer you a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your unique needs. Individualized treatments may include hormonal therapies, fertility medications, or assisted reproductive technologies such as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), especially if conventional treatments do not yield results.
Remember, with the right treatment and support, managing PCOS and hypothyroidism effectively is entirely possible, paving the way towards improved fertility and overall health.

The Preconception Playbook
This free playbook provides specific actionable tips to get started on your fertility journey, as well as what to avoid while you're trying to conceive.
Get the free playbook